Cranial Floor And Posterior Orbital Wall Is Viewfloor.co

Skalle
The neck refers to the collection of structures that connect the head to the torso. It is a complex structure of many bones, muscles, nerves, blood vessels, lymphatics, and other connective tissues. The cervical spine is the bony part of the neck. Its primary function is to support the skull while still allowing for movement. It is the most flexible part of the spine. This flexibility allows.

Side View of the Skull Skull illustration, Bone drawing, Skull art
Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Recovery and long-term effects Takeaway The underlying cause of a skull fracture is a head trauma significant enough to break at least one bone. People with a.

human skull side view Real human skull, Skull side view, Human skull
The skull, also known as the cranium, is the group of bones that forms the head. While many people think of the skull as a single structure, it's actually made up of 22 bones that include the.
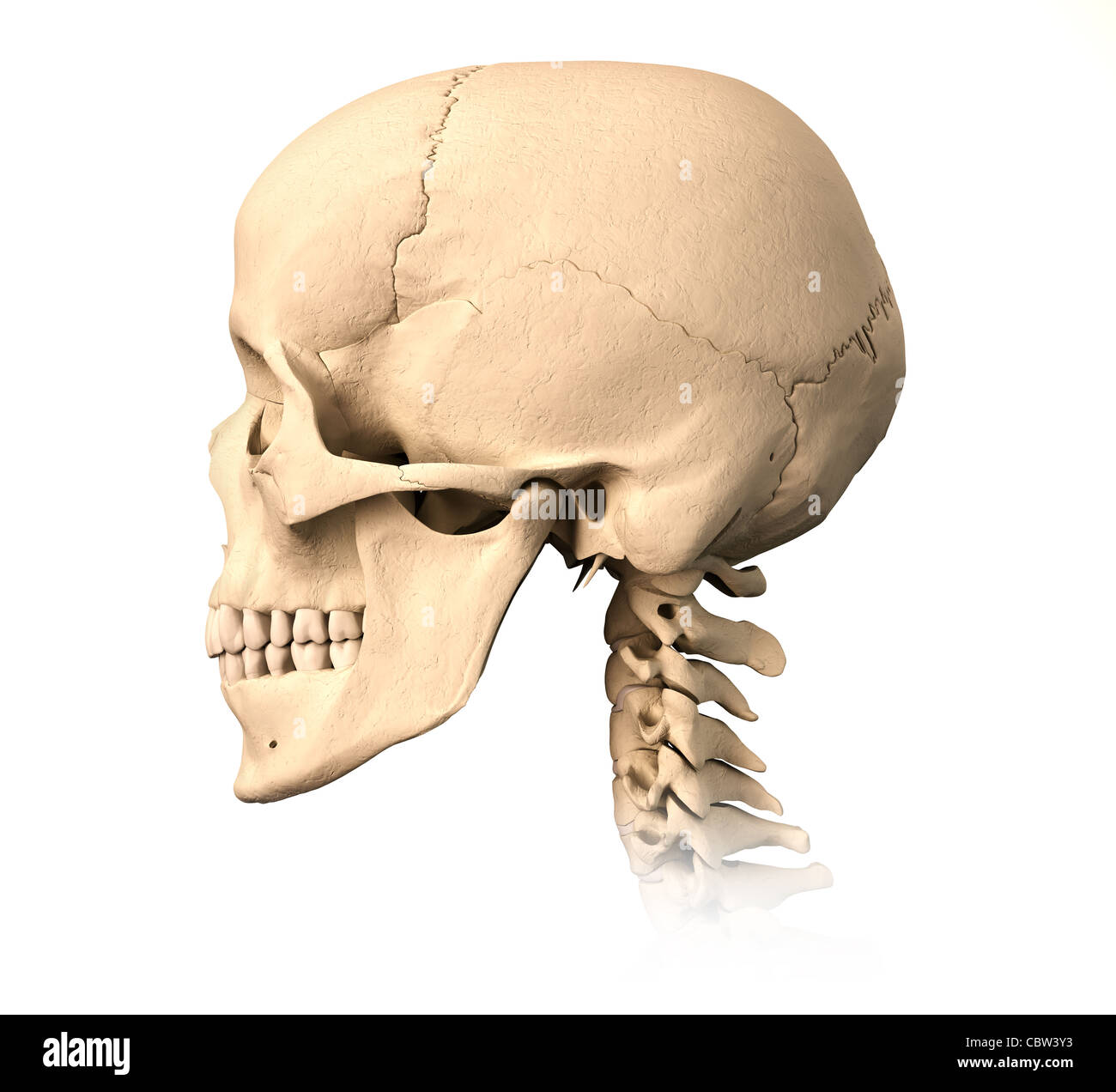
Human Skull Side View Drawing Dreamstime Skull Side Drawing Pencil
What is occipital neuralgia? Most feeling in the back and top of the head is transmitted to the brain by the two greater occipital nerves. There is one nerve on each side of the head.
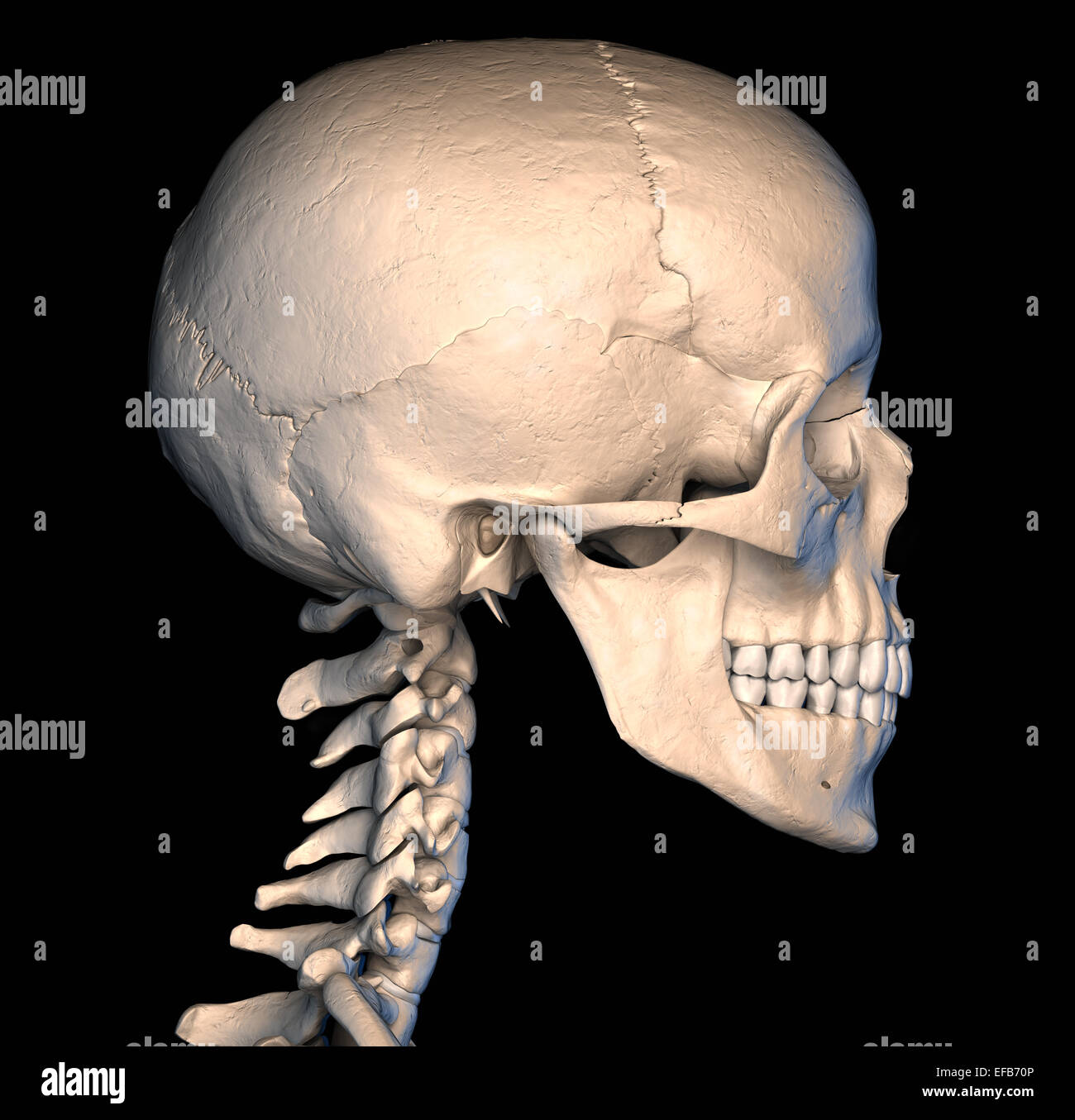
Skull Human Side View White Background High Resolution Stock
Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is a type of vasculitis (blood vessel inflammation) in branches of a large neck artery. A GCA headache is severe and can occur anywhere but is often localized to one side of the head near the temple. Other symptoms include scalp tenderness, vision changes, jaw pain when chewing, and unintended weight loss.; Cervicogenic headache manifests as one-sided pain that.
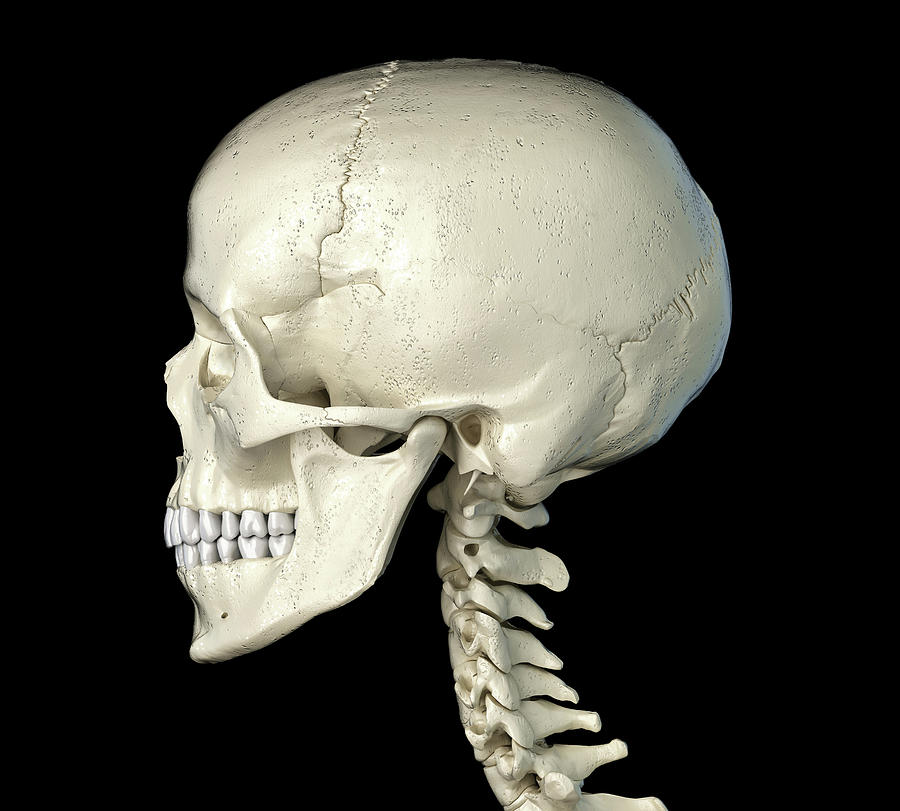
Side Profile Of The Human Skull Photograph by Leonello Calvetti Pixels
1/7 Synonyms: none The human skull consists of about 22 to 30 single bones which are mostly connected together by ossified joints, so called sutures. The skull is divided into the braincase ( cerebral cranium) and the face ( visceral cranium ). The main task of the skull is the protection of the most important organ in the human body: the brain.

skull back Google Search Skull anatomy, Human skull anatomy, Human
skull, skeletal framework of the head of vertebrates, composed of bones or cartilage, which form a unit that protects the brain and some sense organs. The upper jaw, but not the lower, is part of the skull. The human cranium, the part that contains the brain, is globular and relatively large in comparison with the face.

Human Skull Side View HighRes Vector Graphic Getty Images
Figure 1. Parts of the Skull. The skull consists of the rounded brain case that houses the brain and the facial bones that form the upper and lower jaws, nose, orbits, and other facial structures. Watch this video to view a rotating and exploded skull, with color-coded bones.

How To Tell If You Have A Broken Neck JOI Jacksonville Orthopaedic
Drowsiness and progressive loss of consciousness. Dizziness. Confusion. Unequal pupil size. Slurred speech. Loss of movement (paralysis) on the opposite side of the body from the head injury. As more blood fills your brain or the narrow space between your brain and skull, other signs and symptoms may appear, such as:

Skull Side View Silhouette PNG Transparent, Skull Head Black Side View
The skull contains all the bones of the head and is a shell for the brain and the origins of the central nervous system. A first glance shows that this is one large mass of detailed and irregular bone. Upon closer inspection however, it seems that it is intricately constructed of many smaller bone fragment pairs, all unique in shapes and sizes, that bilaterally make up this hollow, three.

The Skull Anatomy and Physiology I
Humans Skull in situ Anatomy of a flat bone - the periosteum of the neurocranium is known as the pericranium Human skull from the front Side bones of skull The human skull is the bone structure that forms the head in the human skeleton. It supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.
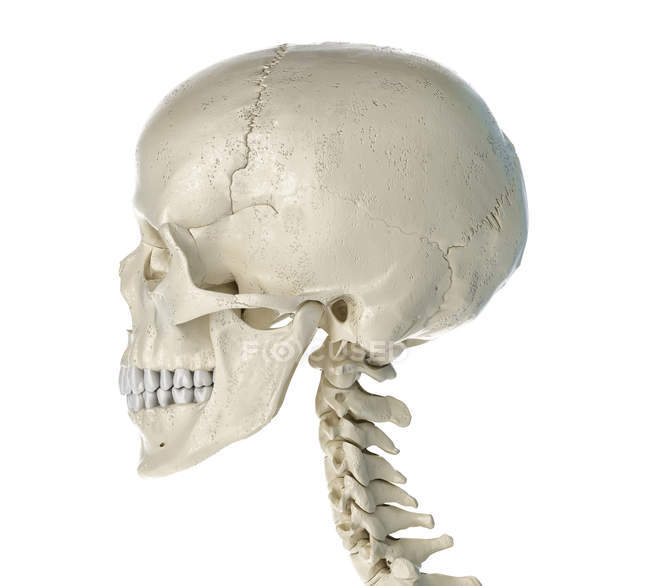
Human skull in side view on white background. — medical, cranium
Occipital neuralgia is a type of headache. It starts in the upper neck or back of the head and can radiate behind the eyes and over the scalp. Damage to the occipital nerves may cause occipital.
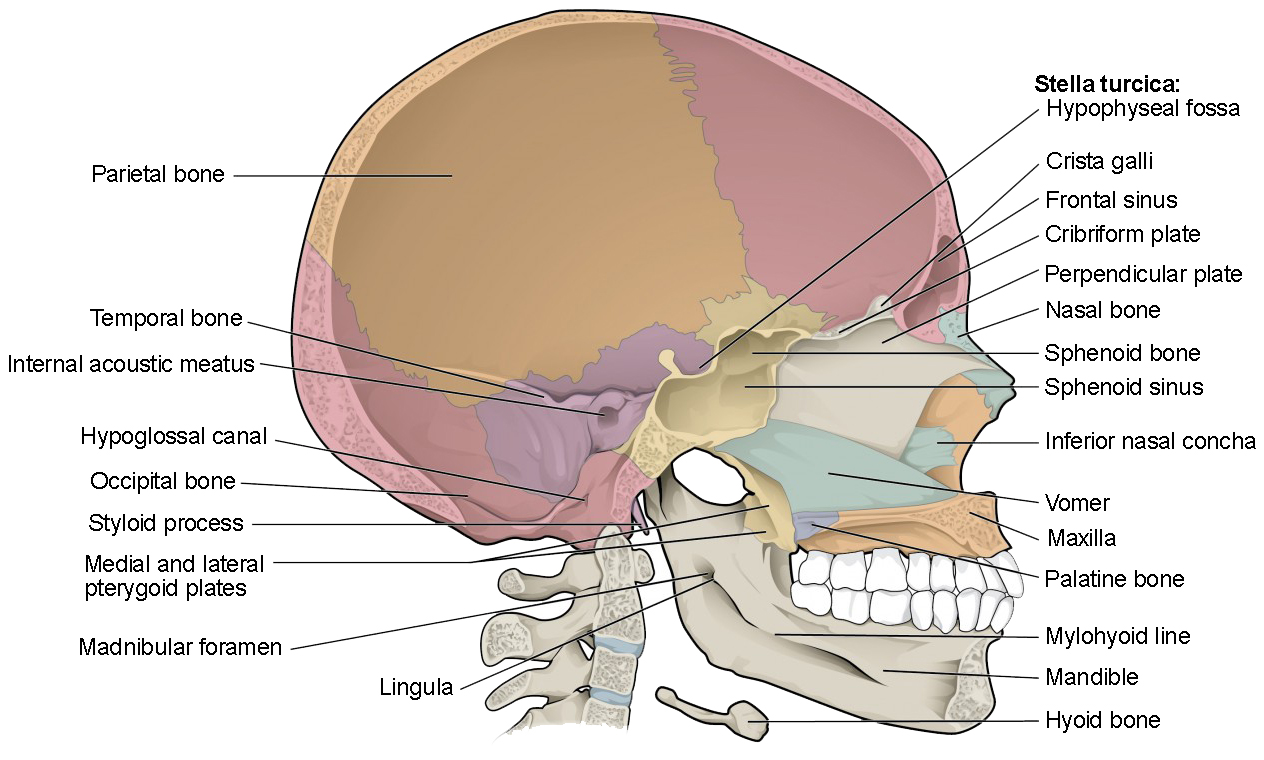
Cranial Floor And Posterior Orbital Wall Is Viewfloor.co
Temporal bone: the bones that form the inside of the sides of the skull and contain the zygomatic processes (the cheekbone), external auditory meatus (ear canal), styloid process and mastoid.
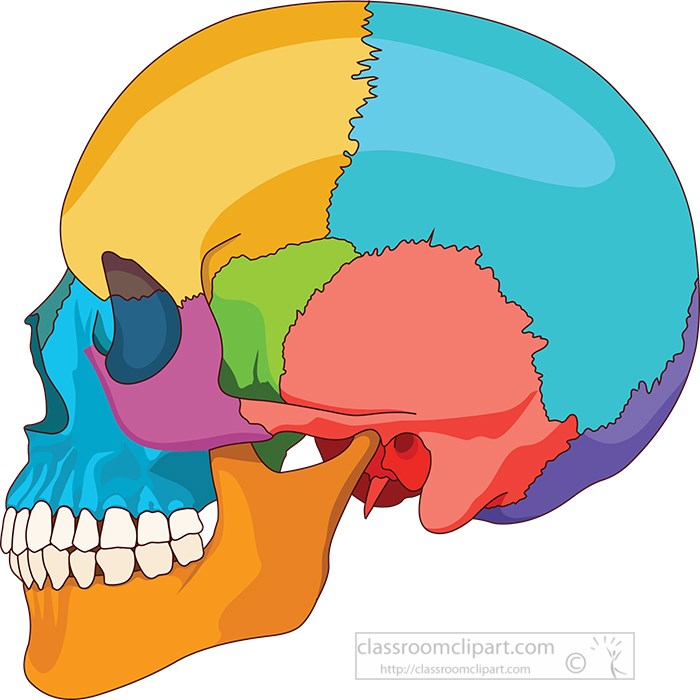
Anatomy Clipart humanskullsideviewanatomyclipart Classroom Clipart
Parts Conditions Treatment The occipital bone is a flat, trapezoid-shaped bone that houses the back part of the brain. It is located at the lower back of the cranium and is one of seven bones that form your skull. This article will review the structure and function of the occipital bone of the skull, as well as problems that can affect the bone.

Skull Side TG Vinyl
Other causes of SCM pain include: injuries such as whiplash or falls. overhead work such as painting, carpentry, or hanging curtains. poor posture, especially when your head is forward or turned.
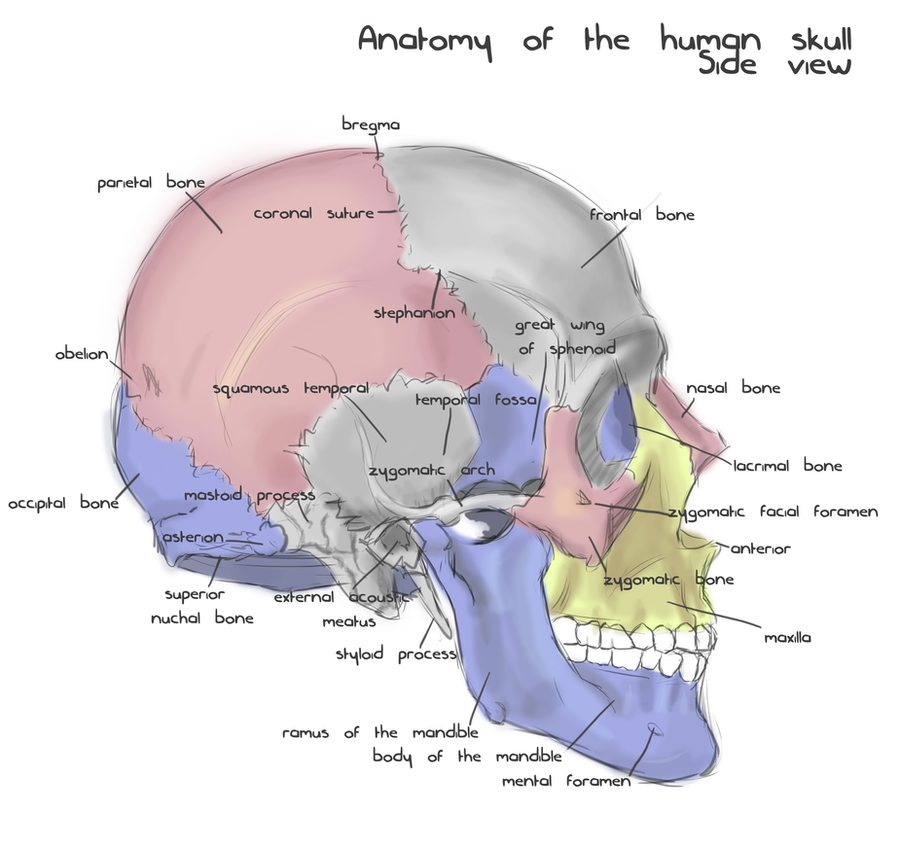
Annotated Human Skull Anatomy Side View By Shevans On Deviantart My
1/2 Synonyms: none The human skull consists of 22 bones (or 29, including the inner ear bones and hyoid bone) which are mostly connected together by ossified joints, so called sutures. The skull is divided into the braincase ( neurocr anium) and the facial skeleton ( viscerocranium ).