Bone Structure Of Hands

ArtStation Palmar Anatomy of the Hand
Skin and Nails The skin normally covers and protects the deep structures of the hand and wrist, but injuries such as cuts and burns can disrupt the skin layer. Fingernails are essentially a specialized part of the skin which protects the fingertips and serves as a tool for certain manual activities.
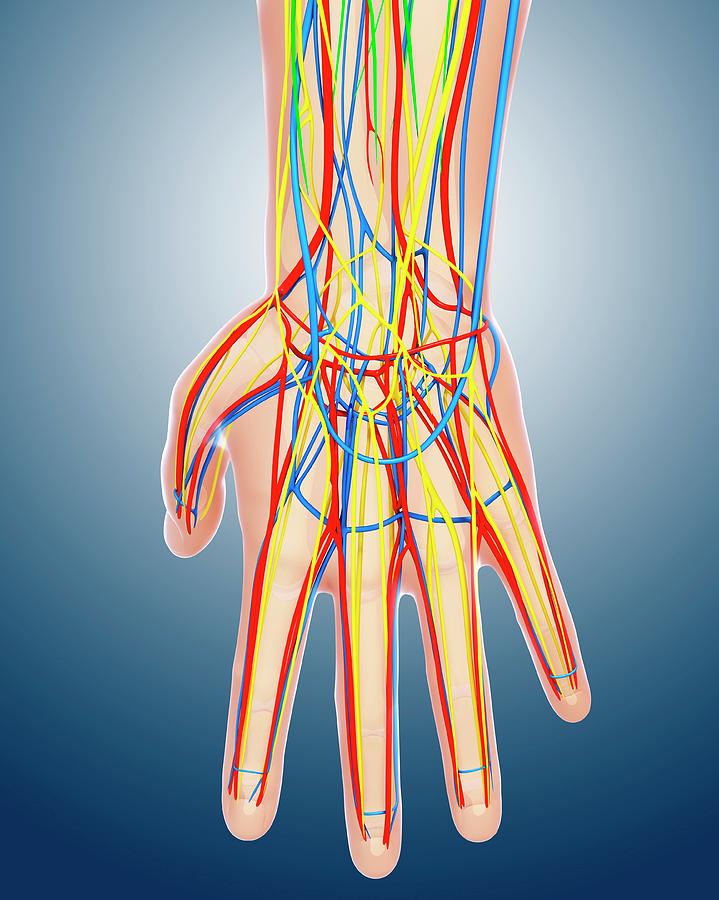
Hand Anatomy Photograph by Pixologicstudio/science Photo Library Fine Art America
The hamate is easily identifiable by its 'hook' like volar projection. The metacarpals articulate with the proximal phalanges, which articulate with the middle phalanges, which finally articulate with the distal phalanges. The thumb has only a proximal and distal phalanx. It opposes the tips of the other fingers and is essential for precision grip.
picture of anatomy of left hand bones
Keratinocytes. Keratinocytes comprise about 90% of the epidermis and are responsible for its structure and barrier functions. Melanocytes. Melanocytes are found at the base of the epidermis and make melanin. This gives the skin its color. Dermis The dermis is the middle layer of the skin. The dermis contains: Blood vessels Lymph vessels

Wrist & Hand Atlas of Anatomy
Hand Anatomy Christopher M. Stewart & Paul A. Ghareeb Chapter First Online: 17 June 2023 882 Accesses Abstract The anatomy of the hand and upper extremity demonstrates a complex interplay of several different tissue types to create a functional tool that is essential for human activity.
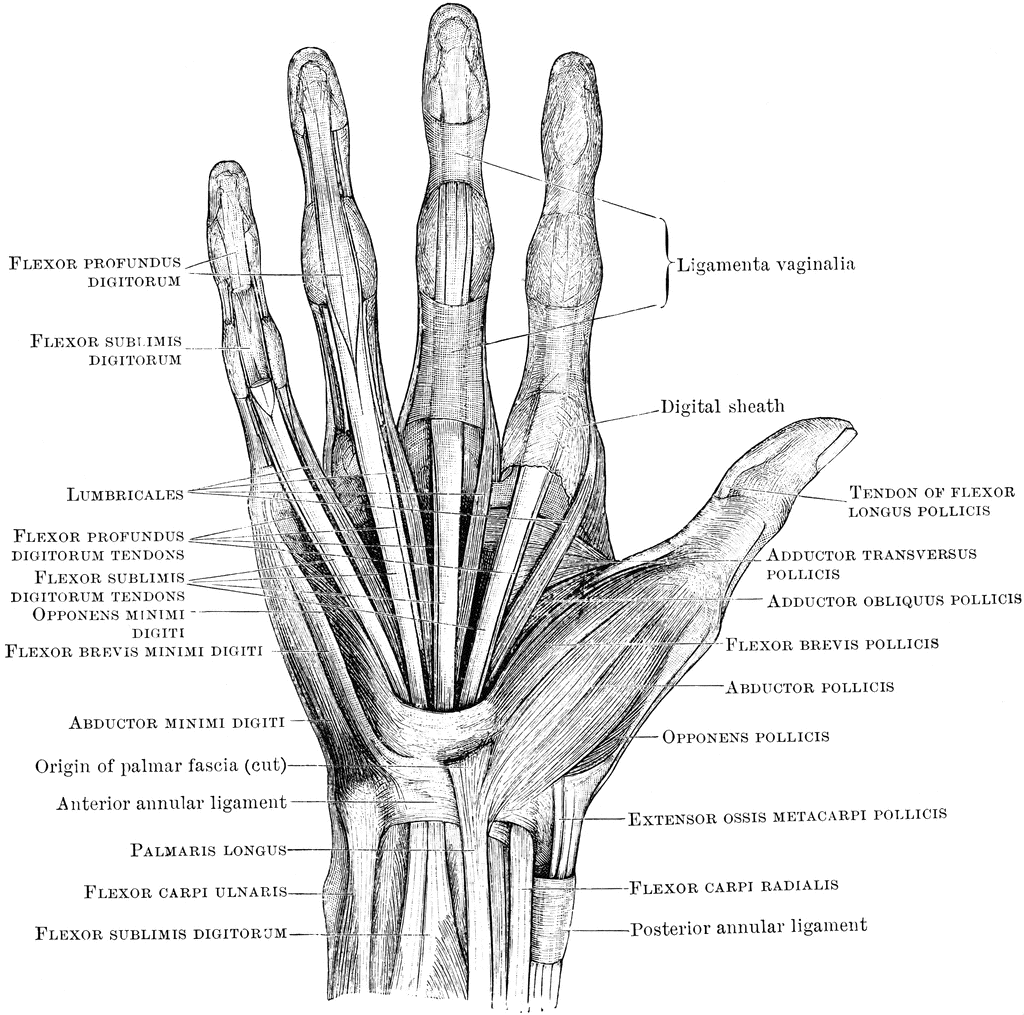
The Forearm, Wrist, and Hand Musculoskeletal Key
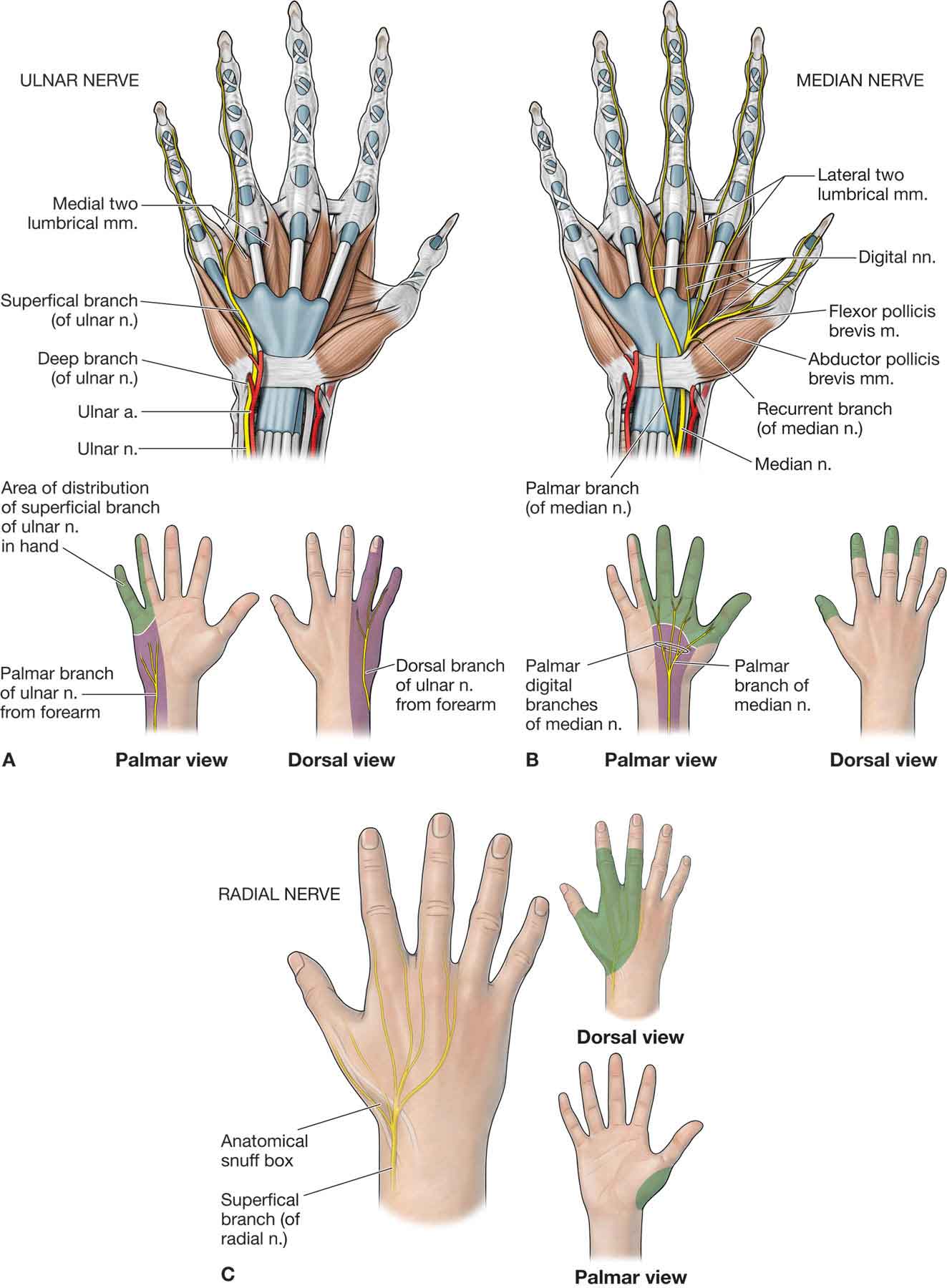
Hand: Anatomy The hand constitutes the distal part of the upper limb and provides the fine, precise movements needed in activities of daily living. It consists of 5 metacarpal bones and 14 phalanges, as well as numerous muscles innervated by the median and ulnar nerves.
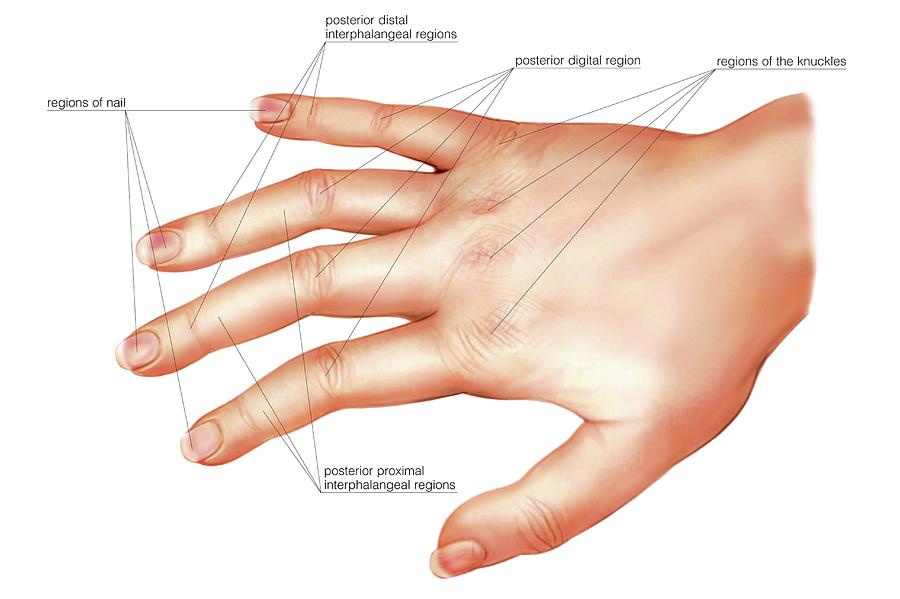
Anatomy Regions Of The Hand Photograph by Asklepios Medical Atlas Pixels
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue guarding muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals ' skin, and it is very similar to pig skin.

hand anatomy featured Brace Access
The layers of the dorsal region of the hand 1. The skin is thin, loose and is covered by hair especially in males. 2. Superficial fascia. 3. The subcutaneous tissue is thin contain veins network, the beginning of the cephalic and basilica veins; superficially branches of the radialis nerve and dorsalis branches of the ulnar nerve.

Hand Anatomy Bone
Find a Doctor Find a Treatment Center Each of your hands has three types of bones: phalanges in your fingers; metacarpals in your mid-hand, and carpals in your wrist.
Tendon Injuries of the Hand HealDove
knuckle. finger. finger flexor tendon. hand, grasping organ at the end of the forelimb of certain vertebrates that exhibits great mobility and flexibility in the digits and in the whole organ. It is made up of the wrist joint, the carpal bones, the metacarpal bones, and the phalanges. The digits include a medial thumb (when viewed with the palm.
Human Wrist and Hand (a) Physical Appearance of Right Hand (Anterior... Download Scientific
There are 27 bones within the wrist and hand. The wrist itself contains eight small bones, called carpals. The carpals join with the two forearm bones, the radius and ulna, forming the wrist joint. Further into the palm, the carpals connect to the metacarpals. There are five metacarpals forming the palm of the hand.

Wrist anatomy, Medical anatomy, Hand therapy
The Dermis Hypodermis The number of skin layers that exists depends on how you count them. You have three main layers of skin—the epidermis , dermis, and hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue). Within these layers are additional layers. If you count the layers within the layers, the skin has eight or even 10 layers.

hand anatomy skin
Show details Anatomy, Skin (Integument), Epidermis Hani Yousef; Mandy Alhajj; Sandeep Sharma. Author Information and Affiliations Last Update: November 14, 2022. Go to: Introduction Skin is the largest organ in the body and covers the body's entire external surface.

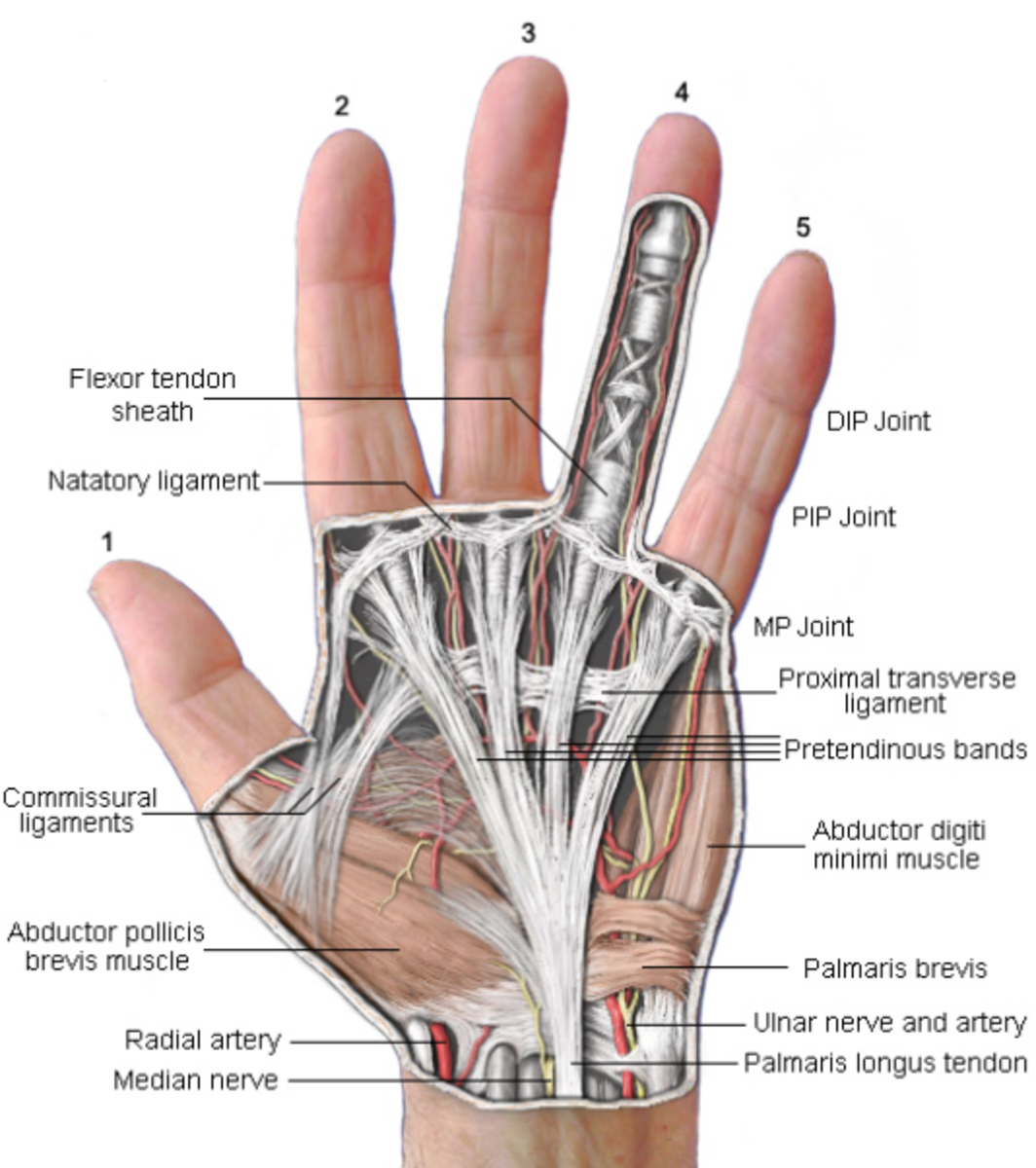
Anatomy and biomechanics of the hand Plastic Surgery Key
The word "hand" is sometimes used by evolutionary anatomists to refer to the appendage of digits on the forelimb such as when researching the homology between the three digits of the bird hand and the dinosaur hand. [2] An adult human male's hand weighs about a pound. [9] Areas Human hand parts Areas of the human hand include:

Anatomy Of Hand Ligaments ANATOMY
Overview The anatomy of the hand is complex, intricate, and fascinating. Its integrity is absolutely essential for our everyday functional living. Our hands may be affected by many disorders,.

Bone Structure Of Hands
Deformities Nerve disorders Finger clubbing Tendinitis Carpal tunnel syndrome Fractured bones Sprains, strains, cuts, and bruises Last medically reviewed on March 28, 2015 Hands are capable of a.

Anatomy regions of the hand Stock Image C020/0213 Science Photo Library
Function What do the hand and wrist do? Your hand and wrist help you interact with the world around you. They're probably the first body part that comes to mind when you think about your sense of touch. They help you do everything throughout your day that involves touching, holding or using something with your fingers. Anatomy