Musculus iliocostalis Muscle anatomy, Body anatomy, Human body muscles
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/2246/wij84lMqTfSBZdKWwTy2Q_superficial-intermediate-deep-back-muscles_latin.jpg)
Musculus iliocostalis Anatomie & Funktion Kenhub
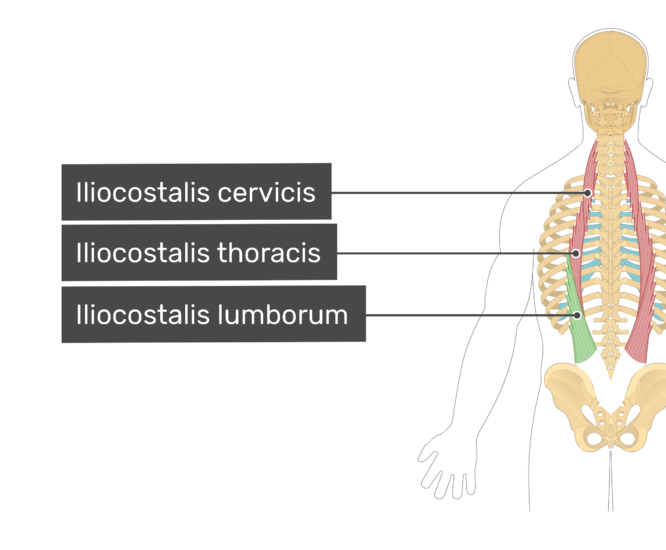
Iliocostalis cervicis arises from the angles of ribs 3-6 and inserts to the transverse processes of vertebrae C4-C6. Iliocostalis thoracis originates from the angles of ribs 7-12 and inserts to the angles of the upper six ribs and transverse process of vertebra C7. Iliocostalis lumborum is divided into lumbar and thoracic parts.

Iliocostalis Lumborum Anatomy Function Diagram Body Maps My XXX Hot Girl
ferred pain of MP of the iliocostalis thoracis-lumborum (ITL) muscle is located at the frontal aspect of the torso (chest, abdomen, and pelvis) (5) (Fig. 1), it can represent a clinical challenge even to seasoned clinicians. In our ED, emergency medicine residents receive di-dactic material, lecturing, and bedside teaching about
Iliocostalis lumborum muscle origin, insertion and action GetBodySmart
These clinical characteristics could be caused by MP of the iliocostalis thoracis-lumborum (ITL) muscle. However, this entity has not been well addressed in the medical literature. In this report we characterize the manifestations, diagnosis, and clinical implications of ITL MP. Study design: Observational assessment.

Musculus iliocostalis Muscle anatomy, Body anatomy, Human body muscles
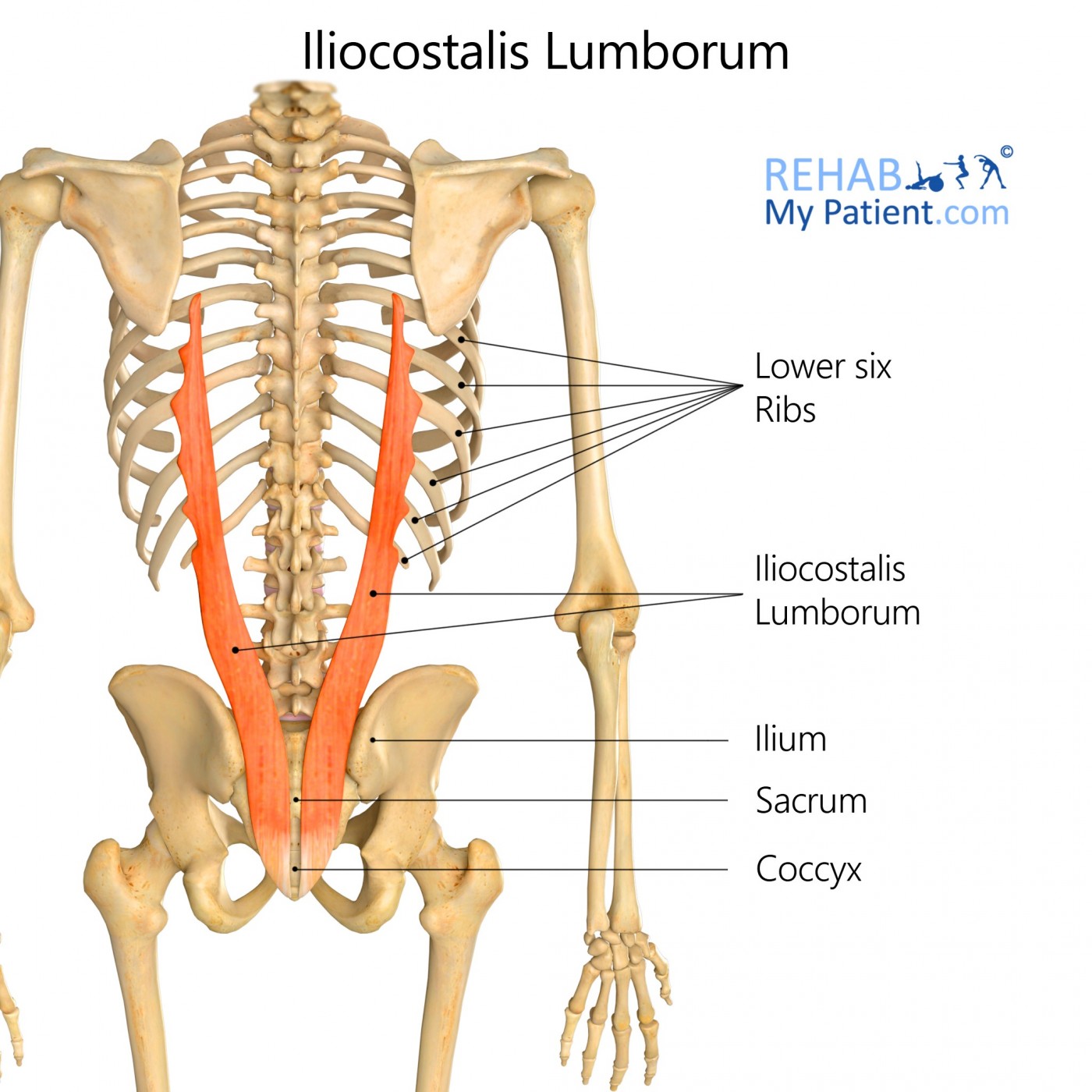
The iliocostalis lumborum is the muscle that attaches to the iliac crest and the back of the ribs. It is part of the iliocostalis column of muscles, which are responsible for the primary movement.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/musculus-iliocostalis-thoracis/Q3eWuNpi6JKrkPWBVp7eg_M._Iliocostalis_thoracis__posterior_view_.png)
Cervical spine Anatomy, ligaments, nerves and injury Kenhub
The M. iliocostalis lumborum in the Dachshund seems more suitable for generating force and stabilization, while in the Border terrier it appears better adapted for contributing large movements. The Dachshund, susceptible to disc degeneration and IVDH, may require more stabilization for its ertebral column, but whether the M. iliocostalis meets.

Iliocostalis Learn Muscles
The quadratus lumborum (QL) muscle resides in the deep and posterior, lateral, and inferior areas of the spine, involving the iliac crest, the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae, and the 12th rib. The muscular organization is complex, and it is difficult to identify precisely the actions that occur through the contraction of fibers. It is an integral part of the thoracolumbar fascia.

Iliocostalis Lumborum Anatomy Origin, Insertion, Actions, Innervation
A six-year-old intact male Chihuahua dog was referred for vomiting, diarrhoea and weight loss. Ultrasonographic (US) and computed tomographic examination revealed a focal thickening in the jejunum, with no signs of gross metastatic disease.

Iliocostalis Lumborum Muscle anatomy, Muscular system anatomy, Human
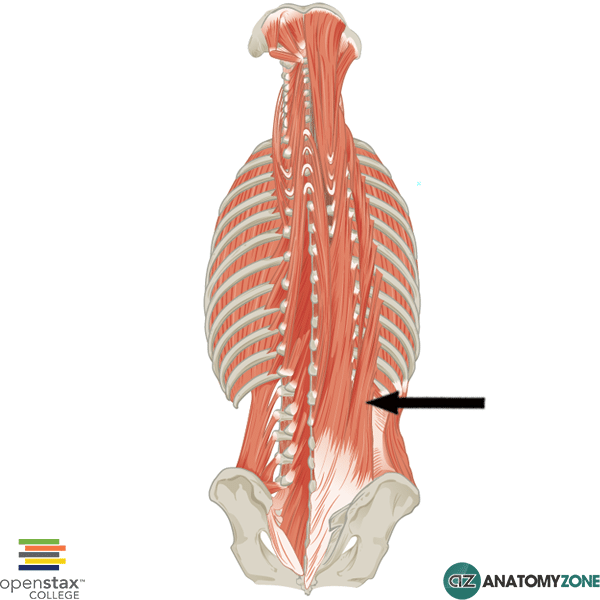
Longissimus muscle (musculus longissimus) The longissimus muscle is a long intrinsic muscle of the back.Along with spinalis and iliocostalis, these three muscles comprise the erector spinae group.The erector spinae is a large musculotendinous complex that runs along the entire length of the vertebral column and comprises the intermediate layer of the intrinsic, or deep, back muscles.
Iliocostalis Lumborum Rehab My Patient
ORCID record for Lluis Ferré Dolcet. ORCID provides an identifier for individuals to use with their name as they engage in research, scholarship, and innovation activities.
The iliocostalis stock illustration. Illustration of posterior 56286509
Longissimus thoracis. The longissimus thoracis muscle is the largest of the erector spinae muscles. It arises from the common origin of the erector spinae muscles (see Iliocostalis Lumborum). In addition, many fibers begin from the transverse and accessory processes of the lumbar vertebrae (see Chapter 7 ). This muscle is the longest muscle of.
Iliocostalis Lumborum AnatomyZone
History. The Veneto Institute Oncologico Veneto (IOV) is a Comprehensive Cancer Centre established in 2005, in consortium with the Hospital of the University of Padua, School of Medicine. IOV offers preventive, curative and palliative services to the population and improves medical knowledge through translational research.
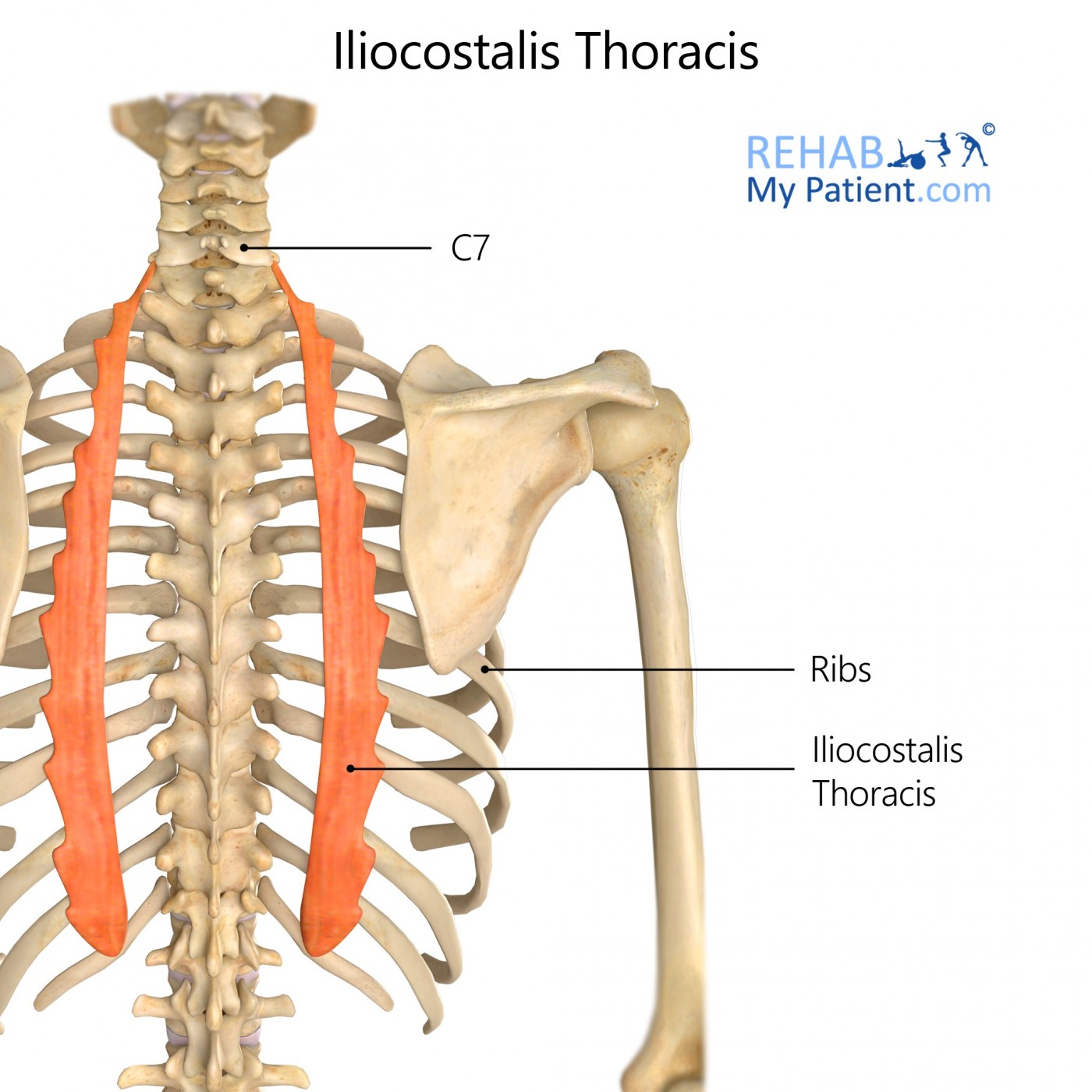
Iliocostalis Thoracis Rehab My Patient
The iliocostalis is a deep muscle of the back. It is located laterally within the erector spinae muscle complex and can be divided into three parts - lumborum, thoracis, and cervicis. Attachments: Arises from the lower thoracic and lumbar vertebrae, sacrum, posterior aspect of the iliac crest, and the sacroiliac and supraspinous ligaments.

Anatomy Stock Images spinemusculusmultifidusquadratuslumborum
The iliocostalis muscles are the most lateral components of the erector spinae group.This subgroup includes the iliocostalis cervicis, iliocostalis thoracis, and iliocostalis lumborum. Iliocostalis lumborum see link.; The iliocostalis thoracis muscle: starts from the superior aspect of the angles of the lower six ribs and ascends to end on the angles of approximately the upper six ribs and.

M. iliocostalis YouTube
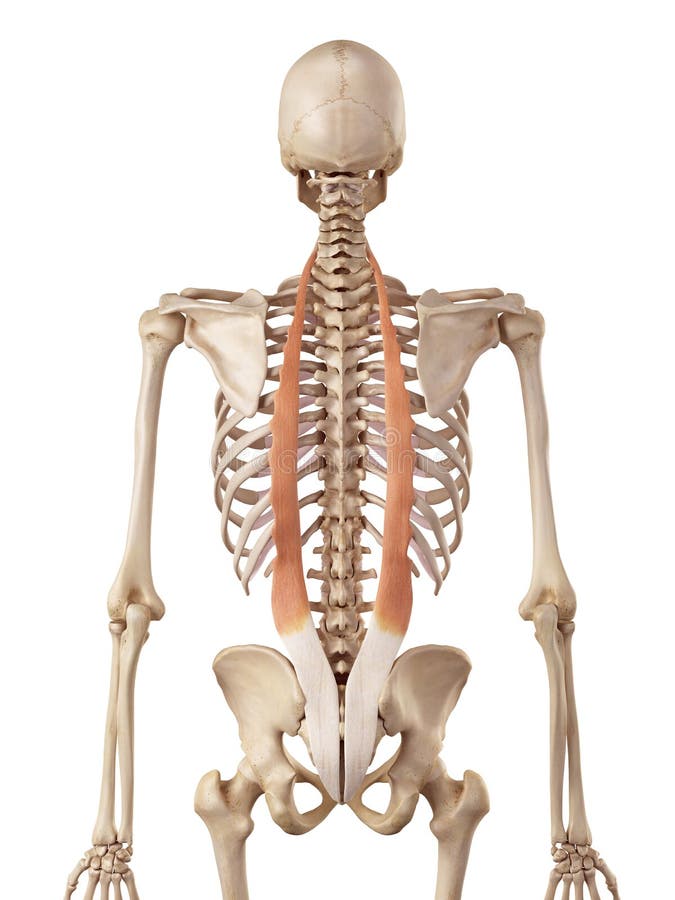
Iliocostalis is a dorsal muscle situated deep to the fleshy section of serratus posterior inferior muscle. Iliocostalis lumborum is the lower (lumbar) portion of that muscle. Injury to iliocostalis lumborum may be indicated by pain concentrated in the lower back or pain in the buttocks. Common daily activities may cause injury to the muscle including lifting a heavy object, rotating while.
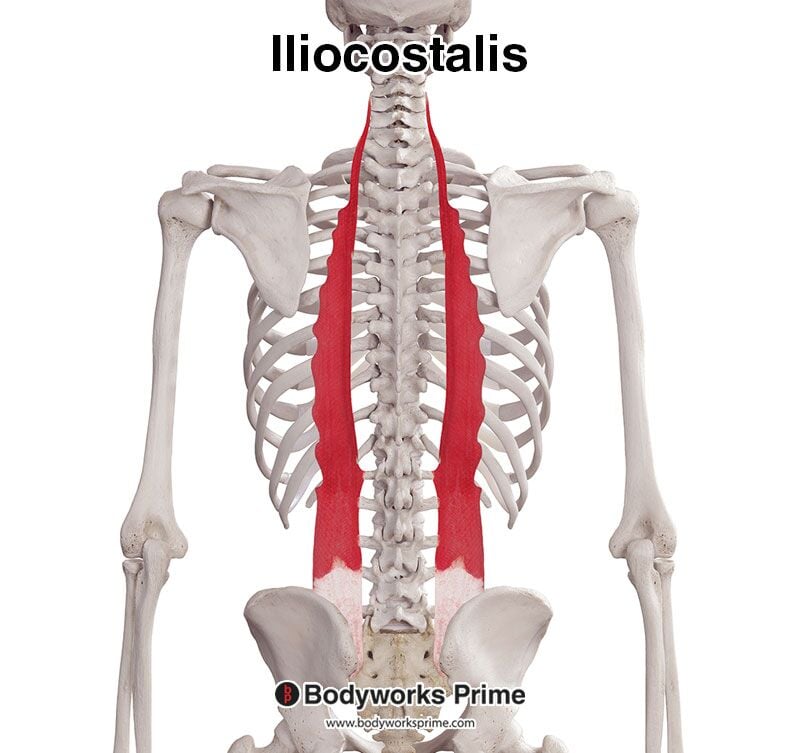
Iliocostalis Muscle Anatomy Bodyworks Prime
however, when considered in combination with the iliocostalis lumborum muscle it showed enhanced potential for production of power and facilitating spinal extension during galloping gaits. This was particularly the case in the greyhound, where the m. longissimus dorsi and the m. iliocostalis lumborum were estimated to have the

Iliocostalis lumbar stock illustration. Illustration of iliocostalis
The fibers of the iliocostalis lumborum muscle travel superiorly along the back and insert onto the: - transverse processes of the first to fourth lumbar vertebrae; - angles of fifth to tenth ribs. There can be variations between individuals regarding the insertion sites for the iliocostalis lumborum muscle (Tubbs, Shoja and Loukas, 2016).