MICROECONOMICS I General Equilibrium I MRS and MRT I Consumers and Firms YouTube
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/mrs1-5c3f6315c9e77c00019e2336.jpg)
Marginal Rate of Substitution MRS Definition
Marginal Rate of Substitution (MRS): Definition What is marginal rate of substitution? The marginal rate of substitution (MRS) is the rate at which a consumer is willing to substitute one.
Microeconomics MRS or Slope of Indifference Curves (Medium Lvl Question) YouTube
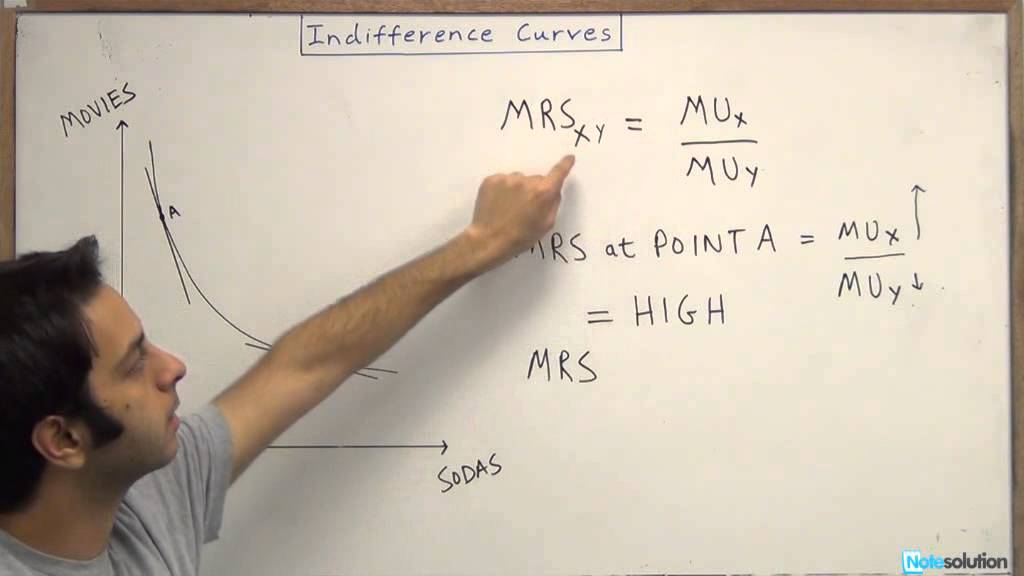
The Marginal Rate of Substitution can be defined as the rate at which a consumer is willing to forgo a number of units good X for one more of good Y at the same utility. T he Marginal Rate of Substitution is used to analyze the indifference curve. Suggested Videos Marginal Rate of Substitution Suppose you and your friend is playing Scrabble.

microeconomics Why do firms bother to produce at equilibrium quantities if at equilibrium
Marginal Rate of Substitution. The Marginal Rate of Substitution (MRS) is defined as the rate at which a consumer is ready to exchange a number of units good X for one more of good Y at the same level of utility. The Marginal Rate of Substitution is used to analyze the indifference curve. This is because the slope of an indifference curve is.

Launching mini supermarket chain Mr.Eco mart Ecoworld In corporation
The Marginal Rate of Substitution (MRS) Calculator is a tool used in economics and utility theory to assess the rate at which a consumer is willing to trade one good for another while maintaining a constant level of satisfaction or utility. This concept plays a vital role in understanding consumer preferences and choices.

Indian Heroine Shweta Chaudhary named face of Mrs ECO International Mrs ECO International PRLog
The marginal rate of substitution of X for Y (MRS) xy is the amount of Y that will be given up for obtaining each additional unit of X. This rate is explained below in Table.2. To have the second combination and yet to be at the same level of satisfaction, the consumer is prepared to forgo 3 units of Y for obtaining an extra unit of X.

Mrs. Eco Clean Saint Michael MN
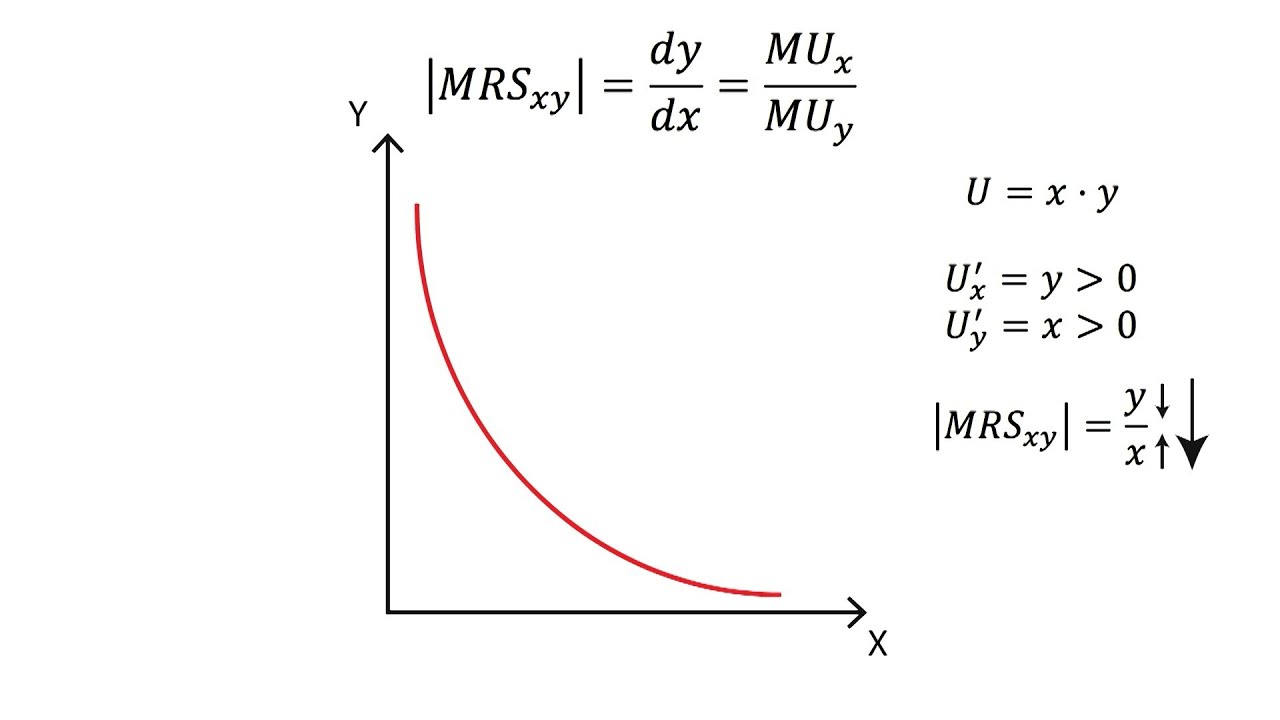
The marginal rate of substitution (MRS) is the quantity of one good that a consumer must sacrifice in order to increase the consumption of another good by one unit while maintaining the same level of total satisfaction. It is the slope of the negative sloping indifference curve and is an important tool to understand consumer behaviour.

Mrs. Earth Eco Missouri 2018 Gets in Shape at Hitch Fit Gym! Hitch Fit Gym
The Marginal Rate of Substitution (MRS) is an economic concept that represents the rate at which a consumer is willing to trade one good for another while maintaining the same level of satisfaction, also known as utility. MRS is determined by the slope of the indifference curve, which is a graph that indicates various combinations of two goods.
A.3 Marginal rate of substitution Consumption Microeconomics YouTube
The amount of one good that a consumer can give up in exchange for more units of another good with equivalent utility is known as the marginal rate of substitution (MRS). MRS measures the relative marginal utility, making it one of the fundamental principles of the modern theory of consumer behaviour.Assumptions of Marginal Rate of Substitution1) The size and shape of the goods are uniform. 2.

Mr. & Ms. ECOSaver
The marginal rate of substitution (MRS) is the quantity of one good that a consumer can forego for additional units of another good at the same utility level. MRS is one of the central tenets in the modern theory of consumer behavior as it measures the relative marginal utility.

Mrs Eco Tourism Universe Myanmar
In economics, the marginal rate of substitution (MRS) is the amount out a nice that a consumer is willing to consuming compared to another good, as longitudinal as the newer good is equally satisfying. MRS is used in indifference theory to analyze consumer behavior.

MRS and Law of Diminishing MRS Economics Class 12th YouTube
ECO 352 - Spring 2010 - Precepts Weeks 1, 2 - Feb. 1, 8 REVIEW OF MICROECONOMICS Concepts to be reviewed Budget constraint: graphical and algebraic representation Preferences, indifference curves. Utility function Marginal rate of substitution (MRS), diminishing MRS algebraic formulation of MRS in terms of the utility function

MICROECONOMICS I General Equilibrium I MRS and MRT I Consumers and Firms YouTube
In economics, the marginal rate of substitution ( MRS) is the rate at which a consumer can give up some amount of one good in exchange for another good while maintaining the same level of utility. At equilibrium consumption levels (assuming no externalities), marginal rates of substitution are identical.

Mrs. ECO Philippines 2019
In microeconomics, the marginal rate of substitution (MRS) is the rate at which a consumer would be willing to give up one good in exchange for another while remaining at the same level of utility. It is a key tool in modern consumer theory and is used to analyze consumer preferences.

Mrs. Eco Philippines 2019 Shiela DeForest
What is Marginal Rate of Substitution? The marginal rate of substitution (MRS) is the rate at which some units of an item can be replaced by another while providing the same level of satisfaction to the consumer. The MRS concept describes the relationship between the consumption of two goods or resources when consumers make rational decisions.

Cynthia Thomalla for the Miss Eco International EcoWear Competition
If we assume that the group is willing to give up one order of onion rings to get an additional order of fries, the MRS is 1:1. Why Marginal Rate of Substitution Matters. The marginal rate of substitution is an important concept in economics because it helps us to understand how consumers make decisions.

The Journey of a Brave Teacher Mr. and Ms. Ecosavers 2015
MRS = 1.24444. FAQ. What is a marginal rate of substitution? A marginal rate of substitution is a measure of the amount of a product a consumer is willing to purchase or consume, with respect to another product. It's essentially measuring the effect the consumption of one good has on the consumption of a separate but related good.