Hypermobility The Physio Company

EhlersDanlos syndrome Choudhury et al. 2009 BMJ Case Reports
Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (hEDS) and hypermobility spectrum disorders (HSD) are incapacitating and painful syndromes involving a generalized connective tissue disorder with joint hypermobility and musculoskeletal complications. A neuropathic component seemed clinically likely given frequent burning sensations, hypoesthesia, or.

EDS symptom chart headachechart Ehlers danlos syndrome symptoms, Ehlers danlos syndrome
Fibromyalgie et Syndrome d'Ehlers-Danlos, une confusionfréquente entre un syndrome très médiatisé et une maladiegénétique oubliée, à tort exclue dans la « rareté ». Pr. Claude HAMONET (Hôtel-Dieu MPR, Garches Génétique), Docteur Nejib Trabelsi (MDPH 91). Le diagnostic de fibromyalgie est à la mode, soutenu par des médecins et.
Le syndrome d'ehlers danlos
Bienvenue dans le monde énigmatique du Syndrome d'Ehlers-Danlos et de la fibromyalgie, un coin sombre de la médecine qui échappe souvent à la compréhension. Pour beaucoup, ces noms sont des énigmes médicales, des maux invisibles qui touchent silencieusement des vies, particulièrement celles des femmes âgées de 30 à 55 ans.

Le syndrome d’EhlersDanlos,Souvent confondu avec la fibromyalgie, fréquent mais rarement
Lorsqu'elle est associée à des douleurs musculo-squelettiques chroniques, le terme syndrome d'hypermobilité (ou hyperlaxité) est utilisé (tel que le syndrome d'Ehlers-Danlos de type hyperlaxité). Le syndrome d'Ehlers-Danlos, fréquent mais rarement diagnostiqué, est confondu avec la fibromyalgie et d'autres maladies; 3.
Le syndrome d’EhlersDanlos,Souvent confondu avec la fibromyalgie, fréquent mais rarement
Mais pour le Pr Claude Hamonet, médecin et anthropologue, spécialiste du syndrome d'Ehlers-Danlos, le SED est sous-diagnostiqué et donc le nombre de cas sous-estimé. Il est souvent confondu.

Le Syndrome d'Ehlers Danlos Les symptomes YouTube
Ehlers Danlos syndrome (EDS) is a group of hereditary connective tissue disorders that manifests clinically with skin hyperelasticity, hypermobility of joints, atrophic scarring, and fragility of blood vessels.[1][2] It is largely diagnosed clinically, although identifying the gene encoding the collagen or proteins interacting with it is necessary to identify the type of EDS. Identifying the.

Hypermobility The Physio Company
Oui, le syndrome d'Ehlers-Danlos existe bel et bien au Québec comme partout ailleurs dans le monde. Non, ce n'est pas de la fibromyalgie ou un résultat de la psychosomatisation. Ce sont les médecins, E. Ehlers du Danemark et H.-A. Danlos de la France qui ont décrit ce syndrome pour la première fois en 1900 pour Ehlers et en 1906 pour.
Surgicalorthodontic treatment in patients with EhlersDanlos syndrome a report of two familial
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is a rare, variable group of heritable connective tissue disorders characterized by skin hyper-extensibility, tissue fragility, and generalized joint hypermobility ( 1 ). Given that connective tissue is distributed throughout the entire body, it is not surprising that EDS features multi-organ system involvement.

Figure 3 from EhlersDanlos Syndrome, Hypermobility Type An Underdiagnosed Hereditary
Fibromyalgie et Syndrome d'Ehlers-Danlos, une confusion fréquente entre un syndrome très médiatisé et une maladie. Le diagnostic de Syndrome d'Ehlers-Danlos est pourtant facile à poser, il est purement clinique, il ne nécessite aucun examen biologique, histologique, génétique ou d'imagerie. Le regroupement de plusieurs des 10.

Pin on Medicine
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is a connective tissue disease that predominantly affects women and has a prevalence of approximately 1 in 2500. 1 There are several different subtypes, with the classical and hypermobility type (EDS-HT) encompassing 90% of cases. 2 EDS-HT, the most common but least severe, has no genetic marker and shares.

Les symptômes des Syndromes d'EhlersDanlos Infographie SED in FRANCE
High overlap in patients diagnosed with hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome or hypermobile spectrum disorders with fibromyalgia and 40 self-reported symptoms and comorbidities. Gaudiano G, Puglisi PA, Fasolino A, Cruccu G, et al. Pain due to Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is associated with deficit of the endogenous pain inhibitory control. Pain Med.
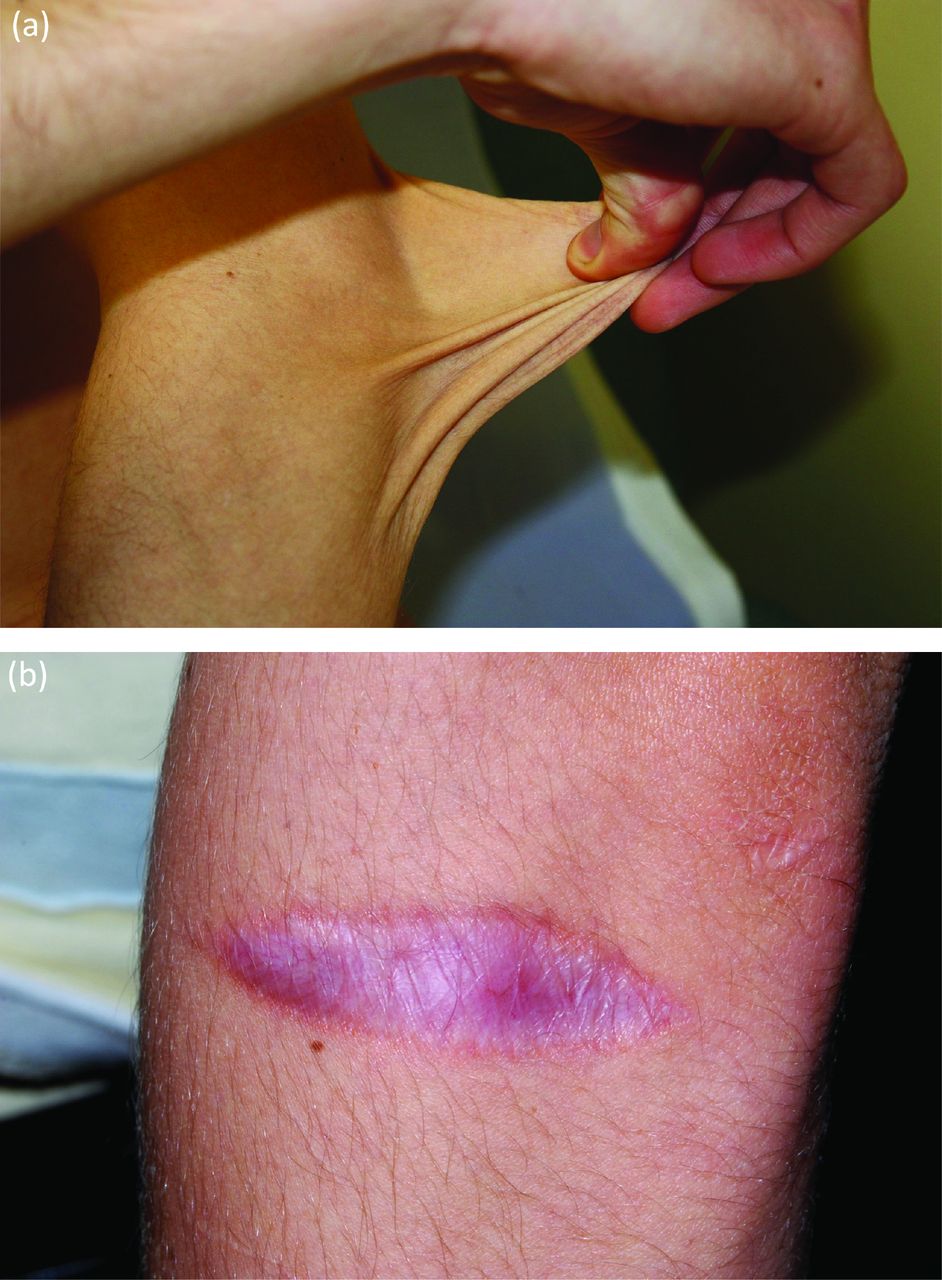
Vascular Ehlers Danlos Syndrome
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is an umbrella term for different heritable soft connective tissue disorders mainly characterized by generalized joint hypermobility, skin texture abnormalities, and visceral and vascular fragility or dysfunctions. Current nosology identifies 6 major EDS variants, with the hypermobility (hEDS), classic (cEDS), and.
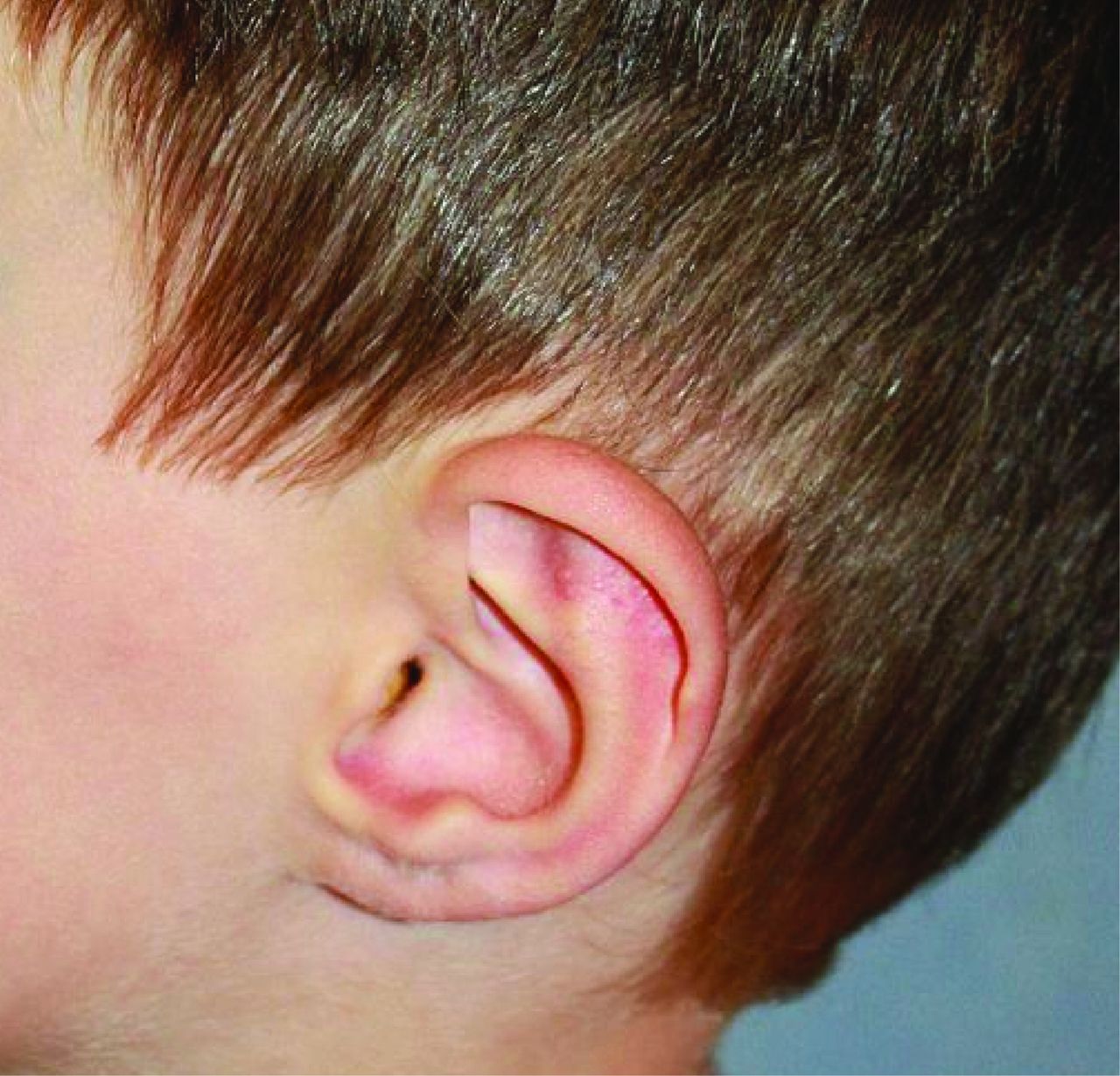
EhlersDanlos syndrome a commonly misunderstood group of conditions RCP Journals
Background Ehlers-Danlos syndrome Type IV (aka Vascular Ehlers Danlos, or vEDS) is a dominantly inherited mutation in the Collagen 3A1 gene (COL3A1). The disease is characterized by tissue friability and age-related susceptibility to arterial aneurysm, dissection and rupture as well as uterine and bowl tears. These clinical manifestations result in major surgical intervention and decreased.

Le syndrome d’EhlersDanlos,Souvent confondu avec la fibromyalgie, fréquent mais rarement
Le syndrome d'Ehlers-Danlos et la fibromyalgie sont deux conditions complexes qui nécessitent une compréhension et un diagnostic précis. Le témoignage belge souligne l'importance d'une évaluation médicale approfondie et d'une prise en charge adaptée à chaque patient.
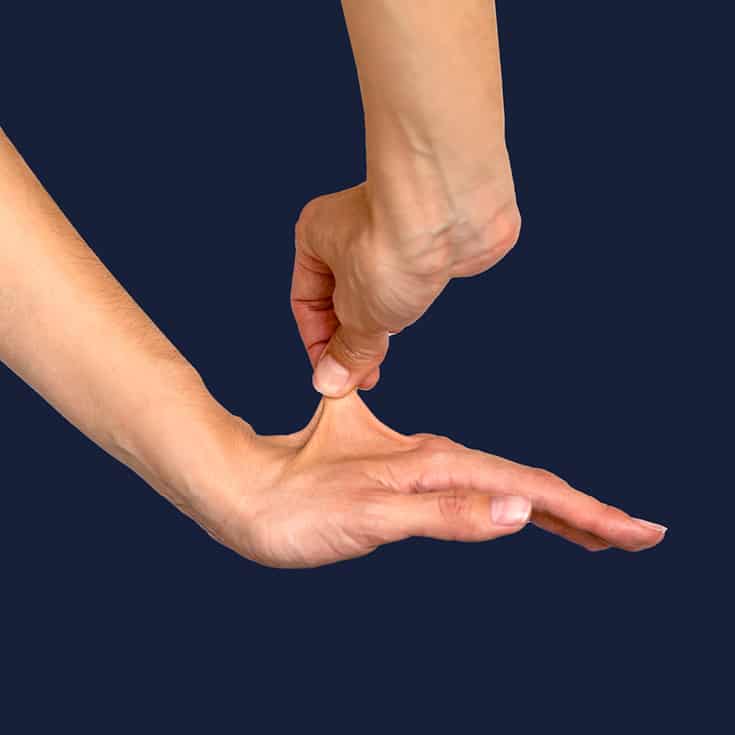
Maladies Rares dépistage et diagnostic
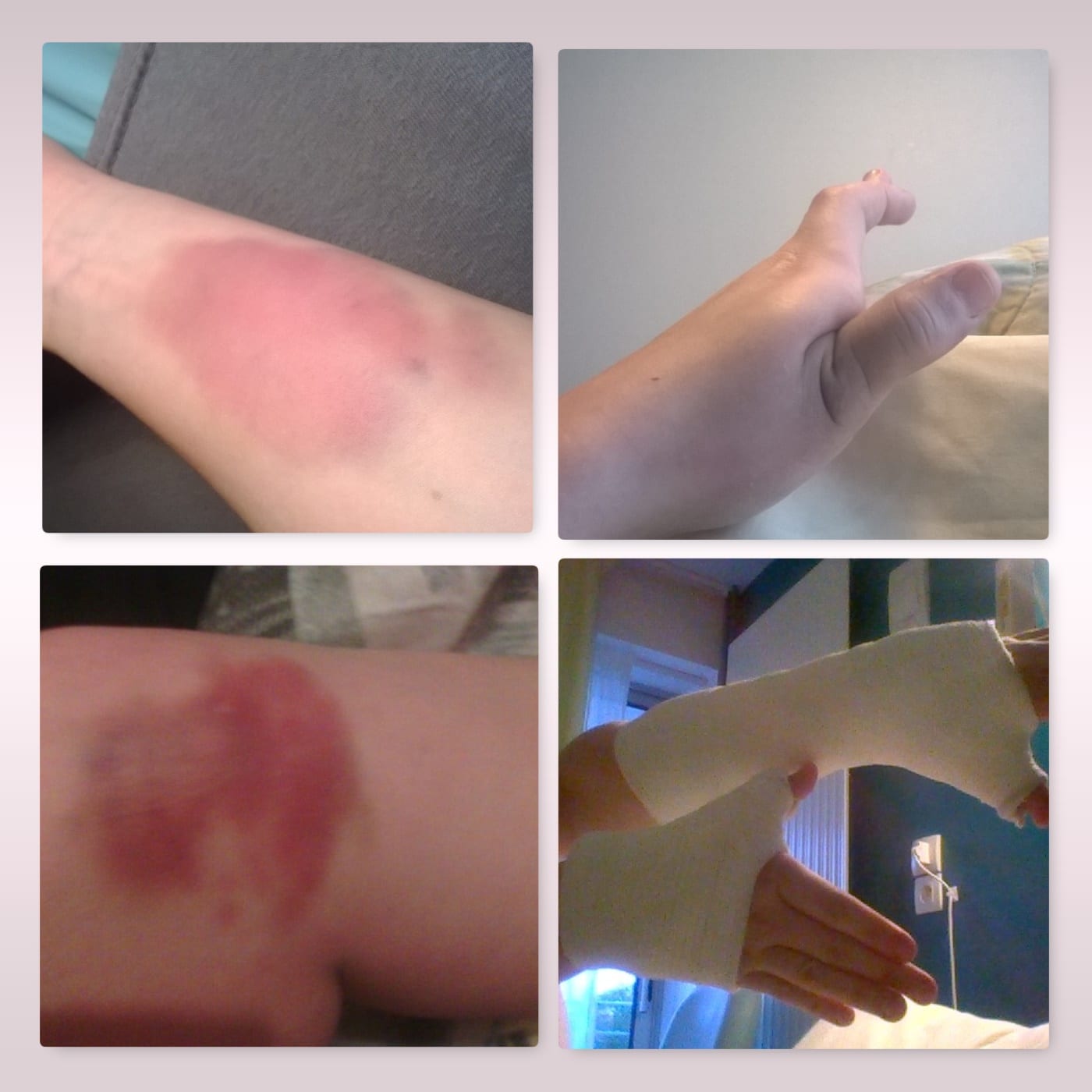
Each type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome has its own symptoms, but the most common EDS symptoms include: Overly flexible (hypermobile) joints — it might feel like your joints are loose or unstable. Soft skin that's thinner and stretches more than it should. Bruising easily or more often than usual.

Pin by Frugal Dutch Mom on Ehlers‐Danlos in 2020 Ehlers danlos syndrome awareness, Ehlers
Fibromyalgia is thought to be the result of Central Sensitization which describes changes in the central and peripheral nervous system that increase sensitivity to painful and nonpainful stimuli. The injuries often observed in patients with hypermobility set the stage for painful joints. Central sensitization is thought to amplify this pain in.