Passé Composé Bildung mit avoir DOS Lernwelt

seinavalcarolina 11/29/15
The passé composé is one form of the French past tense that is used in instances where an event has taken place either at a single point in time in the past, or possibly multiple times in the past, but it's not important or relevant to what is being asked. Let's look at an example together…. Let's say that you are walking home and the.

Einführung des imparfait (Bildung, Ausnahmen, Gebrauch) Unterrichtsmaterial im Fach
The passé composé is the most common French past tense, often used in conjunction with the imperfect.It is extremely important to understand the distinctions between past tenses in order to use them correctly and thus express past events accurately. Before you can compare them, however, be sure that you understand each tense individually, as this will make it a lot easier to figure out how.

Verbes Passé composé Juliette Blue Bourdier, Medievalist
The passé composé conjugation is constructed with the present tense of "avoir" followed by the past participle of the action verb. For example, here's how to conjugate "donner" (to give) in. Auxiliary verb "avoir". To learn more about this auxiliary verb, we have a full post on avoir conjugation and meanings.

Französisch Passé composéÜbersicht ob und wann das Verb mit 'avoir' oder mit ‚être‘ verwendet
Merke: Das passé composé setzt du aus den Hilfsverben avoir oder être und dem participe passé zusammen. Passé composé = Präsensform von être + das angeglichene participe passé des Vollverbs Als kleine Erinnerung findest du hier nochmal die konjugierten Formen von être im Präsens : Je suis Tu es Il / elle / on est Nous sommes Vous êtes

Review Of Präsens Verben 2022
Prendre means "to take" and is a irregular -re verb. In this lesson you will learn about: how prendre in the passé composé is conjugated, which derivatives prendre has in the passé composé, how prendre in the passé composé is pronounced, how prendre in the passé composé is used in sentences,

Pin on Se former en anglais
Passé Composé: Französische Vergangenheitsform. Mit dem Passé composé beschäftigen wir uns in diesem Artikel. Dabei wird erklärt, wie man diese Zeitform der französischen Sprache einsetzt und in welchen Fällen man dies tut. Auch wird auf die Passé composé Bildung mit être und avoir eingegangen und entsprechende Beispiele werden.

French Language Basics, French Basics, French Language Lessons, French Language Learning, French
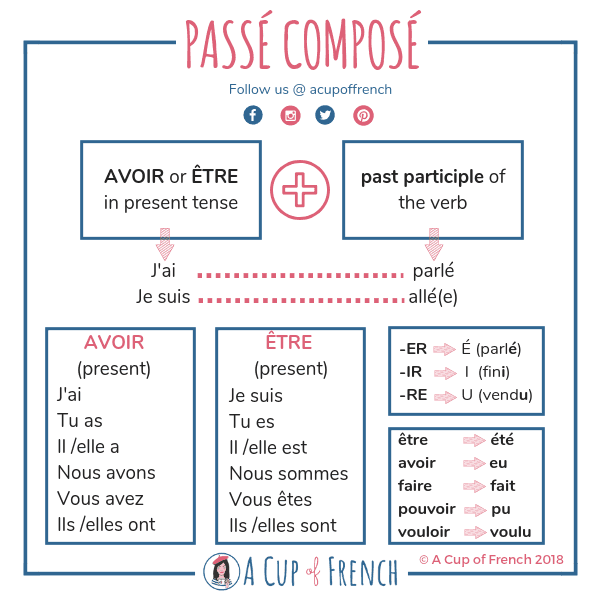
2) How to build the passé composé. Just like the present perfect in English, the passé composé (= literally " compound past ") is made of: Auxiliary in the present + past participle of the verb. For instance: J'ai appelé (= I called) → auxiliary = "ai" + past participle = "appelé". The auxiliaire can be the verbs avoir.

Passé composé Französische Zeiten verstehen, lernen, üben Französisch lernen, Französische
The following formula represents these three parts: Le sujet + L'auxiliaire + Le participe passé Le Sujet When you compose a sentence, a subject is usually included. The subject is the person (s) and/or thing that is performing the action/verb. In French, these are the common subjects: L'Auxiliaire

Pin on Lehrmittel
Was ist das Passé composé? (00:13) Passé composé - Bildung (01:11) Passé composé: être oder avoir? (01:36) Passé composé: Participe passé (02:36) Participe passé - Anpassung (03:23) Das Passé composé ist eine französische Vergangenheitsform. Wann du sie benutzt und wie man das Passé composé bildet, erfährst du hier und im Video ! Inhaltsübersicht
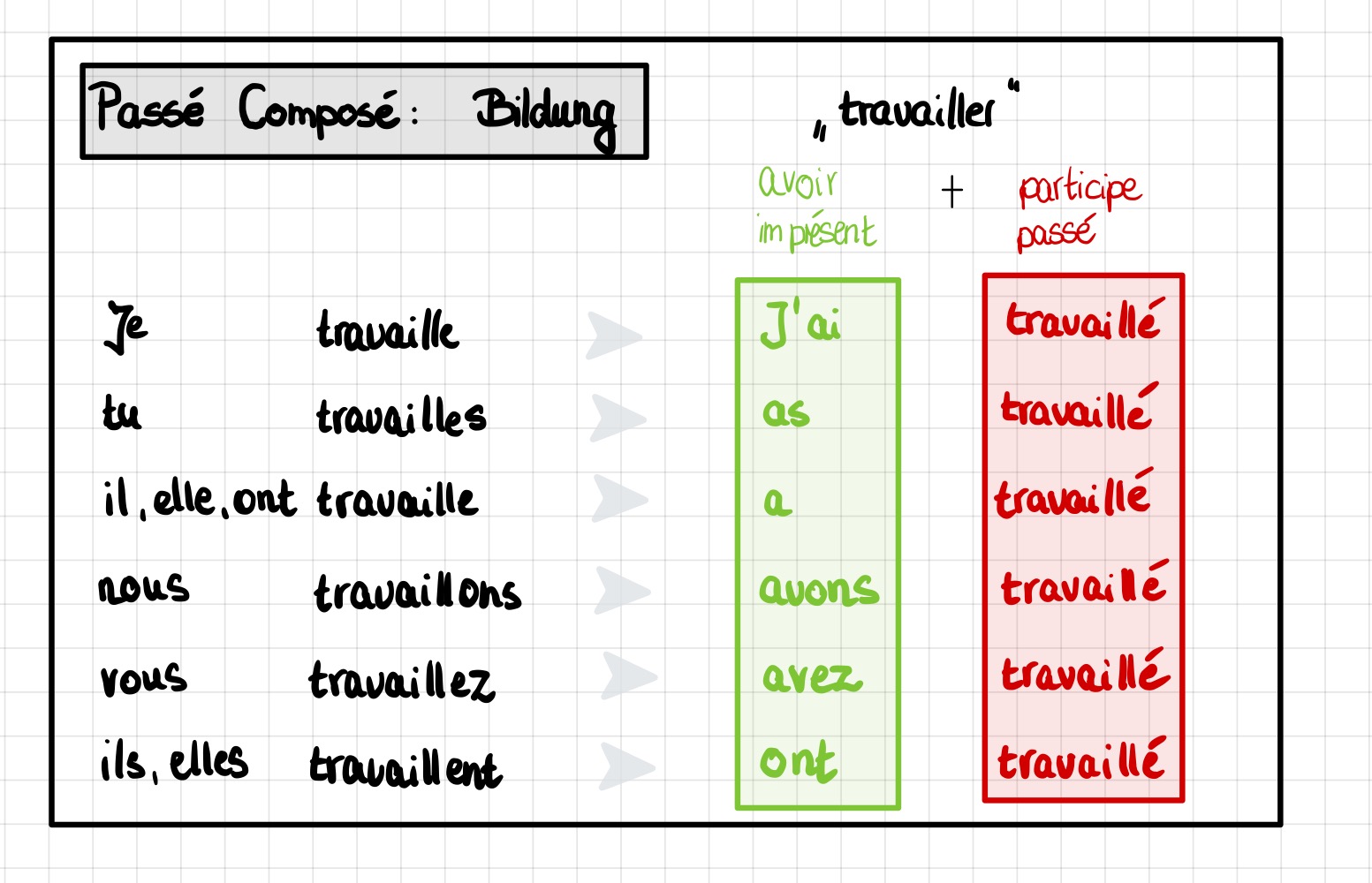
Passé Composé Bildung mit avoir DOS Lernwelt
The passé composé is a compound tense, meaning you need two components to conjugate a verb. A helping verb (être or avoir) conjugated in the present tense. The past participle (participe passé) of the verb you want to conjugate. Let's see how this works in practice! 1. Choose your helping verb/auxiliary verb
passe compose Liberal Dictionary
The passé composé is the most important past tense in French. It corresponds to the English simple past. The passé composé talks about actions that were completed in the past and emphasises their results or consequences in the present. Learn about the passé composé with Lingolia's examples, then check your knowledge in the free exercises.

Passé Composé Bildung mit être DOS Lernwelt
In this French grammar lesson we will learn about venir conjugation in the passé composé.. Venir means "to come" and falls in the second group of -ir verb conjugations.. In this lesson you will learn about: how venir is conjugated in French; how venir is pronounced in French; how venir is used in sentences in French; how to quiz yourself on venir conjugation in the passé composé

Übung Participe passé ǀ Lernwerk TV
The passé composé corresponds mostly to the English simple past or the present perfect. The passé composé talks about specific actions that were completed in the past. In spoken French language, the passé composé is always used instead of the passé simple. We conjugate the passé composé using the auxiliary verbs avoir or être followed.

La conjugaison des verbes avoir, être, aller und faire Unterrichtsmaterial im Fach Französisch
3. Past Participle. The Passé Composé consists out of three parts. A Pronoun. Avoir or Être in the Present Tense. A Past Participle. Of these three elements, only the third is new. The first two you should already know. Here's a recap of the pronouns, and the conjugations of Avoir and Être as a refresher.

(816×567) Teaching french, Grammar chart, French grammar
The vast majority of French verbs form the passé composé with avoir. This means that you'll conjugate avoir the way you normally would and then add the past participle, as in the previous example. Let's do one more together: Subject + avoir + past participle [+ additional details] Je + ai + acheté + des fleurs hier.
Prof FLCE Le passé composé
Elision. Liaison. Aspirated h. Help:IPA/French. v. t. e. The passé composé ( pronounced [pase kɔ̃poze]; 'compound past') is a past tense in the modern French language. It is used to express an action that has been finished completely or incompletely at the time of speech, or at some (possibly unknown) time in the past.