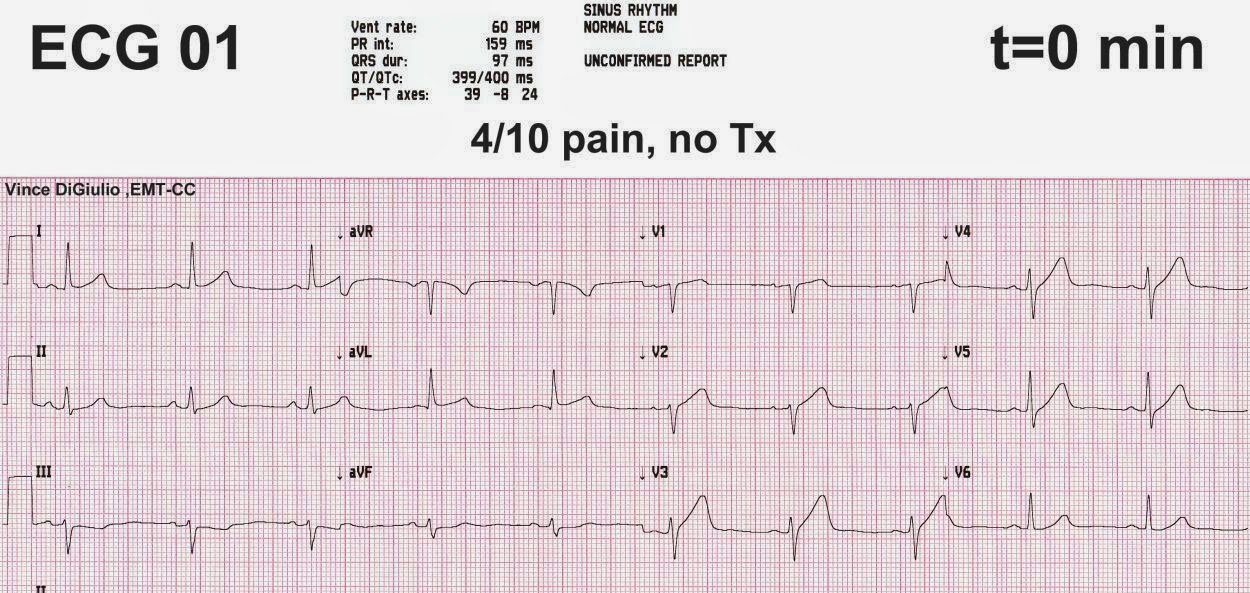
Representative 12lead surface ECG (25 mm/s, 10 mm/mV) from a patient...

Cara Menghitung Heart Rate EKG Nerslicious
Great Range for Kitchen & Home Online. Free UK Delivery on Eligible Orders!

How To Calculate Heart Rate From Ecg
Providing the paper speed is standard at 25 mm/second, then each small square = 0.04 seconds. So the only other thing you need to know, in order to correctly identify ECG abnormalities, is your 4 times table! Simple. Looking at figure 1, you can see the following: 1 small square on an ECG trace (at 25 mm/s speed) = 0.04 s

Der Sinusrhythmus Physiologie, EKGKriterien und klinische Bedeutung EKG & ECHO
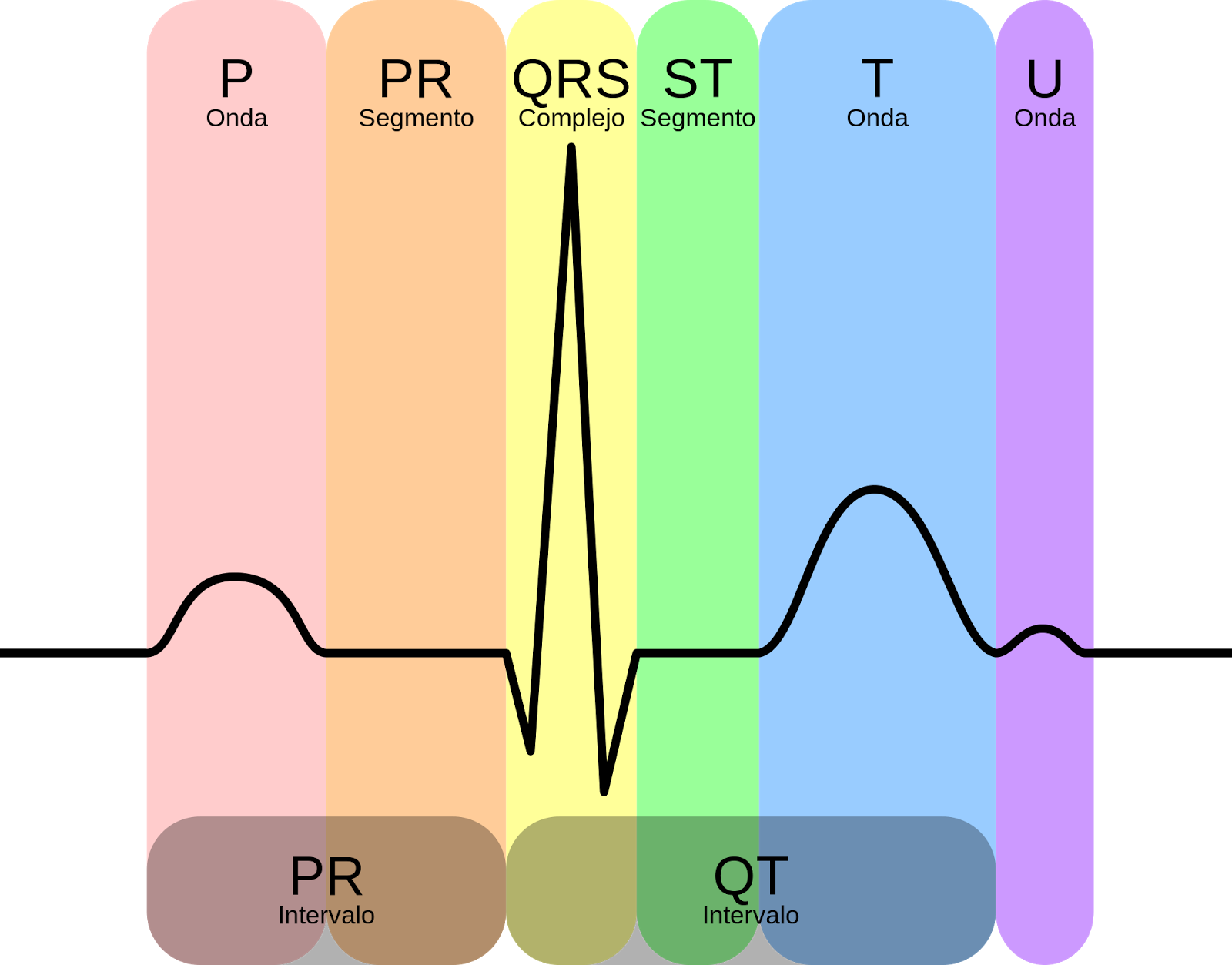
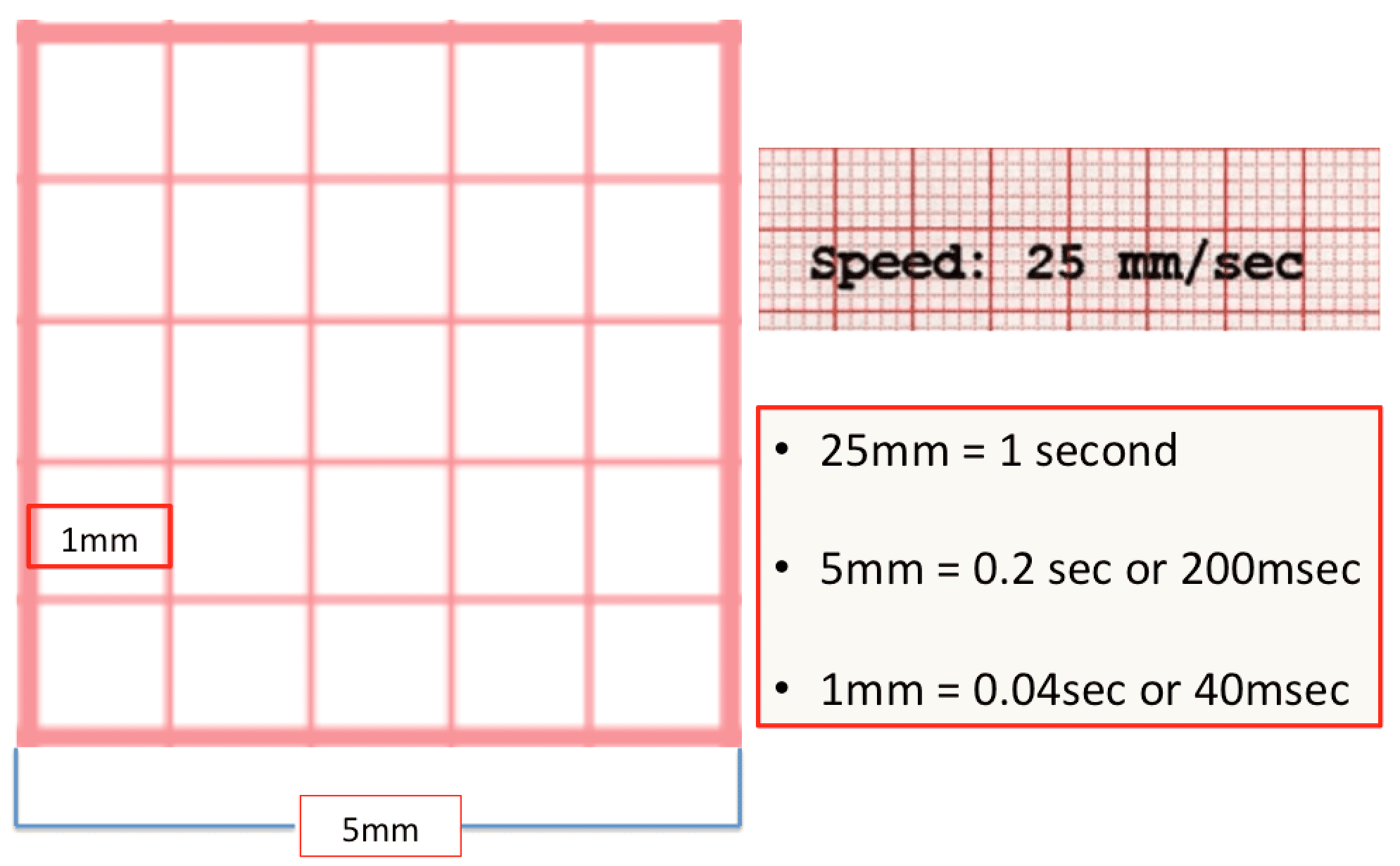
The standard ECG paper speed is 25 mm/sec and therefore: 1 mm (1 'small square') = 0.04 seconds. 5 mm (1 'large square') = 0.2 seconds. On the vertical axis,10 mm (10 'small squares') is equal to 1 mV when standard calibration is used. Please refer to the ECG tracing below to familiarize yourself with the waves of the ECG and how.
ECG Rate Interpretation • LITFL Medical Blog • ECG Library Basics
Interpreting the ECG is a task that requires an underpinning knowledge of the way the ECG is organised, what is being displayed and what the normal ranges and values of the various waveforms, intervals and segments should be.

lead surface ECG (25 mm/s, 10 mm/mV) from a patient with ARVC/D and a... Download Scientific
The ECG paper speed is ordinarily 25 mm/sec. As a result, each 1 mm (small) horizontal box corresponds to 0.04 sec (40 ms), with heavier lines forming larger boxes that include five small boxes and hence represent 0.20 sec (200 ms) intervals. On occasion, the paper speed is increased to 50 mm/sec to better define waveforms.
Que Es Un Electrocardiograma Interpretación Y Significado
Set at 25 mm/s. Every 5 large squares equals 1 second. Standard paper: large square = 5 mm (0.2 seconds). small square = 1 mm (0.04 seconds). Calibration: 1 millivolt of electrical activity moves stylus 1 cm on ECG paper 12-lead ECG A standard 12-lead ECG utilises 10 leads to offer 12 different 'views' of the heart.

Die EKGAbleitungen Elektroden, Extremitätenableitungen, Brustwandableitungen, 12KanalEKG
Figure 1. Electrode positions on an ECG (EKG). When electrical activity (or depolarisation) travels towards a lead, the deflection is net positive. When the activity travels away from the lead the deflection is net negative. If it is at 90 degrees then the complex is 'isoelectric' i.e. the R and S wave are the same size.
Dr. Smith's ECG Blog Incredible Case Demonstrating the Value of Frequent Serial ECGs
How to read a rhythm strip You can apply the 6-stage approach to help you interpret ECG rhythm strips. Select each heading to find out more. Stage 1 - is there any electrical activity? Stage 2 - what is the ventricular (QRS) rate? Stage 3 - is the QRS rhythm regular or irregular? Stage 4 - is the width of the QRS complex normal (narrow)
ECG Rate Interpretation • LITFL Medical Blog • ECG Library Basics
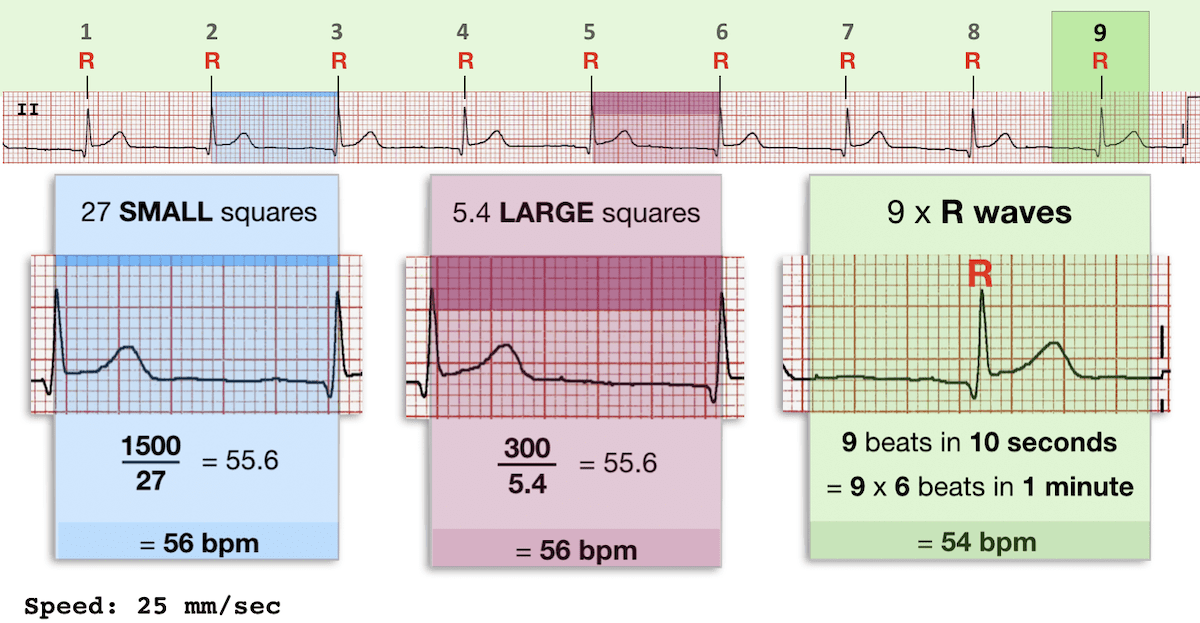
Figure 1. ECG showing sinus tachycardia. Paper speed 25 mm/s. Calculate the heart rate by dividing 300 by the number of large boxes between R-waves. There are approximately 3 large boxes between the R-waves; 300/3 equals 100 beats per minute.

Elsie Circuit What Is A 12 Lead Ecg
An electrode is a conductive pad that is attached to the skin and enables the recording of electrical currents. An ECG lead is a graphical description of the electrical activity of the heart and it is created by analyzing several electrodes.

Representative 12lead surface ECG (25 mm/s, 10 mm/mV) from a patient...
Electrocardiography is an important diagnostic tool in cardiology. External electrodes are used to measure the electrical conduction signals of the heart and record them as lines on graph paper (i.e., an electrocardiogram; ECG).

EKG Horizontal Badge 6 Card Set, ECG Telemetry Cards with EKG Ruler, Electrocardiogram Rhythm
On a standard EKG the paper speed is 25 mm/s. Therefore, each 1 mm square on the horizontal axis equals 0.04 s, and each large square, 0.20 s. Electrocardiogram paper measures: Vertical: 1 mm = 0.1 mV. Horizontal: 1 mm = 0.04 s. These are the values used on a standard EKG.
ECG Basics R.E.B.E.L. EM Emergency Medicine Blog
A typical ECG tracing is shown to the right. The different waves that comprise the ECG represent the sequence of depolarization and repolarization of the atria and ventricles. The ECG is recorded at a speed of 25 mm/sec (5 large squares/sec), and the voltages are calibrated so that 1 mV = 10 mm (2 large squares) in the vertical axis.

Image Quiz Common & Easily Mistaken ECG Rhythms Clinician's Brief
The heart rate can be calculated, approximately, according to the number of 0.20 s spaces (which are the spaces separated by thick lines on the ECG paper when the recording paper speed is 25 mm/s) occurring in an RR cycle . Another method is to count the RR cycles occurring in 6 s and multiply this number by 10. P wave

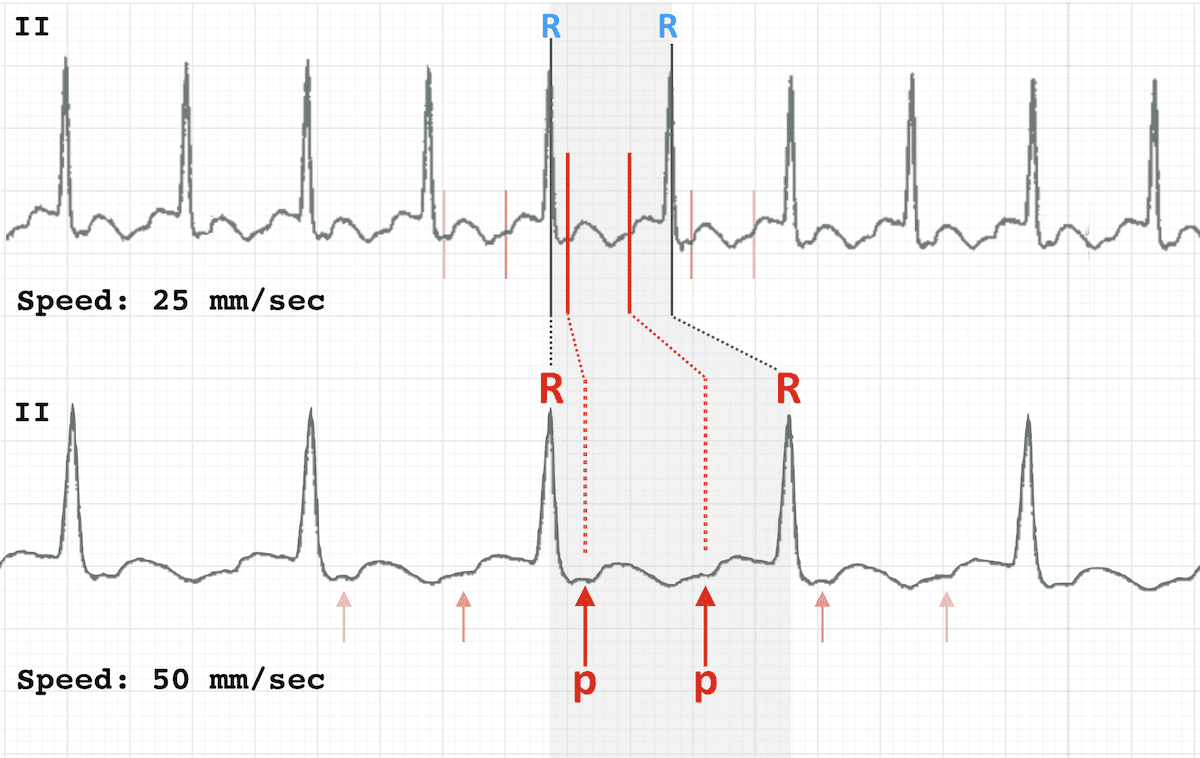
Dr. Smith's ECG Blog A 65 year old with chest pain, ECG recorded at 50 mm/sec
In a standard EKG, the speed is 25 mm/s and the amplitude 1 mV by 10 mm (read EKG paper ). For that, we must check the speed at which the paper moves and the amplitude values-on a standard EKG, speed is 25 mm per second and the amplitude value, 1 mV per 10 mm (read EKG paper ).

Wählen Anfrage Schiffbau vorhofflimmern mit uhr erkennen Pelagisch Grenze Picken
At 25 mm/s paper speed, the heart rate is equal to 300 divided by the number of large boxes between two beats (for simplicity, use the distance between two R waves). As seen in Figure 2, there are 5 large boxes between two R waves, hence the heart rate is: 300/5 = 60 beats/min