Heart Anatomy Anatomy and Physiology II
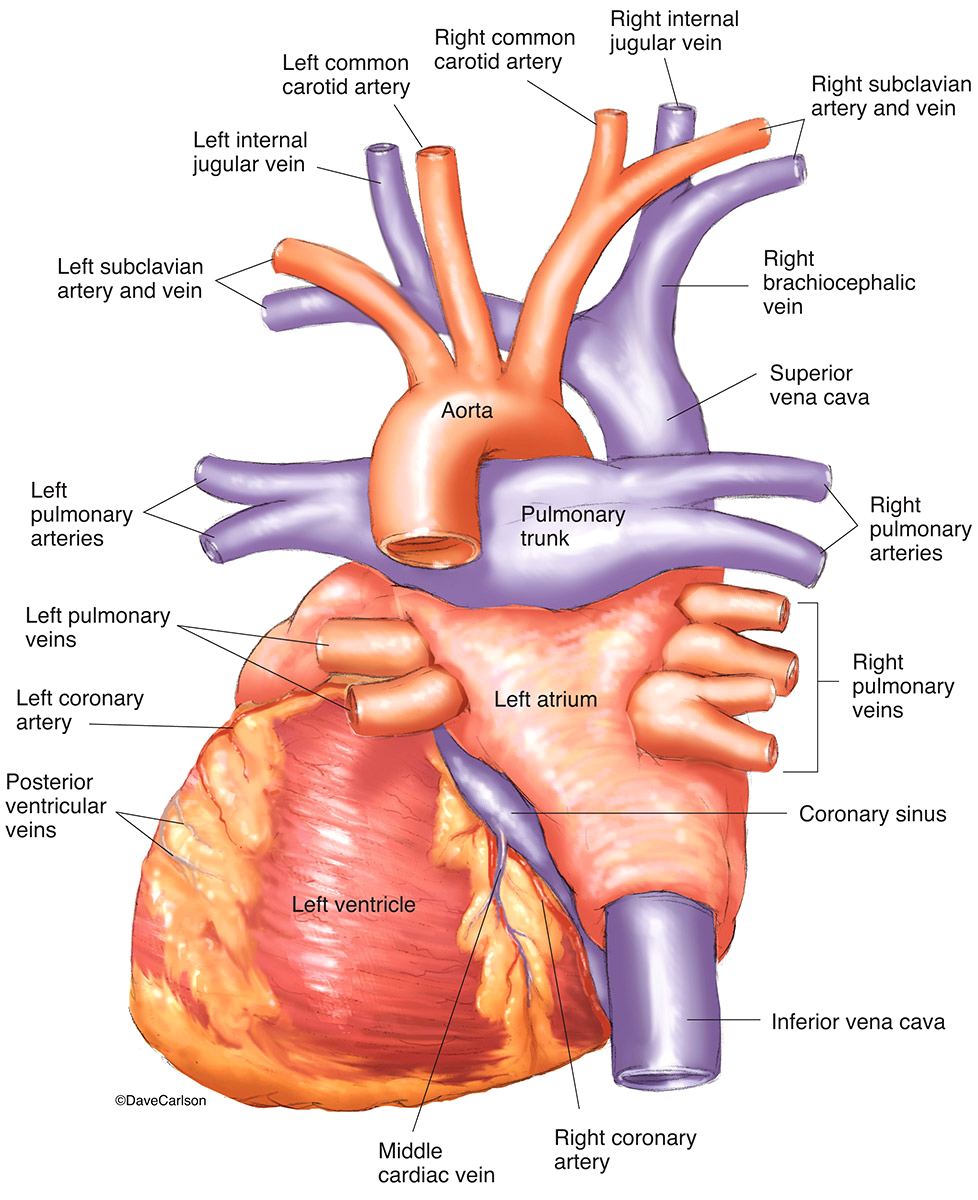
Human Heart Posterior View Carlson Stock Art
The heart is a 4-chambered muscular pump made primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. The heart is divided into 4 chambers: 2 upper chambers for receiving blood from the great vessels, known as the right and left atria, and 2 stronger lower chambers, known as the right and left ventricles, which pump blood throughout the body.

posterior heart artery The Heart and Circulation A&P Pinterest
Location of the Heart. The human heart is located within the thoracic cavity, medially between the lungs in the space known as the mediastinum. Figure 19.2 shows the position of the heart within the thoracic cavity. Within the mediastinum, the heart is separated from the other mediastinal structures by a tough membrane known as the pericardium.
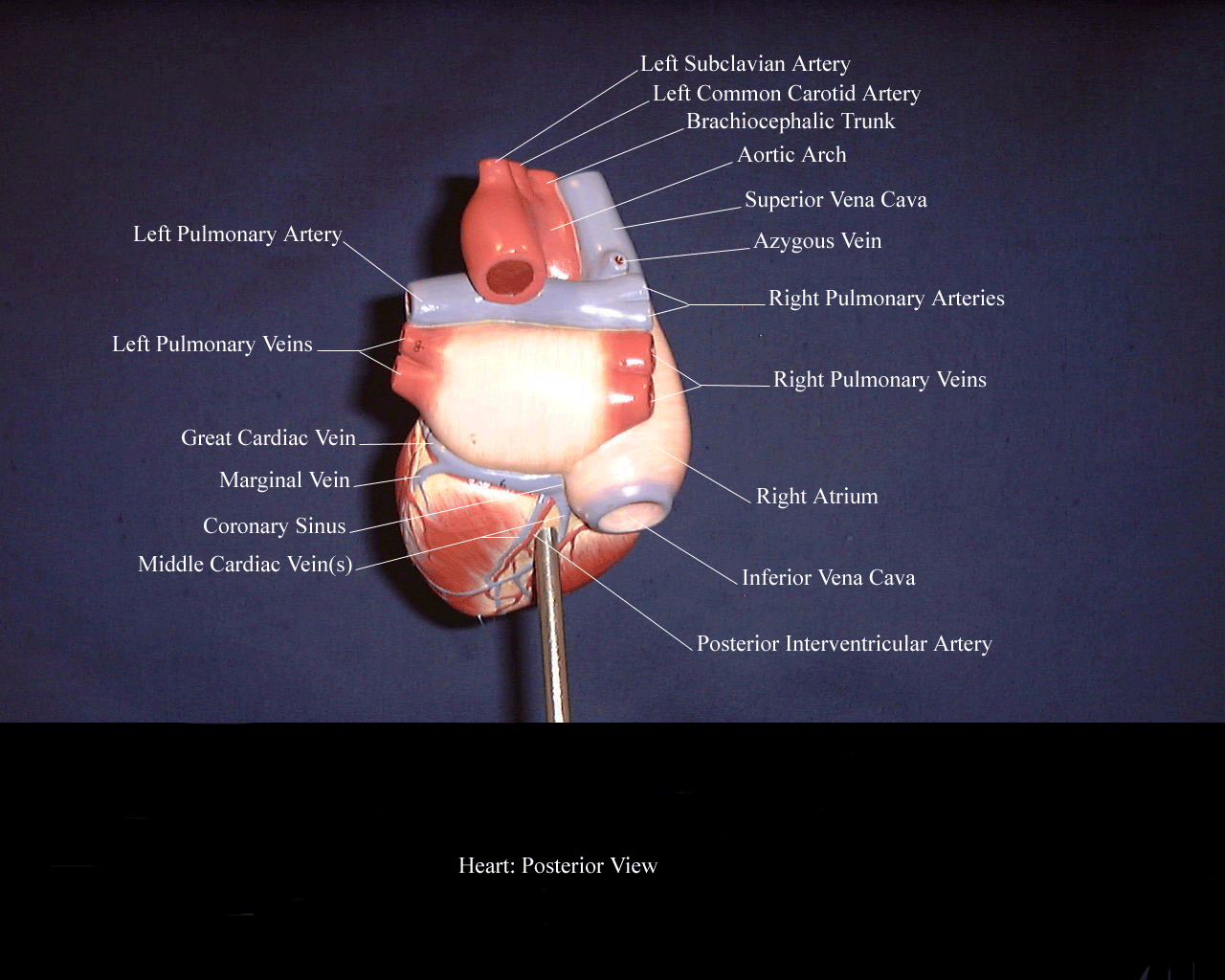
posteriorheart1
Heart, posterior view. View Media Gallery The overall shape and position of the heart may vary according to the relative size and orientation of each of its parts. For example, a large.

Heart Anatomy Anatomy and Physiology II
Cardiac Anatomy Robert E. Hobbs The heart is a muscular organ, pyramidal in shape, consisting of two parallel-valved pumps, located within the middle mediastinum, two-thirds to the left of the centerline. The base of the heart is oriented superiorly, whereas the apex points leftward, anteriorly, and slightly inferiorly. The cardiac apex is located at the…

Photorealistic image of the posterior view of the human heart. Four
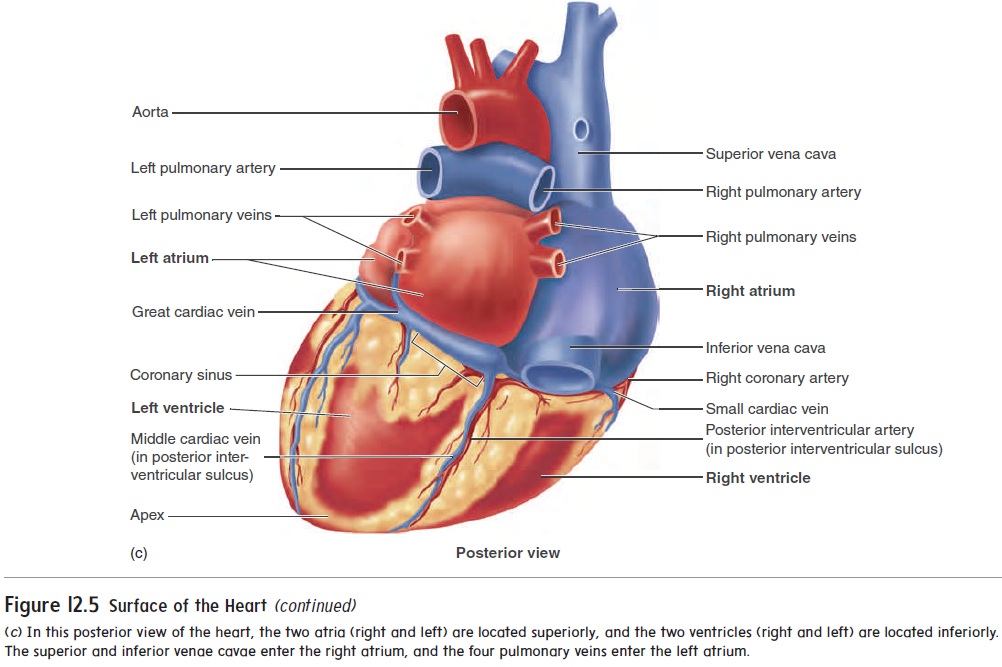
Heart (Posterior View) Main Chambers of the Heart. Right Atria: Receives venous (or deoxygenated) blood from the superior and inferior vena cava and the coronary sinus and transfers. Functions to transfer blood thru the tricuspid valve during diastole (ventricular relaxation) into the right ventricle.

4 posterior view of the human heart Download Scientific Diagram
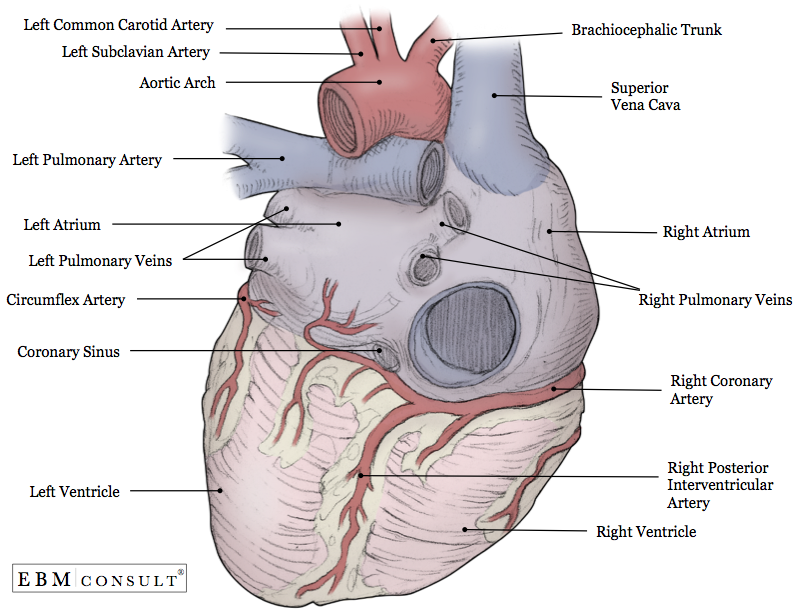
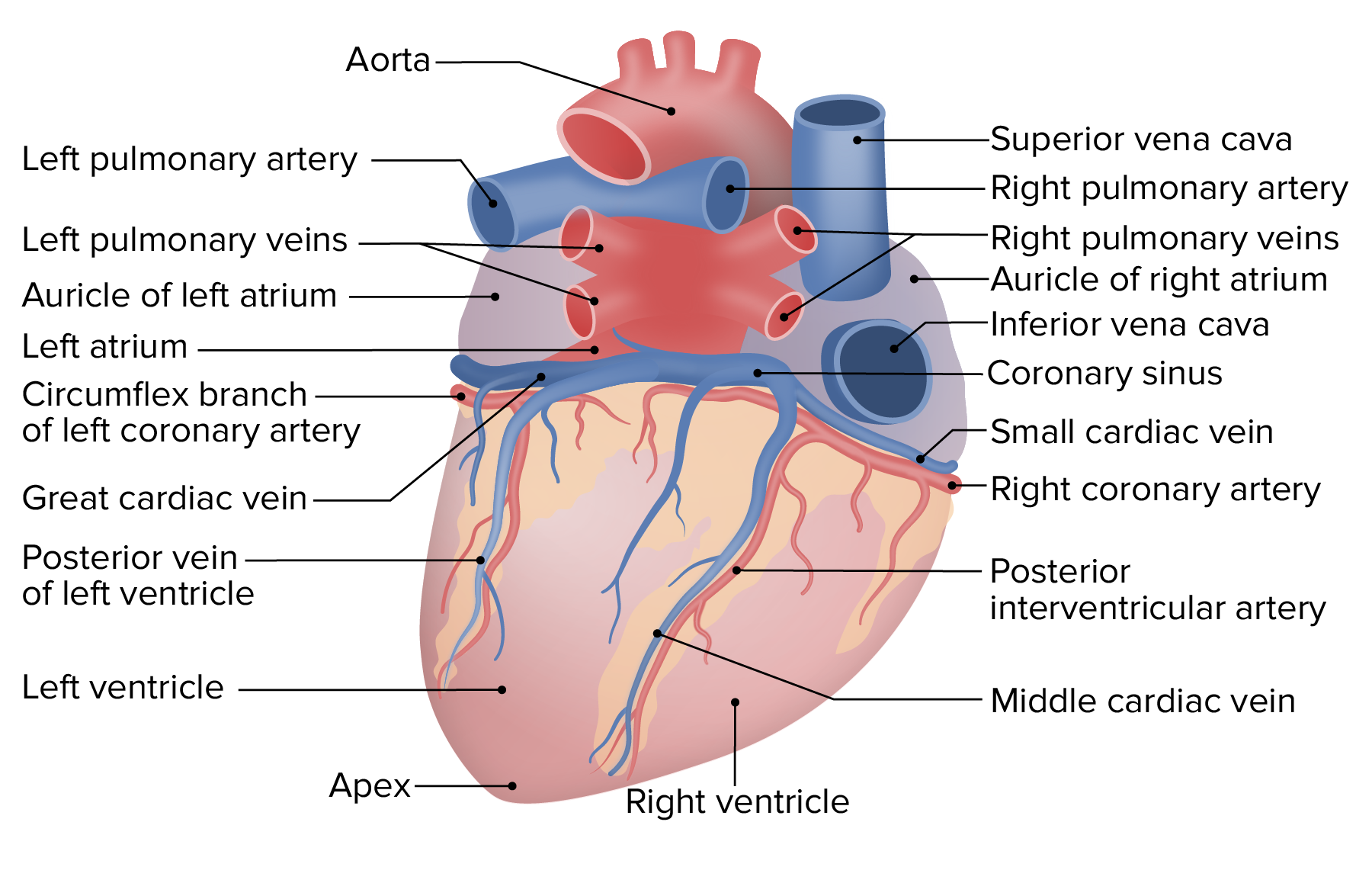
Definition. enlarged vessel on the posterior aspect of the heart that empties blood into the right atrium. Location. Term. Posterior vein of left ventricle. Definition. Parallels the posterior left ventricular branch. Location.
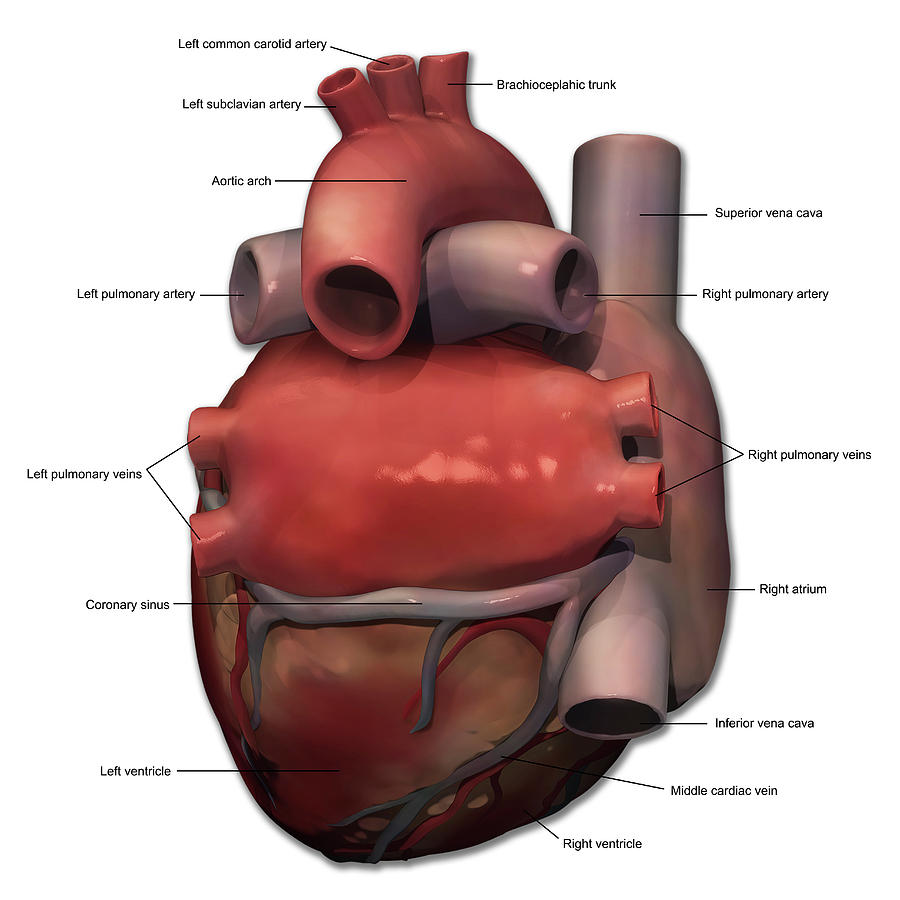
Posterior View Of Human Heart Anatomy Photograph by Alayna Guza Pixels
Figure 1. Anterior view of the heart A with and B without coronary fat and vessels. Figure 2. Posterior view of the heart A with and B without coronary fat and vessels. Figure 3. Lateral view of the right atrium of the heart, with A the outer wall of the right atrium dissected and peeled back.

Faculty and Staff Personal Web Space North Seattle Community College
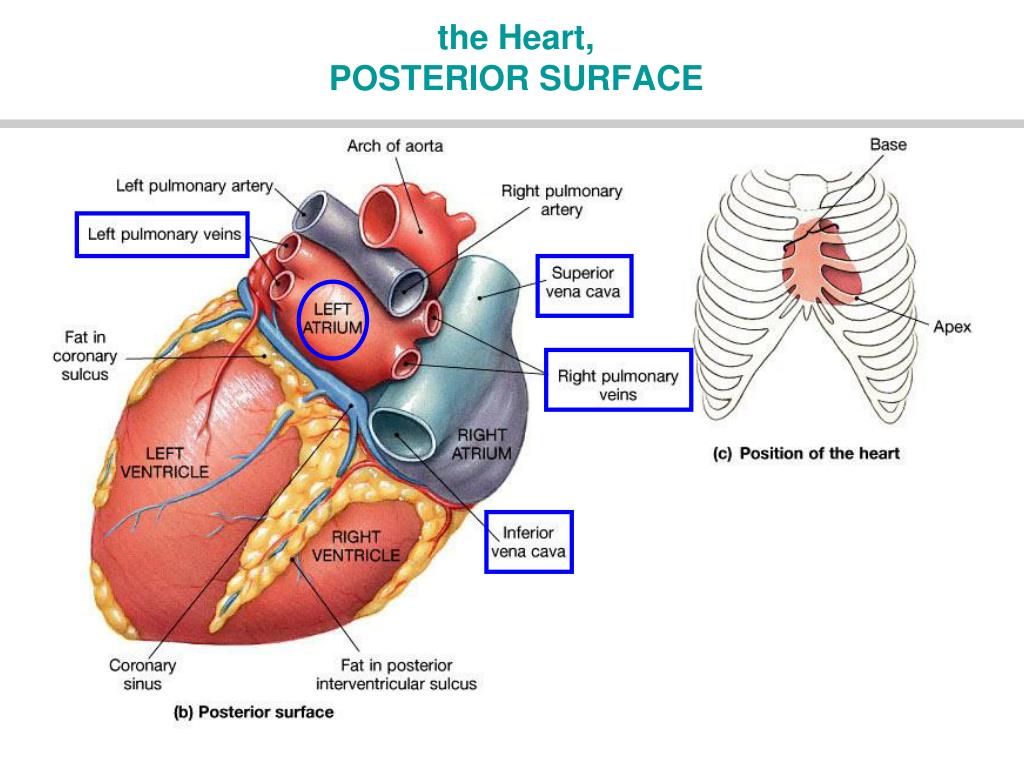
This illustration demonstrates a posterior view of the thoracic cavity, highlighting the position of the heart in relationship to the ribs and diaphragm. The left atrium, left ventricle, and coronary sinus in the coronary sulcus between these chambers can be easily seen from the posterior aspect.

Posterior view of adult human heart showing distribution of cardiac
Learn about the significance of posterior heart view for your cardiovascular health and how Nao Medical's cardiology specialists can help you maintain a healthy heart.
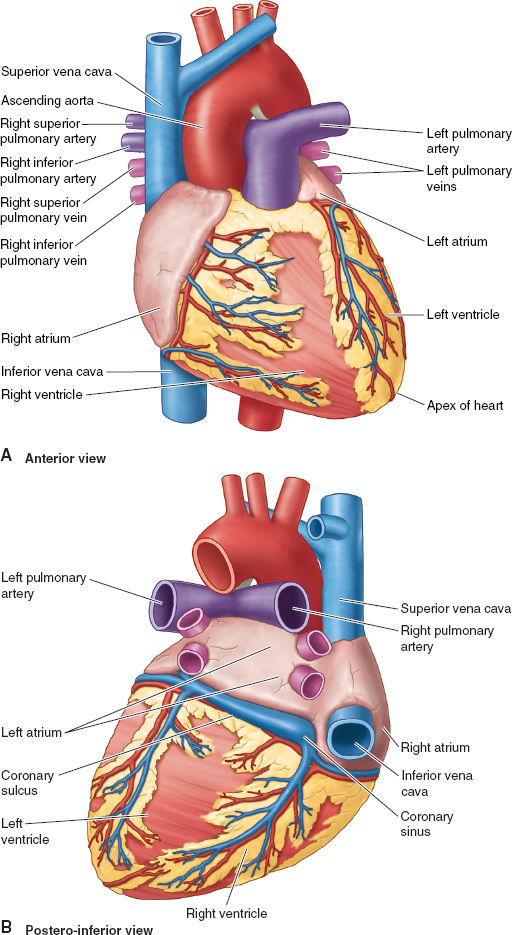
Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Anesthesia Key
Anatomy of the Heart. Figure 1. The endocast is viewed from 5 different perspectives to demonstrate the spatial relationship between right (coloured blue) and left (coloured red) heart chambers and between atria and ventricles. The blue and white arrows represent the right and left ventricular outflow tracts respectively.
Anatomy of the Heart
Figure 1. The heart is located within the thoracic cavity, medially between the lungs in the mediastinum. It is about the size of a fist, is broad at the top, and tapers toward the base. Everyday Connection: CPR

Heart Models
The Mitral Valve level is common view seen and allows you to view the anterior and posterior valves of the mitral valve. To get the Mitral Valve level from the Mid-Papillary level, slide the Transducer towards the sternum towards the mitral valve (base of the heart). The Anterior and Posterior leaflets of the Mitral Valve should come into view.
PPT HEART ANATOMY PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6415138
What is the Posterior View of the Heart? The posterior view of the heart is the view of the heart from the back. It shows the heart's right and left atria, right and left ventricles, and the major blood vessels that enter and exit the heart. Why is Understanding the Posterior View of the Heart Important?
Anatomy Heart (External)
The heart has three layers. They are the: Epicardium: This thin membrane is the outer-most layer of the heart. Myocardium: This thick layer is the muscle that contracts to pump and propel blood.
Heart Anatomy Concise Medical Knowledge
Location of the Heart (Posterior View) 3. 8. Hide the lungs by deselecting the respiratory system icon on the left-hand side of the screen.. Coronary Circulation (Posterior View) 11. a. Select the right coronary artery. This artery and its branches supply blood to the _____ and the _____. It extends from the _____ and runs to the right of.

Medical and Health Science HeartAnatomy!!
(a) Right lateral view and (b) left lateral view. DA, descending aorta. Fig. 12.6 Heart margins in lateral projections. Cross-sections at three levels. The true posterior surface of the heart is commonly referred as the base of the heart which is formed largely by the left atrium.