(PDF) Breeding Enhancement of Musca domestica L. 1758 Egg Load as a Measure of Optimal Larval

Кровососущие насекомые средней полосы России 34 фото смотреть онлайн
Adult house flies, Musca domestica L., are mechanical vectors of more than 100 devastating diseases that have severe consequences for human and animal health. House fly larvae play a vital role as decomposers of animal wastes, and thus live in intimate association with many animal pathogens. We have sequenced and analyzed the genome of the house fly using DNA from female flies.

Protect Health.......Protect Life Family Muscidae..Genus Musca(House Flies)
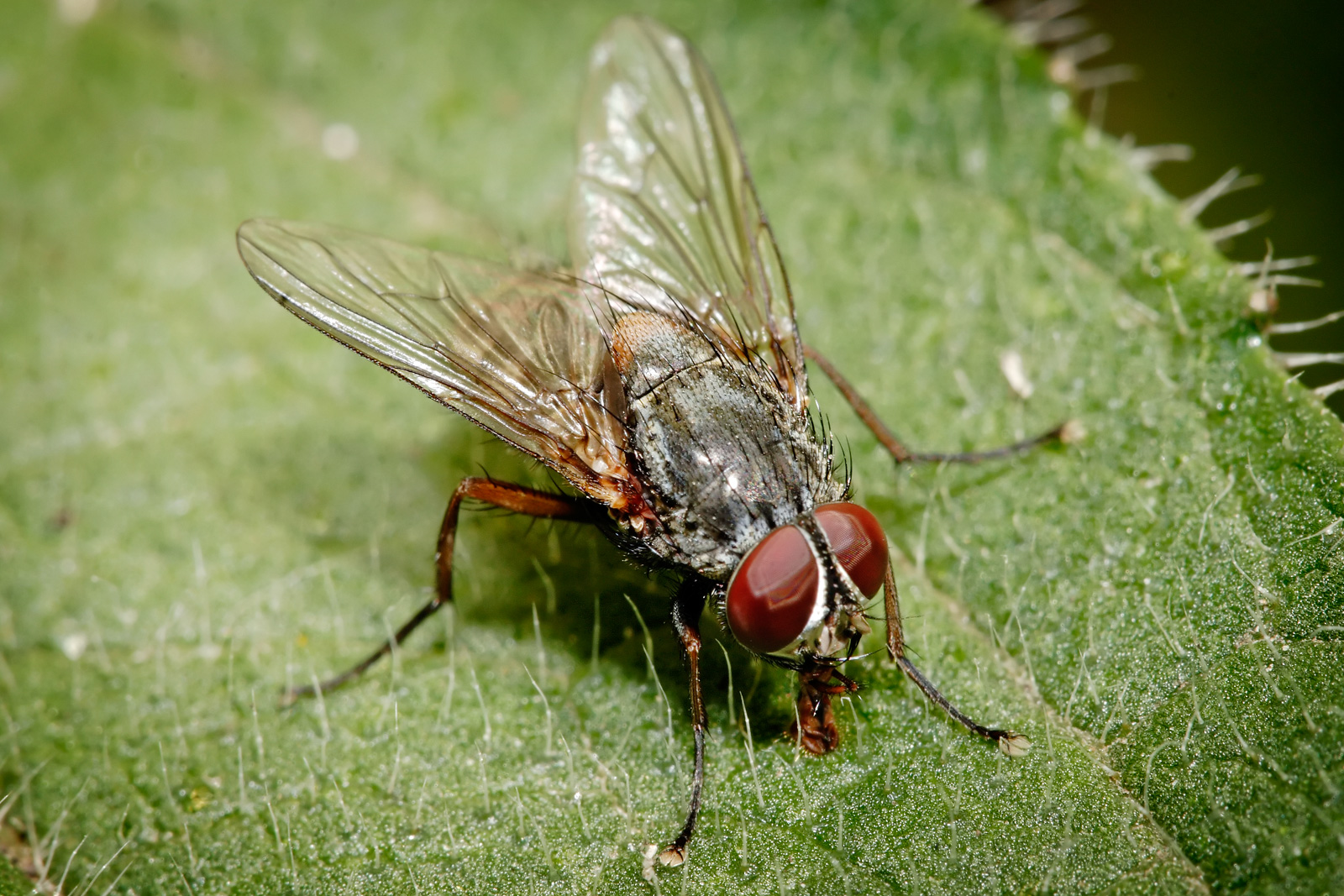
The housefly ( Musca domestica) is a fly of the suborder Cyclorrhapha. It possibly originated in the Middle East, and spread around the world as a commensal of humans. It is the most common fly species found in houses.

Mean (±S.E.) of development time () from egg hatch to adult formation... Download Scientific
housefly, ( Musca domestica ), a common insect of the family Muscidae (order Diptera ). About 90 percent of all flies occurring in human habitations are houseflies. Once a major nuisance and hazard to public health in cities, houseflies are still a problem wherever decomposing organic waste and garbage are allowed to accumulate.

Eggs of housefly Heidi & HansJuergen Koch
Musca domestica L. (Diptera: Muscidae), better known as the common housefly, is increasingly considered to be a new, alternative protein source for animal nutrition. By transferring low-value organic side streams into high-value protein products, its commercial production contributes to a circular economy.

Learn more about Musca domestica, the risks this fly poses to you and your animals, and how to
The house fly, Musca domestica Linnaeus, is a well-known cosmopolitan pest of both farm and home. This species is always found in association with humans or the activities of humans. It is the most common species found on hog and poultry farms, horse stables and ranches.

(PDF) Breeding Enhancement of Musca domestica L. 1758 Egg Load as a Measure of Optimal Larval
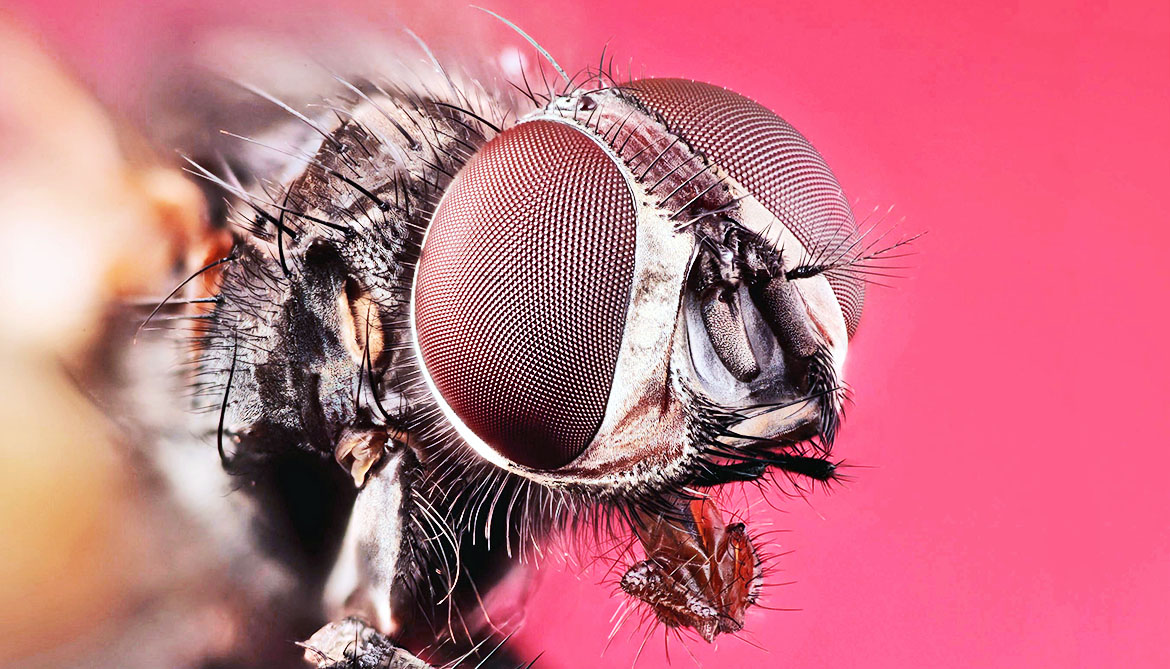
Adult house flies (Musca domestica Linnaeus) are 6 to 7 mm long. Females tend to be larger and have a relatively wide space between the eyes compared to males.. Adult females lay eggs singly but in small piles in a nutrient-rich, moist location. They can lay as many as 500 eggs over a three to four day period, and several flies will deposit.

Daily variation in egg laying of two Musca domestica strains (GK and... Download Scientific
Musca domestica (Linnaeus, 1758) is a muscoid species that is widespread throughout the world and acts as a mechanical vector of different enteropathogens primarily in underdeveloped countries.

Musca domestica carrying Dermatobia hominis eggs in the lateralventral... Download Scientific
The adult house fly ( Musca domestica) is 6-7 mm long, yellowish-grey to dark grey in colour, with four narrow black stripes on the thorax, reddish-brown eyes and clear, translucent wings. Female house flies will typically only mate once and retain the sperm for future egg fertilization.
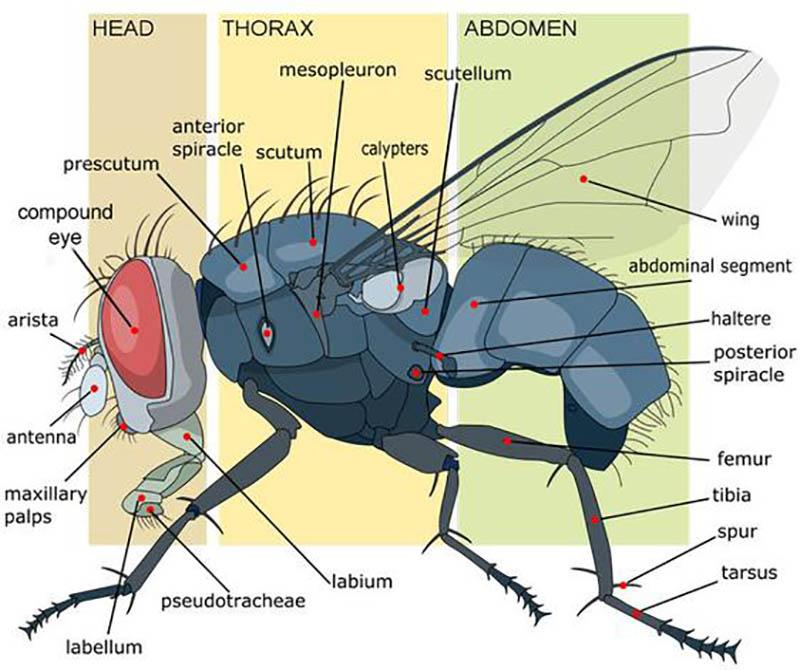
Top 13 Sự thật thú vị nhất về loài ruồi
The housefly ( Musca domestica L.) lives in close association with its microbiota and its symbionts are suggested to have pivotal roles in processes such as metabolism and immune response, but.

Figure 1 from Efficacy of Herbal Fly Repellent Product (Keetguard Liquid) to Control Musca
The house fly, Musca domestica, is one of the best-known and most widely distributed insects known to humans. Courtship and copulatory behaviors are the most important and the most complex behaviors exhibited by the house fly.

Musca_domestica_1170 Futurity
The house fly, Musca domestica L. (Diptera: Muscidae), is a global pest of humans and animals that carries scores of pathogens and costs up to $1 billion per year in the United States alone. Information is reviewed on recognition, distribution, biology, dispersal, and associations with microbes.
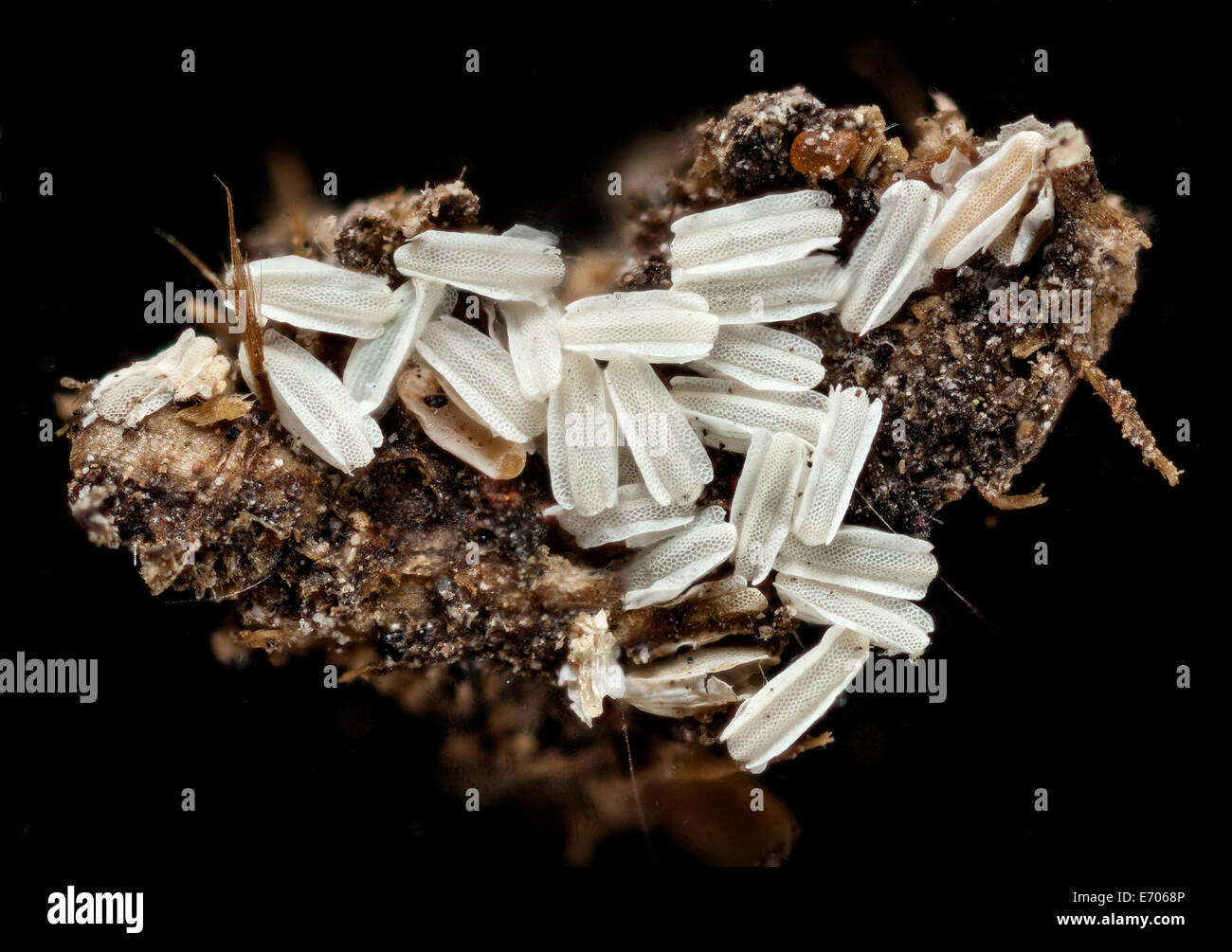
Macro photograph of Housefly eggs, Musca domestica Stock Photo Alamy
A Carefully Curated Range Of The Best Apple Trees Perfect For Garden Soils. Sustainably Grown Trees Sent In Eco Packaging & Delivered By A Trusted Courier Network.

47 Best Of Musca Domestica Life Cycle insectza
Egg Fertilization Site within Musca domestica L. 115 robust and appear less flexible than those covering the rest of the chamber. These apical spines number about 150 and range from 6 to 7 t~m in length, the longer spines being located towards the periphery. They cover a nearly circular area about 50/~m in diameter and are spatially arranged.

Temporal distribution () of egglaying females in two Musca domestica... Download Scientific
The concept that housefly (Musca domestica) can be used to convert waste to high protein feedstuff has been considered for decades .. Egg production. From approximately 5 days after emergence, flies were provided with oviposition substrate in the form of 100 g of cattle manure in a 100 mm petri dish. Flies were allowed to oviposit for a 4.
Musca domestica, House Fly (Diptera Muscidae)
Housefly (Musca domestica L. 1758) larvae are used in various parts of the world for animal feeding either by exposing substrates for natural oviposition or in industrial systems involving an adult rearing unit to produce eggs that are then placed in a substrate suitable for larval development. In order to develop M. domestica rearing system in Benin, effects of five types of food (pineapple.

Housefly laying eggs on wet paper Heidi & HansJuergen Koch
Musca domestica By Jonelle Doctor Geographic Range Habitat Physical Description Development Reproduction Lifespan/Longevity Behavior Communication and Perception Food Habits Predation Ecosystem Roles Economic Importance for Humans: Positive Economic Importance for Humans: Negative Conservation Status Contributors References Geographic Range