Modal Verbs and Example Sentences Lessons For English

Pin on Modals in English
One more common way to express obligation, necessity or a lack of obligation is with the semi-modal 'need'. A semi-modal is a word that acts like both a modal verb and a main verb.. Present and Future 'Need' as a modal. As a modal verb, 'need' is most typically used in negative sentences or in affirmative sentences with a negative meaning.

Modal Verbs Types And Uses English Learn Site Gambaran
Modal need is usually restricted to questions and negative sentences.. Many grammars talk about function words, the kinds of words you learn about in grammar lessons, and lexical words, normal verbs adjectives nouns and so forth that you learn as vocabulary. Using these categories, modal verbs are considered function words, main verbs are.

Modal Verbs in English English Study Here
Need to is a modal auxiliary verb that we use to express need or requirement. Let's dive deeper. Need to is used both as an auxiliary and an ordinary verb to express necessity. Auxiliary form (need to) He needn't smoke so much, it's really bad for his health.

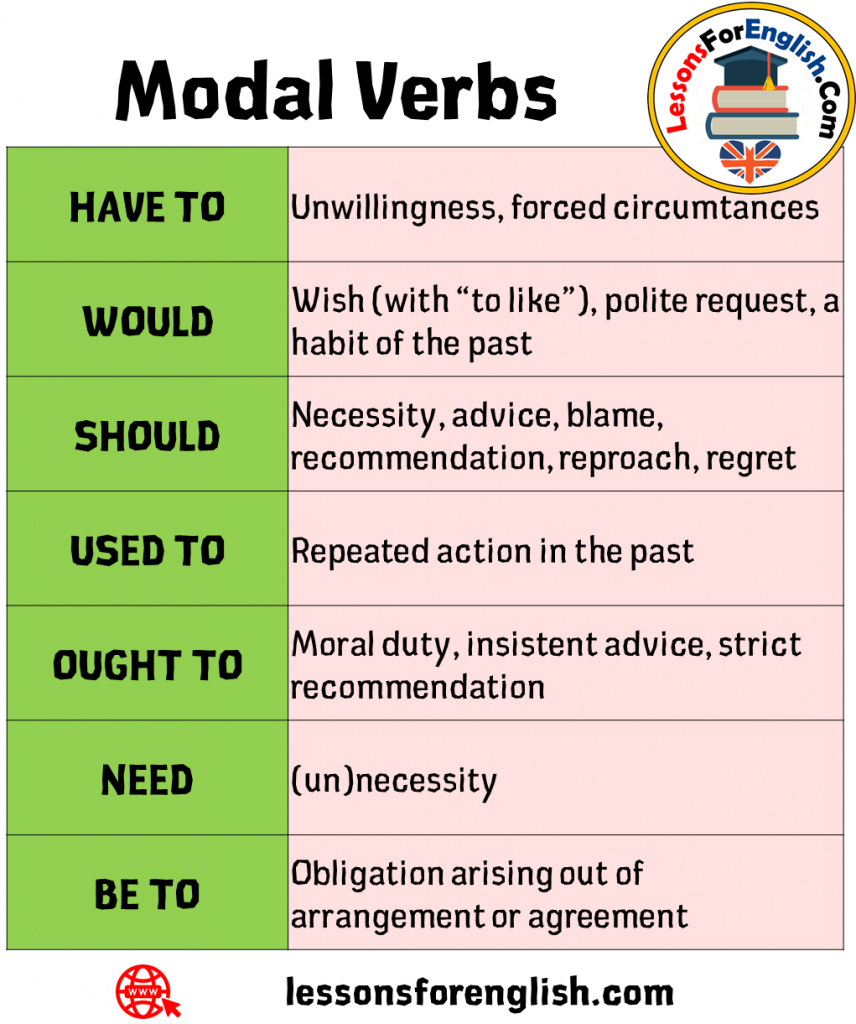
Modal Verbs In English How To Use Modals English Grammar Here Images
"Need" is an interesting verb in English, as it can be used both as a main verb and a modal verb. For example "I need to get some bread" (main verb) and "We needn't go now" (modal auxiliary). Here are some of the ways you can use "need", with explanations and examples. Need As A Main Verb. You can use "need" as a main verb.

Pin on can
Need as a modal verb is used rarely and only in quite formal situations. In all ordinary situations use have to. See need in the Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary. Check pronunciation: need_2. Nearby words. née adjective; need verb; need modal verb; need noun; need-blind adjective;

Ana's ESL blog Modal verbs
Grammar Point modal verbs modal verbs. The modal verbs are can, could, may, might, must, ought to, shall, should, will and would. Dare, need, have to and used to also share some of the features of modal verbs.; Modal verbs have only one form. They have no -ing or -ed forms and do not add -s to the 3rd person singular form:. He can speak three languages. She will try and visit tomorrow.
Modal Verbs and Example Sentences Lessons For English
Need is used both as an ordinary verb and as an auxiliary verb. As an ordinary verb need is used in the sense of 'require'.. Modal Auxiliary Verbs Can May and Can: differences Could May Might Will Would Shall Should Should: other uses Must Must: uses Must and have to: The Difference Ought to Need Had better Should, Ought and Must: The.

English Grammar Modal Verbs ESLBuzz Learning English
All you need to do is use the modal verb and then the base form of the verb. For example: We can eat ice cream tomorrow. Other Rules for Using Modals. Modals are more straightforward than you think. Remember these four rules when using modal verbs. Constructing Verb Phrases. As seen in the structures above, modal verbs always come first in verb.

how to use modal verbs Archives English Grammar Here
Modal verbs show possibility, intent, ability, or necessity. Common examples of modal verbs include can, should, and must . Because they're a type of auxiliary verb (helper verb), they're used alongside the infinitive form of the main verb of a sentence. Modal verbs are used to express certain hypothetical conditions, such as advisability.

What is Modal Class
Modal verbs are used alongside the main verb to provide additional context regarding possibility, intention, permission, or obligation.. They are used alongside the main verb to change its tense, mood, or voice and need to be conjugated for tense and subject-verb agreement. Examples: Auxiliary verbs in a sentence Allan is riding a bike.

Modal verbs have to, must, need to Mingleish
Explanation. You have to go to school because you are still young. I had to go to school when I was your age, too. Have to is used to express general obligation, while had to is used to describe an obligation that took place in the past. Rule 4: We can use need to to express that something is important for you to do, but rather at a given.

Modal Verbs for Necessity ("Need")
Using Need as a Modal Verb. When need is used as a modal verb Opens in new window, it is most usually used in negative sentences Opens in new window and it doesn't change its tense Opens in new window and doesn't add '-s' for the third person singular. Survey the following examples:

MODAL VERBS
If the Ngram viewer is any guide, the bare infinitive following "need" used to be more popular than the to-infinitive.For the bare infinitive, we go from the sublime past, The Life and Adventures of Robinson Crusoe by Daniel Defoe (1719) As to the carpenters, I scarce need mention how useful they were.. to the ridiculous modern, The Last Job Search Guide You'll Ever Need by S. J. Rothberg (2002):

English Modal Verbs of Necessity Need (verb) (without to) is used in negative and interrogati
Need as a Main Verb: Need can also function as a main verb, meaning to require or be necessary. When need is used as a main verb, it is typically followed by an object and an infinitive (with or without to ), indicating what is needed or required. Here are some examples: I need a new pair of shoes. They need to hire more staff to handle the.

Modal Verbs English Lessons English in General
Hi MRamos2022, It's an interesting question. A modal verb, as defined by the Cambridge Dictionary, is "a verb used with another verb to express an idea such as possibility that is not expressed by the main verb". Will, shall and would fit this description - they are all used with another verb and cannot be used alone, and they express some kind of meaning or attitude that modifies the main.

MODAL VERB NEED ESL worksheet by spankevich
1. When need behaves like a modal verb, it is commonly used in the negative form ( i.e., needn't) or in affirmative statements with a negative sense ( i.e., no one need worry ). Like any other modal verb, it is followed by a bare infinitive ( i.e., infinitive without "to") and expresses the absence of obligation or necessity. 2.