NMR Theory Chemistry LibreTexts
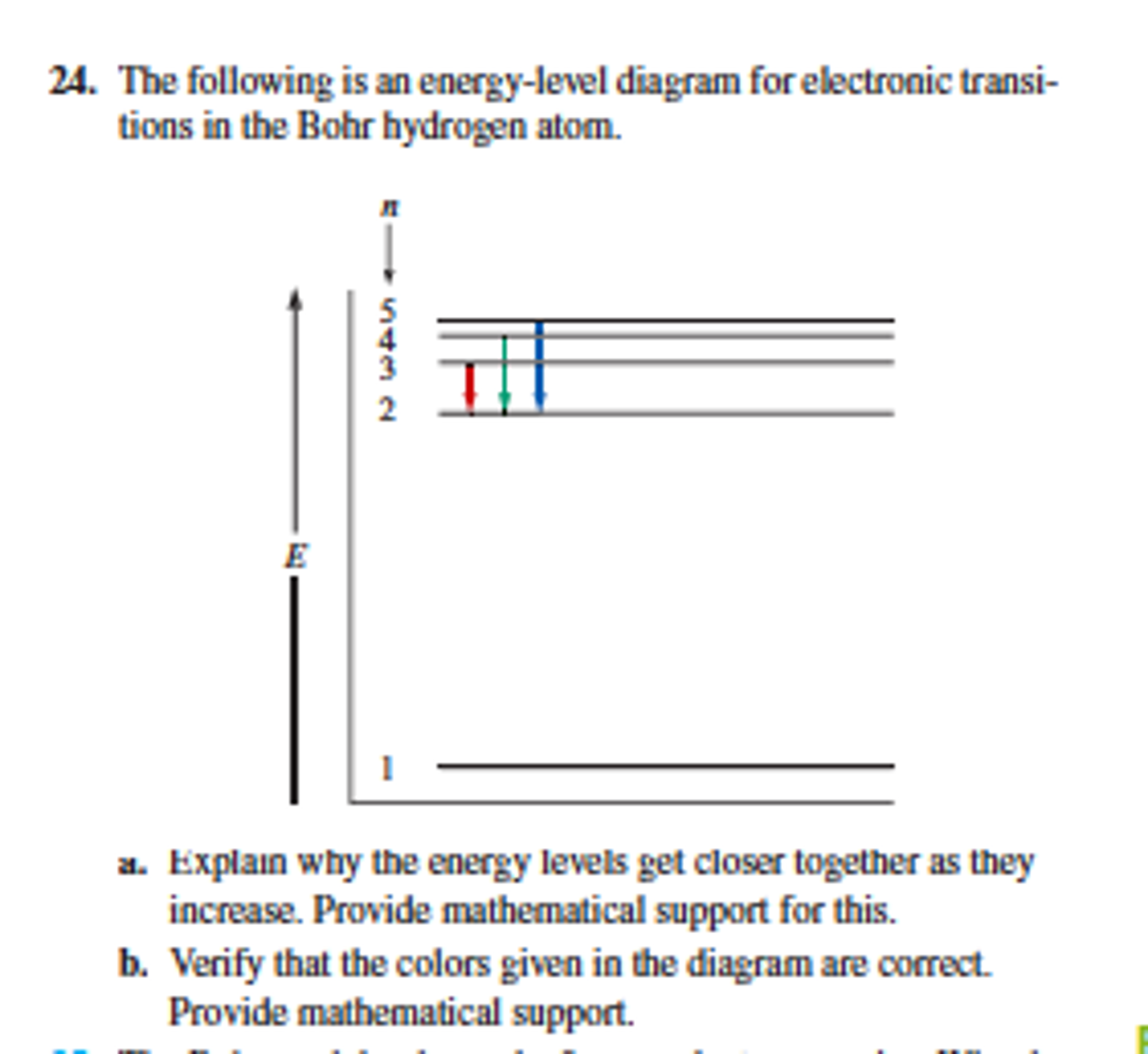
Solved The following is an energylevel diagram for
energy level, in physics, any discrete value from a set of values of total energy for a subatomic particle confined by a force to a limited space or for a system of such particles, such as an atom or a nucleus. A particular hydrogen atom, for example, may exist in any of several configurations, each having a different energy.

physical chemistry LennardJones potential and vibrational energy level diagram explanation
Introduction Glossary History Background Fundamentals Experiments Formulations Equations Interpretations Advanced topics Scientists v t e A quantum mechanical system or particle that is bound —that is, confined spatially—can only take on certain discrete values of energy, called energy levels.

Schematic energylevel diagram of Tb 3+ and Eu 3+ in Ca 8 MgTb(PO 4 )... Download Scientific
Chemists use the energy level diagram as well as electron configuration notation to represent which energy level, subshell, and orbital are occupied by electrons in any particular atom. Chemists use this information in these ways: To predict what type of bonding will occur with a particular element and show exactly which electrons are being used

The schematic energy level diagram for the levels (central panel)... Download Scientific Diagram
Energy level diagrams are the representation of placements or arrangements of orbitals (also known as subshells) according to their increasing energy levels. Above is the blank energy level diagram which can be used to represent the electrons for any atom under study. Energy level diagrams are known as Grotrian diagrams.

Energy level diagram of π 4 He + atom. On the left scale the... Download Scientific Diagram
An energy level diagram, or energy band diagram, is a graphical representation of the allowed energy states of a system. The most common type of energy level diagram is the molecular orbital energy level diagram. This type of diagram shows the energies of the orbitals in a molecule.
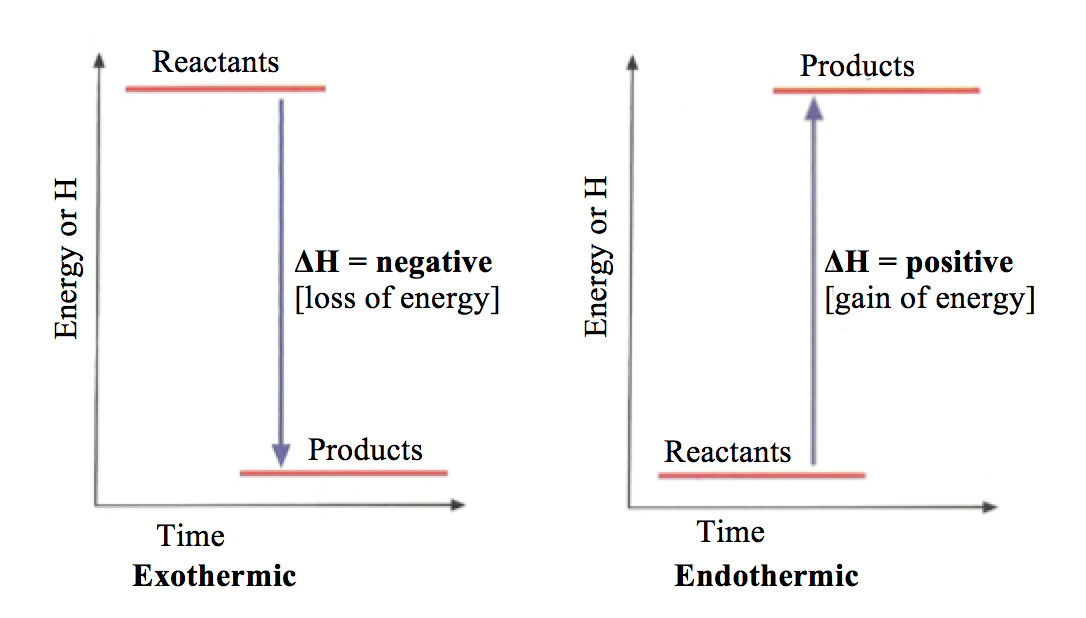
iGCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION HELP Acids & Energetics
Energy-Level Diagrams. Because electrons in the σ 1 s orbital interact simultaneously with both nuclei, they have a lower energy than electrons that interact with only one nucleus. This means that the σ 1 s molecular orbital has a lower energy than either of the hydrogen 1s atomic orbitals. Conversely, electrons in the \( \sigma _{1s}^{\star } \) orbital interact with only one hydrogen.

Energy level diagram illustrating the relationship among the various... Download Scientific
Energy Diagrams. Endothermic and exothermic reactions can be visually represented by energy-level diagrams like the ones in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\). In endothermic reactions, the reactants have higher bond energy (stronger bonds) than the products.Strong bonds have lower potential energy than weak bonds.
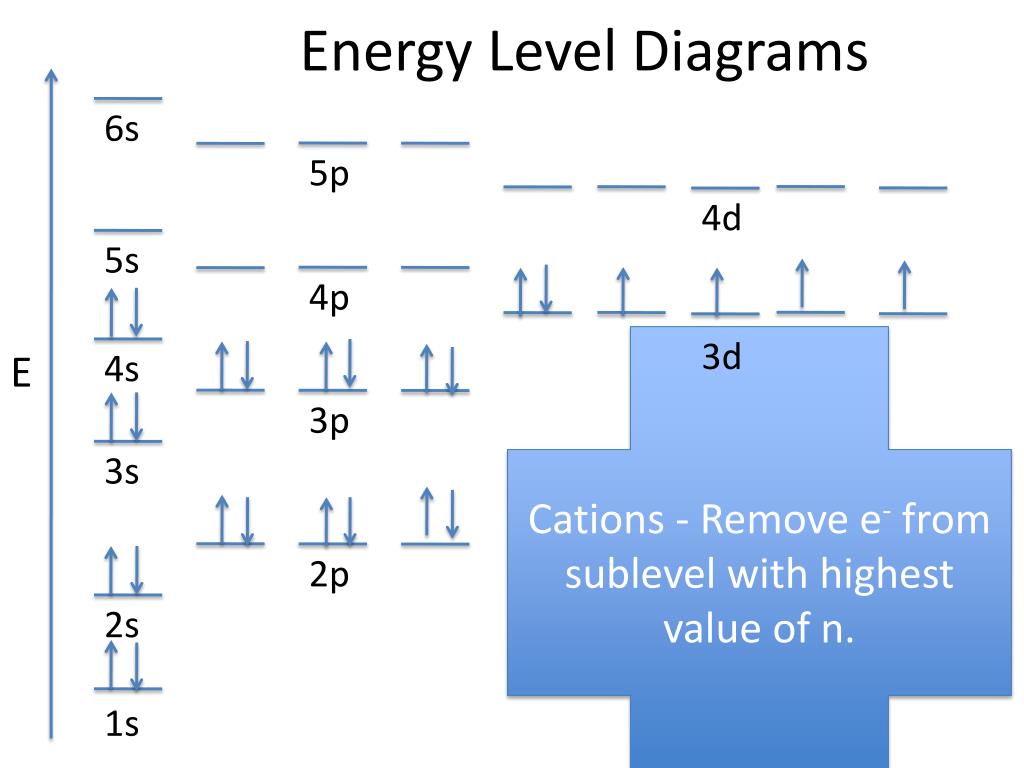
PPT Energy Level Diagrams PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2061569
Elements of Energy Diagrams. First of all, it should be noted that we will be confining ourselves to energy diagrams for 1-dimensional motion. This dimension will be represented by the horizontal axis, and the vertical axis will have units of energy. Secondly, the physical systems represented by energy diagrams will involve only one.
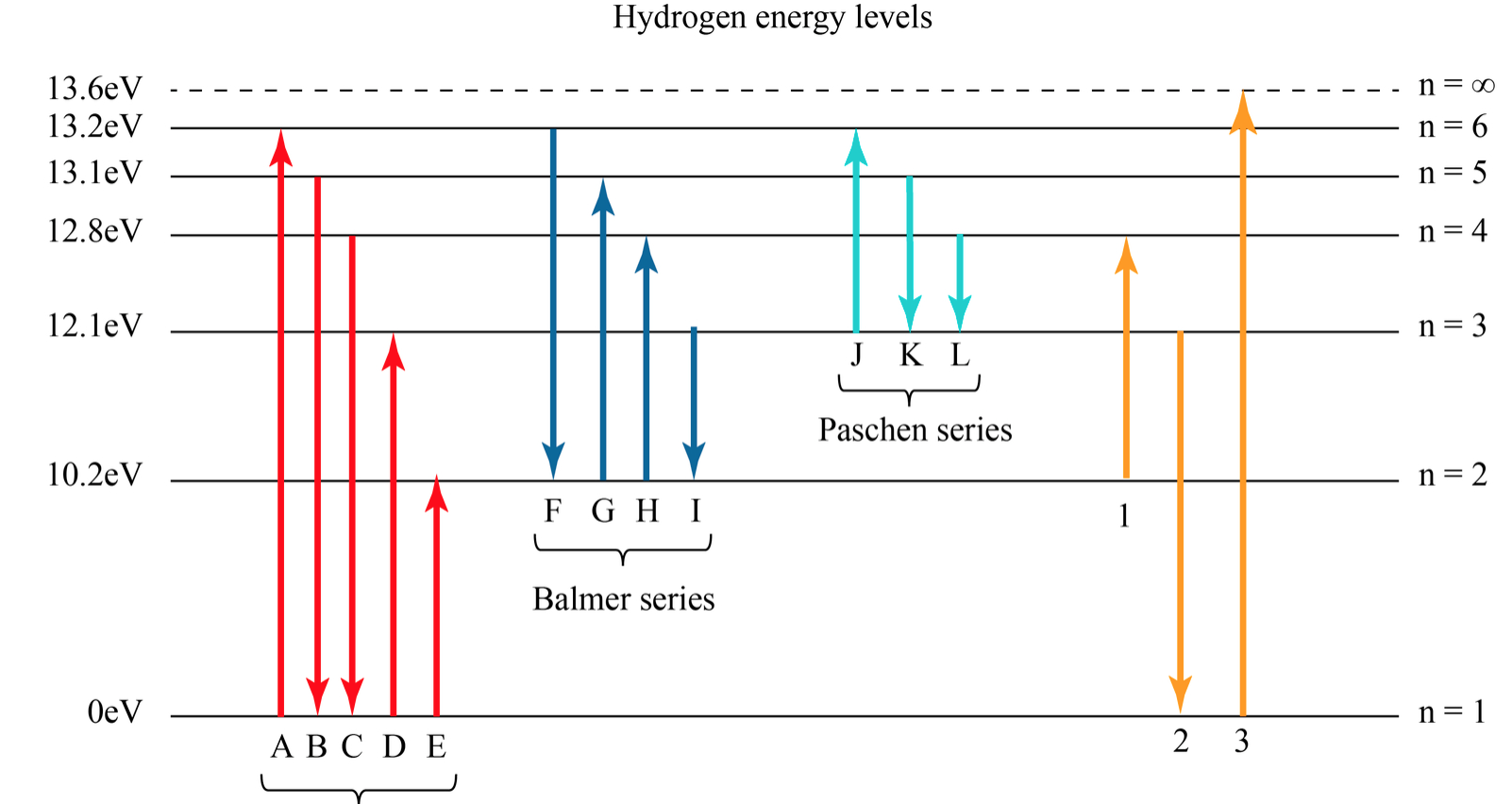
Solved Hydrogen Energy Level DiagramThe orbitals of
What is an energy level diagram? In chemistry, an electron shell, or energy level, may be imagined as an orbit with electrons around the nucleus of an atom. Bohr developed this model of the atom which says the electrons revolve around the nucleus in a circular path called an orbit.

Energy Diagram — Overview & Parts Expii
A nuclear energy level diagram is a graphical representation that depicts the energy states of a nucleus. It provides valuable information about the quantum mechanical properties of atomic nuclei and the transitions between different energy levels. These diagrams play a significant role in understanding nuclear structure, nuclear reactions, and.
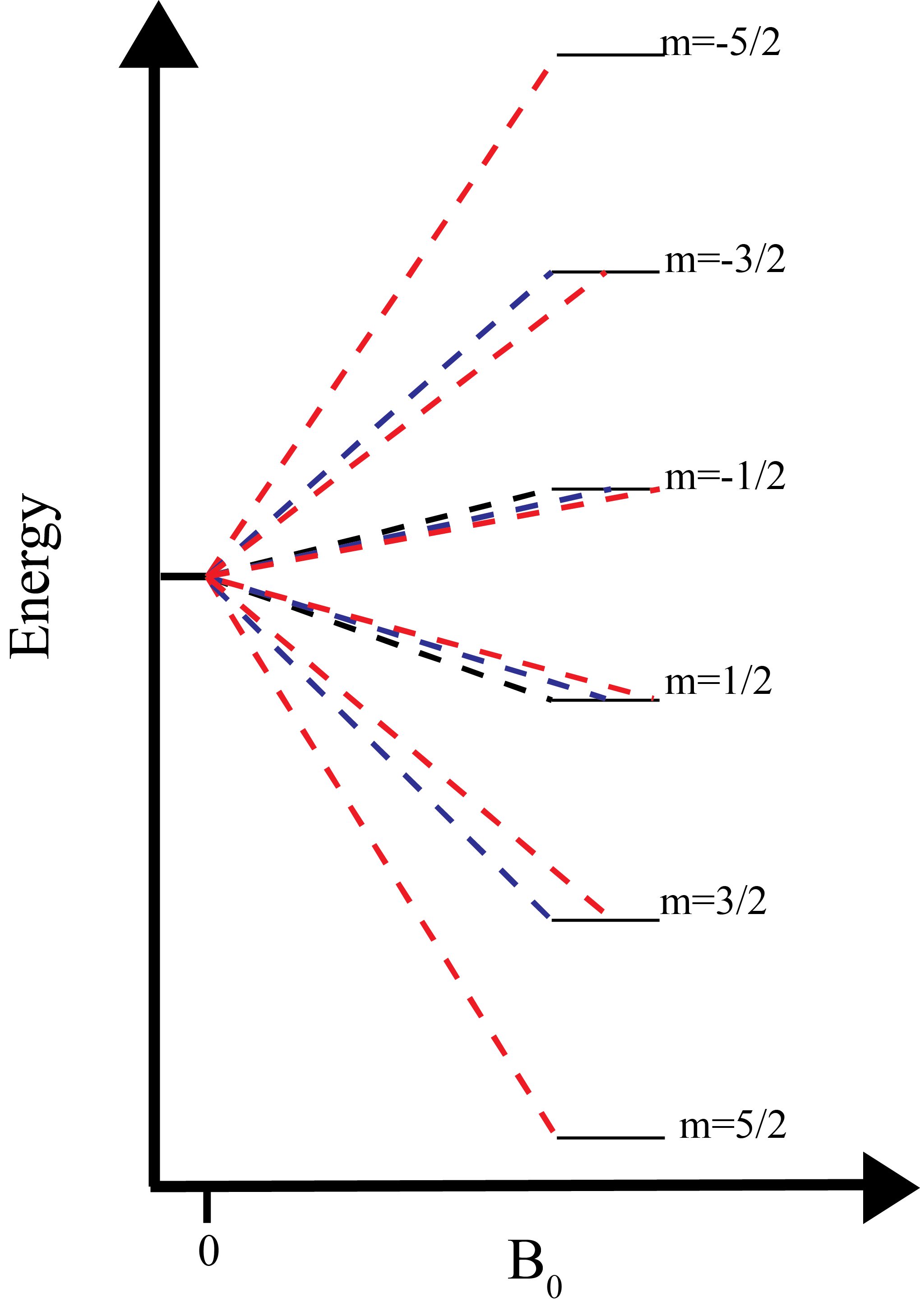
NMR Theory Chemistry LibreTexts
The energy level diagram gives us a way to show what energy the electron has without having to draw an atom with a bunch of circles all the time. Let's say our pretend atom has electron energy levels of zero eV, four eV, six eV, and seven eV. Note that moving left or right on an energy level diagram doesn't actually represent anything.

Schematic energy level alignment of various CGLs. Energy level diagrams... Download Scientific
Energy level diagrams are a means of analyzing the energies electrons can accept and release as they transition from one accepted orbital to another. These energies differences correspond to the wavelengths of light in the discreet spectral lines emitted by an atom as it goes through de-excitation or by the wavelengths absorbed in an absorption.

Energy level diagrams Endothermic & Exothermic reactions
Figure 6.24 Generalized energy-level diagram for atomic orbitals in an atom with two or more electrons (not to scale). Electrons in successive atoms on the periodic table tend to fill low-energy orbitals first. Thus, many students find it confusing that, for example, the 5 p orbitals fill immediately after the 4 d, and immediately before the 6 s.

Energy Level Definition, Equation (w/ Diagrams) Sciencing
The energy for the first energy level is equal to negative 13.6. E two is equal to negative 3.4, and E three is equal to negative 1.51 electron volts. So energy is quantized using the Bohr models, you can't have a value of energy in between those energies.
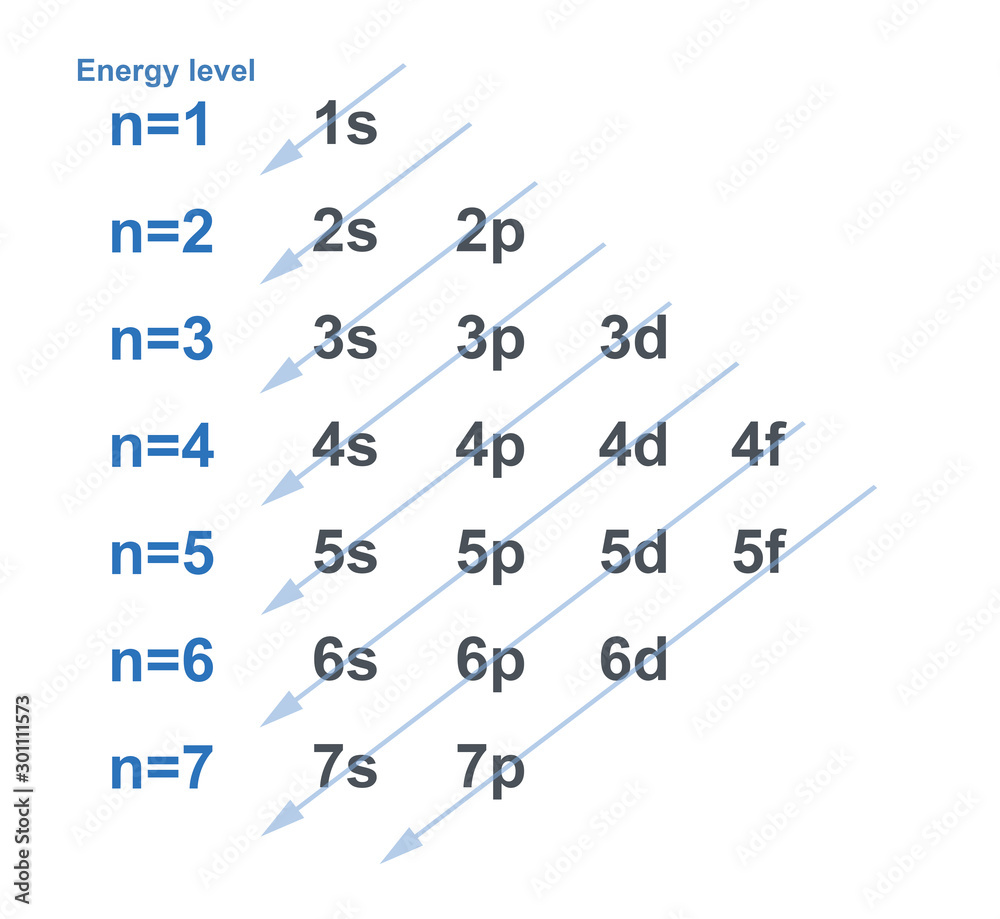
chart of electron configuration with each energy level for element in chemistry. Stock
To view previous Energy Level Diagrams from past reviews, please refer to the list at the bottom of the page. In these diagrams, energy values are plotted vertically in MeV, based on the ground state as zero. Uncertain levels or transitions are indicated by dashed lines; levels which are known to be particularly broad are cross-hatched. Values.

Atomic Energy Level Diagram alternator
Key points Bohr's model of hydrogen is based on the nonclassical assumption that electrons travel in specific shells, or orbits, around the nucleus. Bohr's model calculated the following energies for an electron in the shell, n : E ( n) = − 1 n 2 ⋅ 13.6 eV