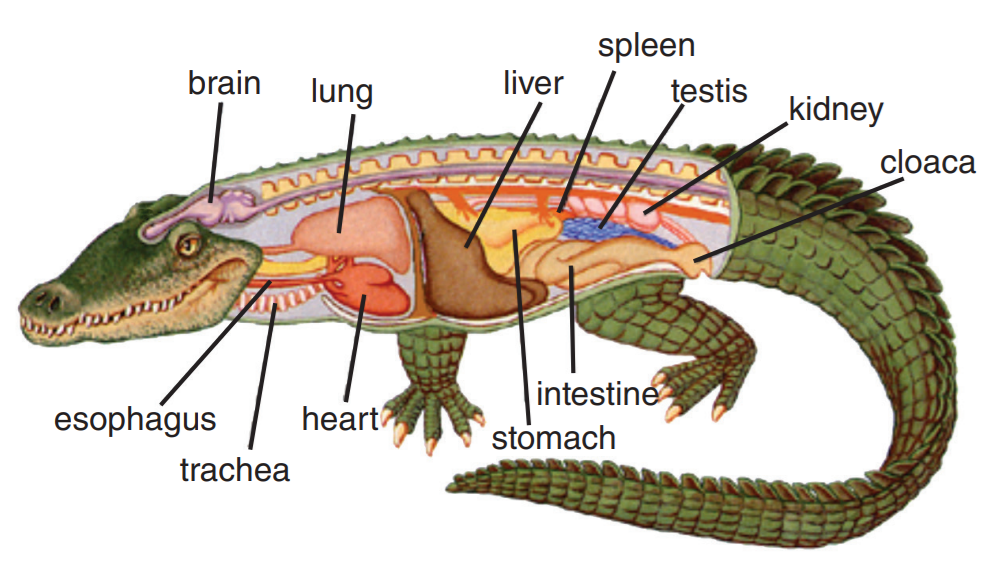
American alligator anatomy American alligator, Alligator, Anatomy

Famemaster 4D Vision Crocodile Anatomy Model Panama STEM Education
A long bone-enclosed nasal passage leads from the exterior nostril openings to the interior nostril openings, or choanae, located at the extreme posterior end of the palate; a membranous flap in front of the choanae constitutes the posterior closure of the mouth cavity. As a result, the crocodile can breathe even if its mouth is open underwater.
Waste Management for Alligator Farming and Ranching Oklahoma State University
Along some of India's mangrove-lined coasts, including Odisha's Bhitarkanika, the world's largest reptile lurks. With teeth that rip, jaws that crush and a b.

American alligator anatomy American alligator, Alligator, Anatomy
Characteristics Skulls and scutes of American, Nile and Saltwater crocodiles, with post-occipital scutes highlighted in red, nuchal shield in blue and dorsal scutes in green Crocodiles, like dinosaurs, have the abdominal ribs modified into gastralia. A crocodile's physical traits allow it to be a successful predator.

How to Draw Crocodiles by on DeviantArt Crocodile illustration
Genus Crocodylus Scientific Name Crocodylus acutus Read our Complete Guide to Classification of Animals. Crocodile Conservation Status Least Concern Crocodile Locations Africa Asia Central-America North-America Oceania South-America Crocodile Facts

Animal Anatomy preview Crocodile Ecorche. Sculpted by Tan Bi Animal anatomy
The saltwater crocodile is the largest living reptile. [5] Males can grow up to a weight of 1,000-1,500 kg (2,200-3,300 lb) and a length of 6 m (20 ft), rarely exceeding 6.3 m (21 ft). [6] [7] Females are much smaller and rarely surpass 3 m (9.8 ft).

crocodile Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help
This chapter presents a general overview of the anatomy, physiology, and treatment methodology for crocodilians. Most crocodilians grow to be larger than other reptile species and, therefore, have significant space requirements. Like most animals requiring an aquatic environment, crocodilians need water that is clean and free of disease.
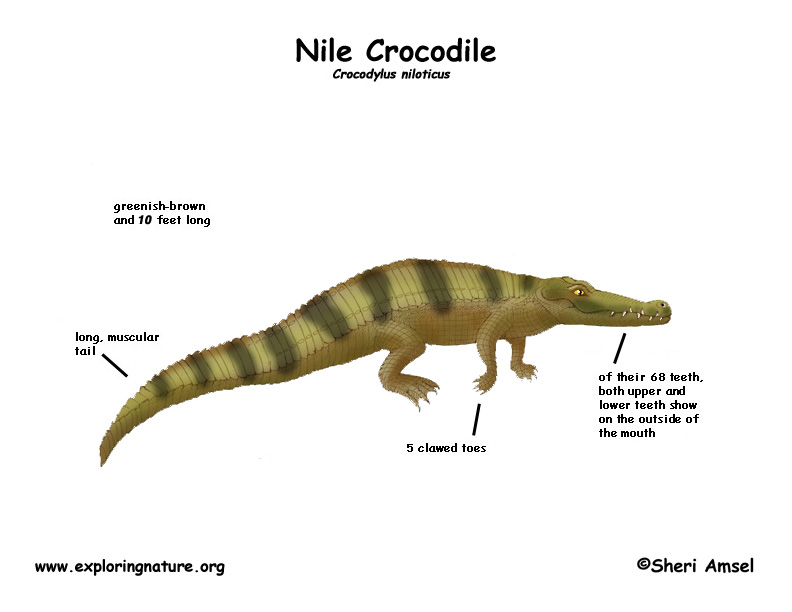
Crocodile (Nile)
To identify a crocodile, understand the di˜erences between species and place the crocodile in the evoltionary tree, it is essential to understand the creatures anatomy. Here is our guide to the anatomy of a crocodile. Phylogenic Classification: Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Reptilia Order: Crocodilia The Vertebral Column

Crocodile Anatomy Close by wavenwater on DeviantArt
Head The crocodile has a long V-shaped snout full of teeth. The fourth tooth on a crocodile's lower jaw is visible over the upper lip in a crocodile, and the tongue of a crocodile, anchored to the bottom of its mouth, cannot move. Eyes The eyes of a crocodile produce tears but not due to any emotion in the reptile.

How Fast Can a Crocodile Run Their Speed Explained Trickles N Trees
The awesome anatomy of the crocodile Jul 3, 2017 The crocodile rocks: A crocodile dozing off next to the water might look like a slow and clumsy animal, but in actual fact his anatomy is rather complex. We take a look at how he is well designed to thrive in his habitat. SWIMMING CHAMPION

Crocodile anatomy by IronMitten on DeviantArt
The phylogenetic position of crocodilians in relation to birds and mammals makes them an interesting animal model for investigating the evolution of the nervous system in amniote vertebrates. A few neuroanatomical atlases are available for reptiles, but with a growing interest in these animals within the comparative neurosciences, a need for these anatomical reference templates is becoming.

Diagram showing parts of crocodile Royalty Free Vector Image
The anatomy and position of the CVB (D1). In the crocodile, the saccular regions are not projections from the rest of the lung so that the entire lung is readily dissected from the surrounding organs and has an outer contour that is smooth and loaf-like (Figs. 1B and.

Anatomy Of A Crocodile
Background and Aim: Present study provides with more anatomical information on the structure and form of the bones forming the cranium of the Nile crocodile helps in understanding the.
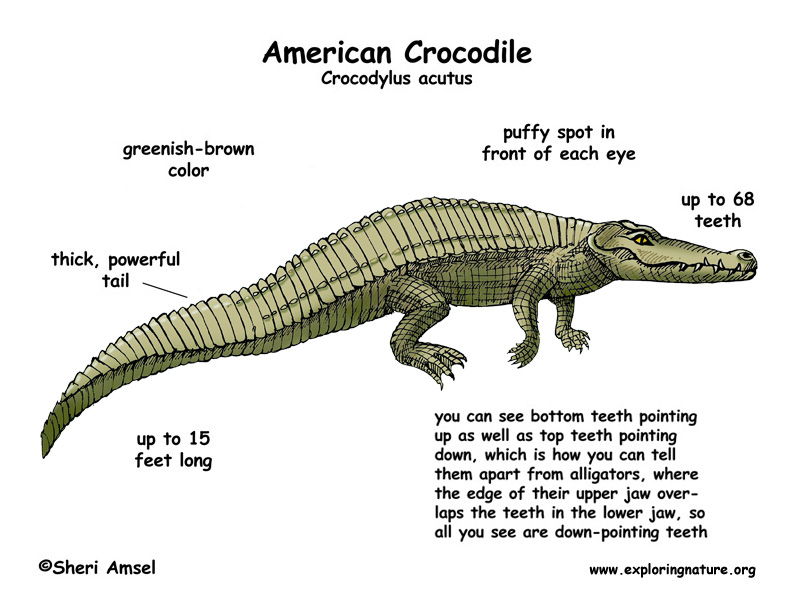
Crocodile (American)
The Basic Anatomy of a Crocodile To understand the ear structure of a crocodile, it is essential to have a basic understanding of their overall anatomy. Crocodiles are reptiles known for their powerful bite and strong jaws. They are often mistaken for alligators, but there are distinct differences between the two species.
Anatomy of a Crocodile The Poke
A Closer Look: Crocodile Eye Anatomy. Crocodile eyes are similar to those of other reptiles, but with some key differences. The eye is protected by a bony ring called the sclerotic ring, which gives the eye extra support and protection. The iris, or colored part of the eye, can vary in color from yellow to brown and even red.
Male Crocodile Reproductive System Crocodile
The Crocodilian Body In general, the body form of crocodilians is "lizard-like". They have a long tail and the limbs are short and straddled sideways from the body rather than being erect beneath it, as in mammals. The elongated snout of crocodilians is probably one of their most distinctive features.
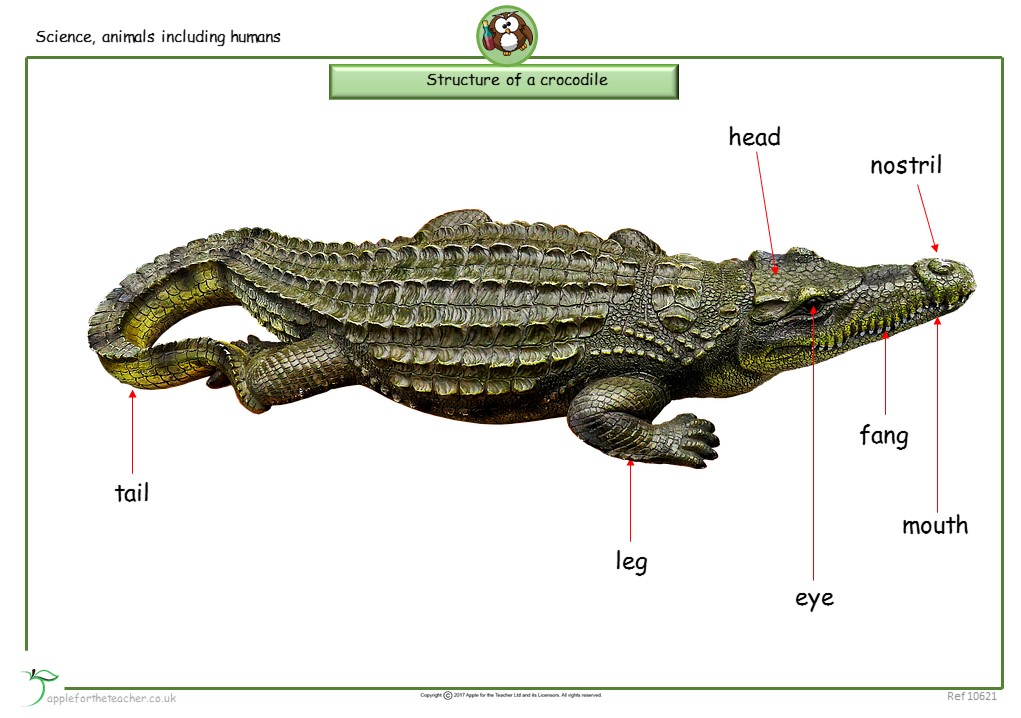
Structure Of A Crocodile Apple For The Teacher Ltd
One side of the heart sends blood that is full of oxygen out to most of the body. The other side pulls blood back toward the lungs to give it an oxygen refill. But crocodile (and alligator) hearts have an extra valve that mammal and bird hearts don't have.