Medial temporal atrophy (MTA) scoring illustrated on T1weighted MRI.... Download Scientific
Careers in Radiologic Technology ASRT
Abstract. Background: Medial temporal lobe atrophy (MTA) is a sensitive radiologic marker for Alzheimer disease (AD) and associated with cognitive impairment. The value of MTA in the oldest old (>85 years old) is largely unknown.
Radiography Exam New England School of Dental Assisting
A general problem with the MTA score is the inconsist-ently dened cuto value. Various cutos for pathological MTA scores can be found in the literature, diering by age groups and education level. For example, Velickaite and colleagues [8] elaborated that "at age 75, gender and edu-cation are confounders for MTA grading. A score of ≥ 2 is
Radiologist Assistant (RA) Registered Radiologist Assistant The Radiologic Technologist
Objective The aim of the study is to visually rate major forms of dementia using global cortical atrophy (GCA), medial temporal lobe atrophy (MTA), and Fazeka's scales and Koedam's score using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The purpose is to correlate the visual rating scales (VRS) with severity of dementia. Materials and Methods Thirty patients fulfilling DSM 5 (Diagnostic and.
Demand for Radiologist Assistants Grows as Role Expands
Scores of MTA correlated to age and Mini-mental state examination score. When used to detect DAT from NC, the MTA showed highest diagnostic value than other scales, and when the cutoff score of 1.5 of MTA scale, it obtained an optimal sensitivity (84.5%) and specificity (79.1%) respectively, with a 15.5% of false negative rate.
Diagnosis Nerd Radiography Assistants & Imaging Support Workers
Brain Ischemia. Imaging in Acute Stroke. Vascular territories of the Brain.
Imagistica cerebrală în diagnosticul diferențial al demenței Savage Rose
Objective To provide age-specific medial temporal lobe atrophy (MTA) cut-off scores for routine clinical practice as marker for Alzheimer's disease (AD). Methods Patients with AD (n = 832, mean age 81.8 years) were compared with patients with subjective cognitive impairment (n = 333, mean age 71.8 years) in a large single-centre memory clinic. Mean of right and left MTA scores was determined.

CJC Student Association of Radiologic Technology Digos
Objective To evaluate the diagnostic performance and reliability of the medial temporal lobe atrophy (MTA) scale in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Methods A systematic literature search of MEDLINE and EMBASE databases was performed to select studies that evaluated the diagnostic performance or reliability of MTA scale, published up to January 21, 2021. Pooled estimates of sensitivity and.
The Radiology Assistant Dementia Role of MRI
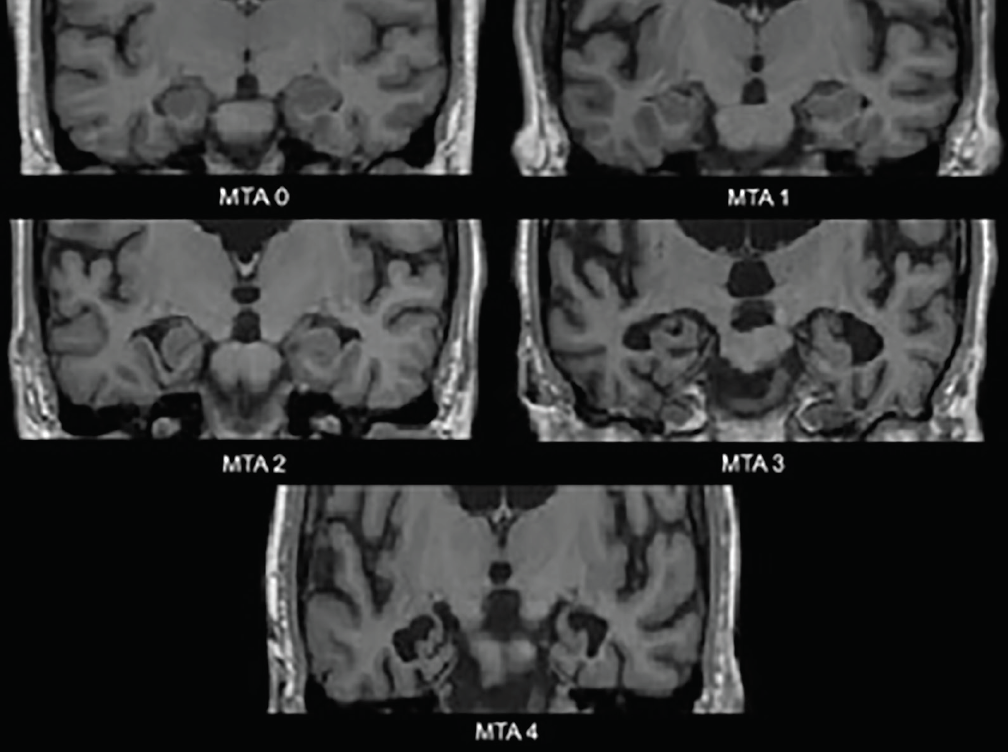
The MTA-score (Scheltens) should be rated on coronal T1-weighted images. on a slice through the corpus of the hippocampus (level of the anterior pons). The scale is based on a visual score of the width of the choroid fissure, the width of the temporal horn, and the height of the hippocampal formation. < 75 years: score 2 or more is abnormal.

MTA in Front of MRI Machine in Radiology Stock Image Image of people, machine 33010943
The MTA score, published by Scheltens and colleagues in 1992 [ 4 ], is a simple measure by which mesiotemporal atrophy can be quantified. Using the width of the choroidal fissure, temporal horn, and height of the hippocampal formation, atrophy is evaluated in five grades (0-4).

Medial temporal atrophy (MTA) scoring illustrated on T1weighted MRI.... Download Scientific
Medial temporal lobe atrophy (MTA) is considered as a biomarker for Alzheimer's disease (AD) [ 1 - 6] and visual MTA ratings are available for clinical use [ 7 ]. There is debate as to what cut-off scores should be used in clinical practice to optimally differentiate AD from controls without dementia [ 8] or with other types of dementia [ 9, 10 ].

Radiologist and Assistant in the Control Room of Computed Tomography at Hospital Stock Photo
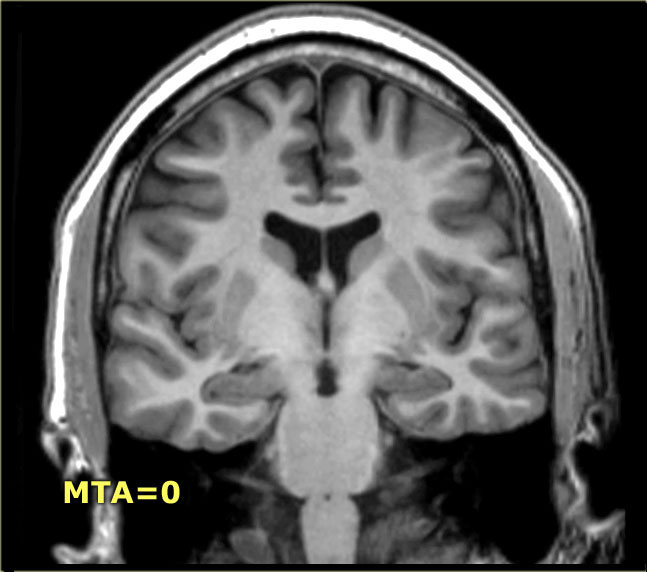
MTA score: 0: no CSF is visible around the hippocampus (normal); 1: choroid fissure is slightly widened; 2: moderate widening of the choroid fissure, mild enlargement of the temporal horn and mild loss of hippocampal height; 3: marked widening of the choroid fissure, moderate enlargement of the temporal horn, and moderate loss of hippocampal hei.

Image
To assess inter-modality agreement and accuracy for medial temporal lobe atrophy (MTA) ratings across radiologists with varying clinical experience in a non-demented population. Methods Four raters (two junior radiologists and two senior neuroradiologists) rated MTA on CT and MRI scans using Scheltens' MTA scale.

Radiographs of case 1. (a) The first visit during working length... Download Scientific Diagram
The Radiology Assistant : Epilepsy - Role of MRI Epilepsy - Role of MRI Laurens De Cocker, Felice D'Arco and Philippe Demaerel and Robin Smithuis Publicationdate 2012-09-01 In many patients with epilepsy antiepileptic drug treatment is unable to control the seizures.

Team Doctors Mta Radiology Hospital Stock Photo 148769429 Shutterstock
The MTA score is a visual score performed on MRI of the brain using coronal T1 weighted images in a plane parallel to the brainstem axis and through the hippocampus at the level of the anterior pons 5. The score is also validated for assessment on CT brain 6.
Radiology Assistants and Radiology Physician Assistants Collaborative Imaging
MTA-scale for Medial Temporal lobe Atrophy Fazekas scale for WM lesions Normal ageing Strategic infarctions Koedam score for Parietal Atrophy FDG-PET Specific Diseases Alzheimers Disease Presenile AD Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) Vascular Dementia (VaD) Strategic infarcts and small vessel disease Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy (CAA)
Radiologists find their voice in a patientcentric era
Results. Patients with AD had higher MTA scores (mean, 2.13) and ERICA scores (mean, 2.05) than patients with SCD (P < .001).An ERICA score of 2 or greater achieved a higher diagnostic accuracy (91%) than the MTA score (74%), with a sensitivity of 83% versus 57% and a specificity of 98% versus 92% in discriminating dementia caused by AD from SCD (P < .001).