Liver Anatomy Concise Medical Knowledge
stomach discomfort or pain. nose bleeds. abnormal blood vessels on the skin ( spider angiomas) itchy skin. weakness. a low sex drive. More serious symptoms include: yellowing of the skin and eyes.
Liver Anatomy Concise Medical Knowledge
If you need help for a liver condition, give us a call at (877) LIVER MD/ (877) 548-3763 or get in touch using our online request form. The liver removes toxins from the body's blood supply, maintains healthy blood sugar levels, regulates blood clotting, and performs hundreds of other vital functions. Learn more about the liver and why it is.
Liver The Gut Liver Axis And The Intersection With The Microbiome
When a person has a liver problem, one of the most common symptoms is jaundice. With jaundice, the skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow because of too much bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is a yellow waste product the liver gets rid of when it breaks down red blood cells. Higher levels of bilirubin indicate a possible problem in the liver.

Liver Function, Anatomy and Parts of the Human Liver
1. Liver Fibrosis Overview, Causes, and Burden. The buildup of scar tissue in the liver, or cirrhosis, is a public health concern that affects over 600,000 American adults [].The progression of liver cirrhosis is increasingly detrimental as scar tissue accumulates, given it directly interferes with liver function and contributes to gradual liver failure, which can ultimately lead to the death.
Liver Sections Diagram
According to the literature 15, 44, 45, the average human liver has a volume of 1500 cm 3, and contains 10-20% of blood, while it possesses about 10 6 lobules. This would give a lobule volume of.

Liver Function, Anatomy and Parts of the Human Liver
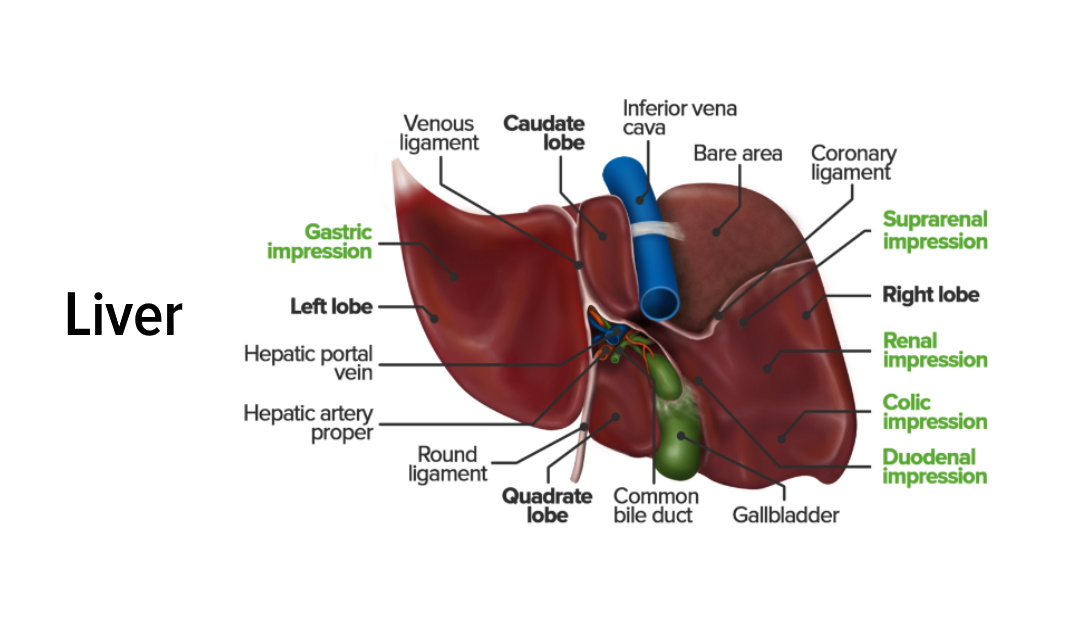
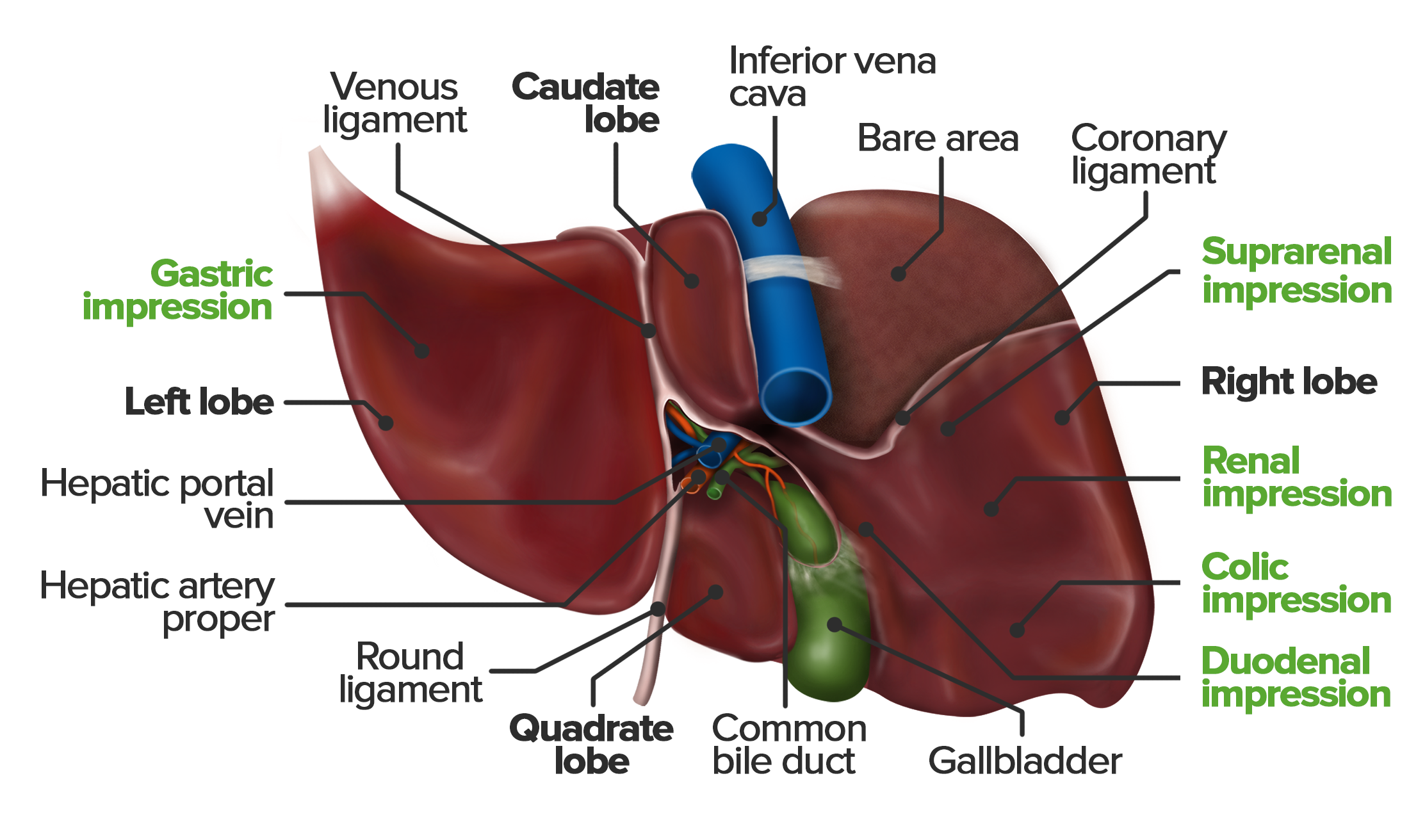
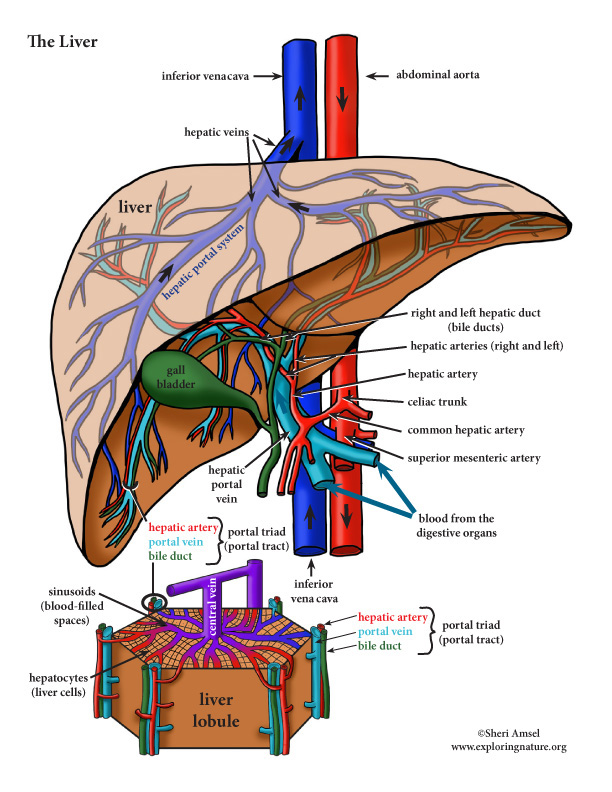
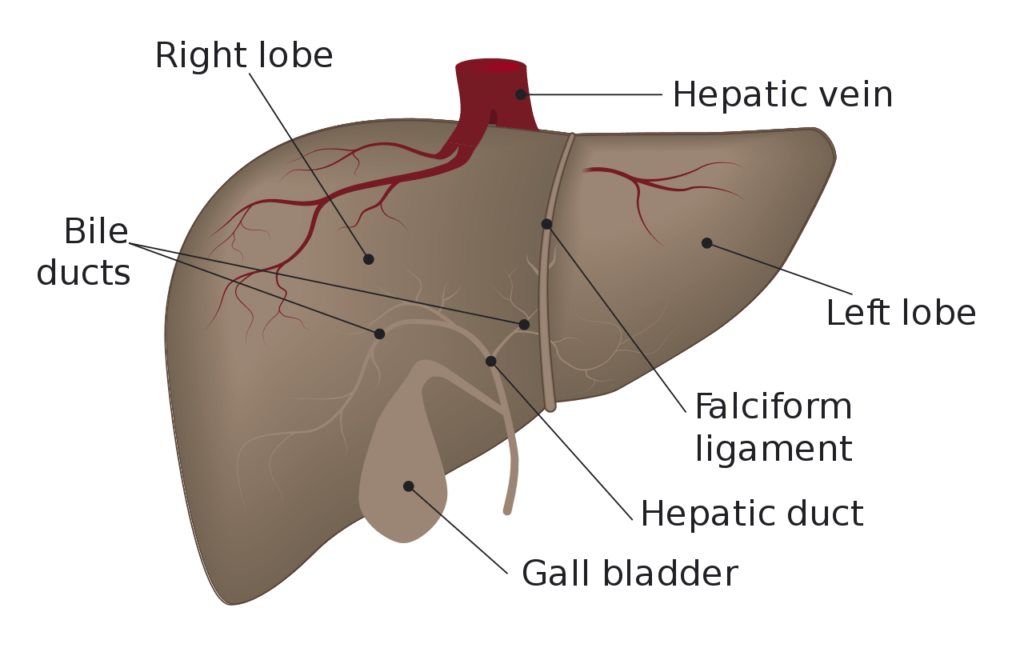
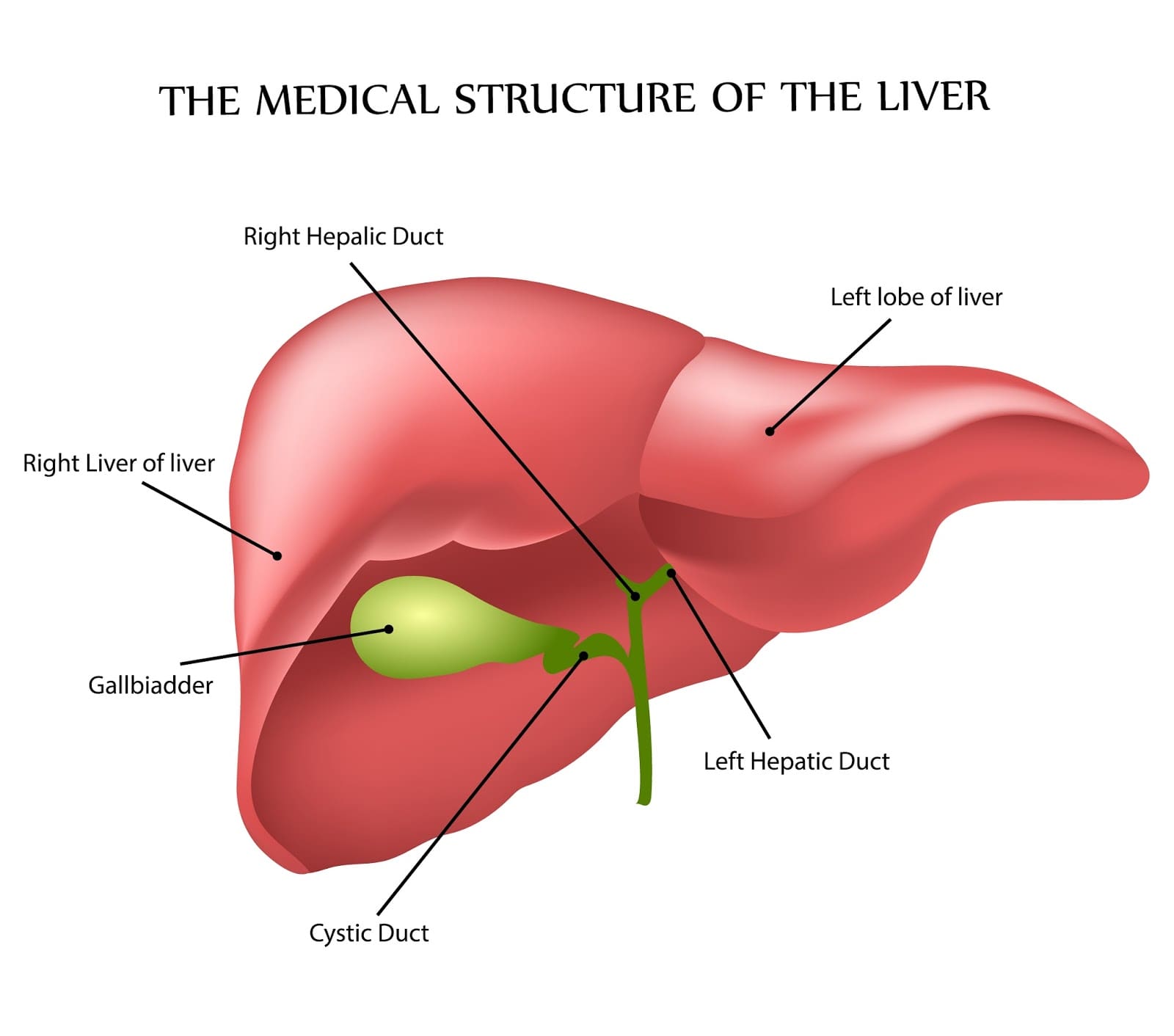
In addition, it has an endocrine and immunological function. The liver is divided into eight segments referring to the Couinaud system, each of which has an individual blood supply (arterial and portal venous) and biliary drainage, which is the basis for most modern liver surgery and live-related split liver transplantation.
Liver Structures and Functions A Closer Look (Advanced)
Most types of liver disease do not cause any symptoms in the early stages. Once you start to get symptoms of liver disease, your liver is already damaged and scarred. This is known as cirrhosis. Symptoms of cirrhosis include: feeling very tired and weak all the time. loss of appetite - which may lead to weight loss.

Diseases of the Liver Chart/Poster Laminated
Location and Structure of the Liver. Location of liver in the human body. The liver is around the size of an American football at about 16 cm. Weighing in at around 1.5 kg in men and 1.2 kg in women the liver accounts for about 1/32 of total adult body weight. The fetal liver is considerably larger in proportion to the rest of the fetus.
Liver structure and anatomical organ function explanation outline
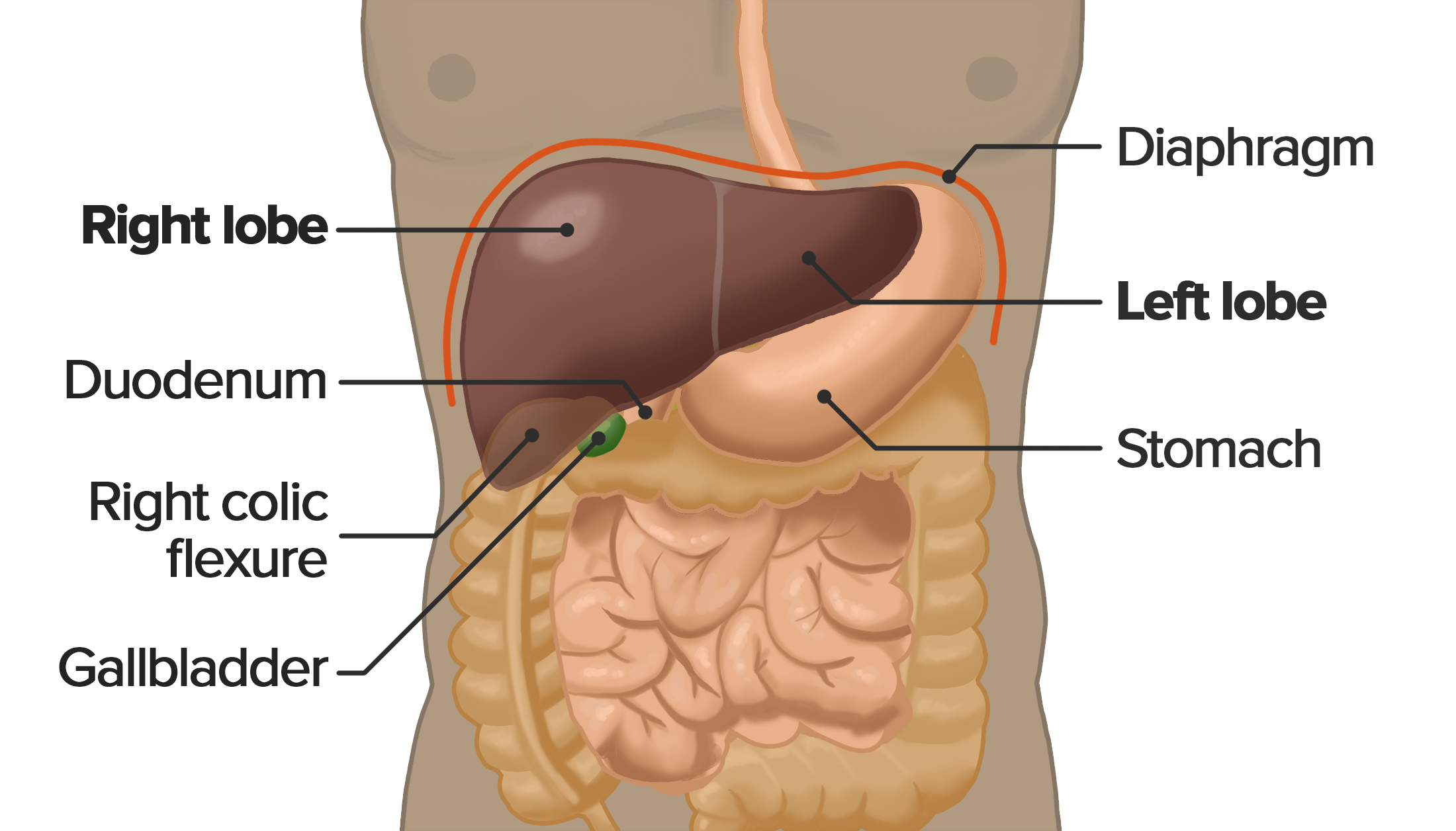
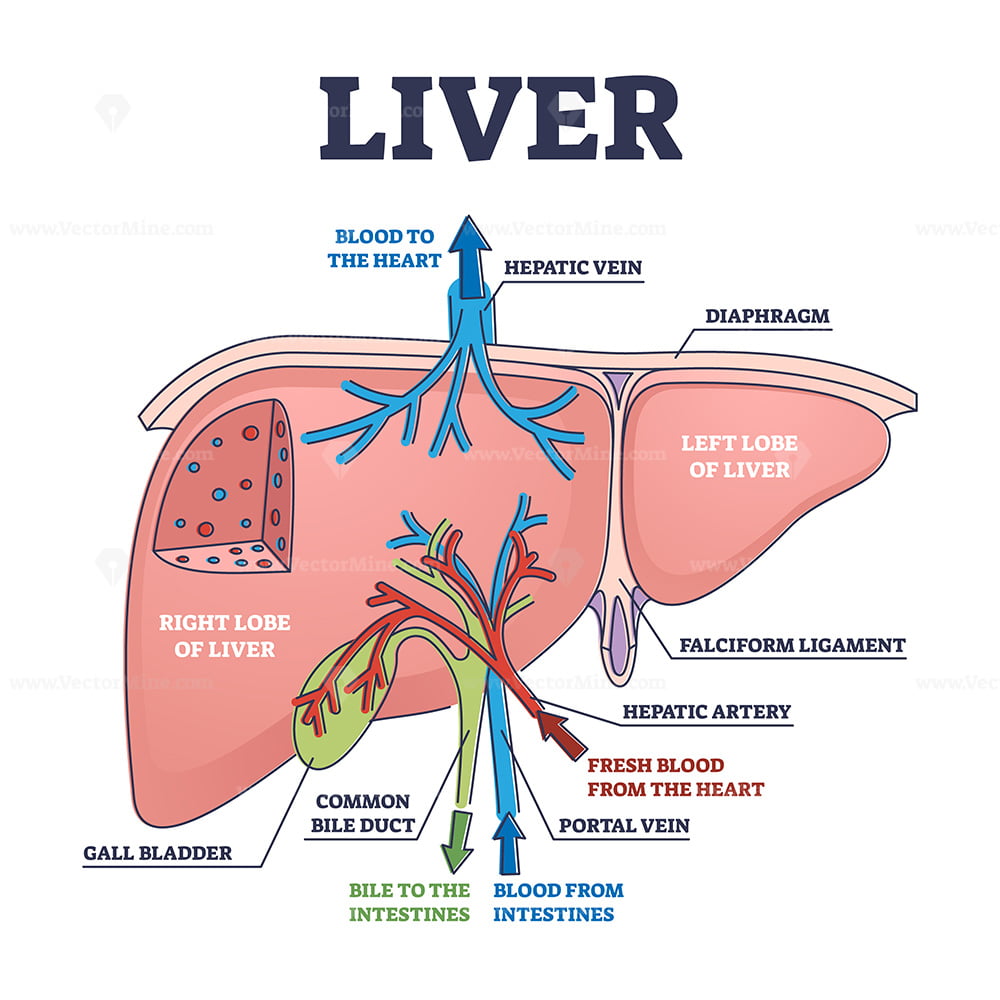
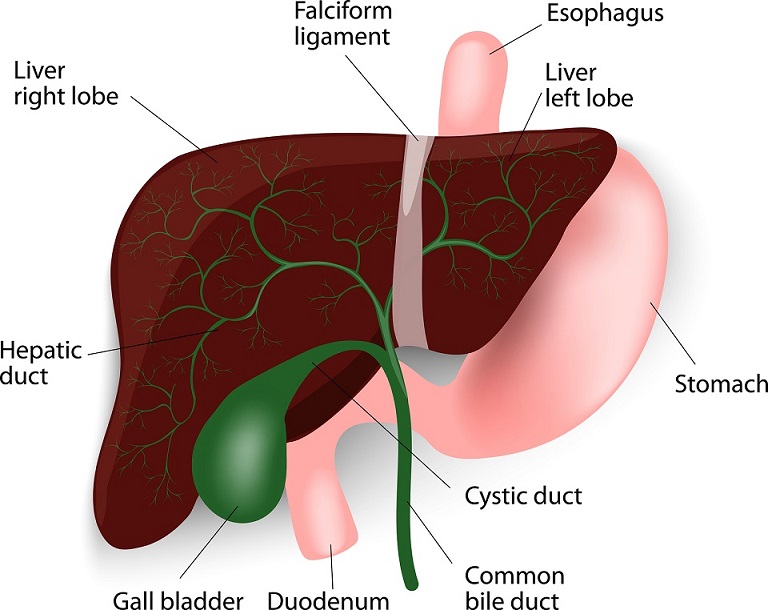
The liver is a large organ found in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen. It is a multifunctional accessory organ of the gastrointestinal tract and performs several essential functions such as detoxification, protein synthesis, bile production and nutrient storage to name only a few. It is the largest gland in the human body, weighing.
Liver Function, Anatomy and Parts of the Human Liver
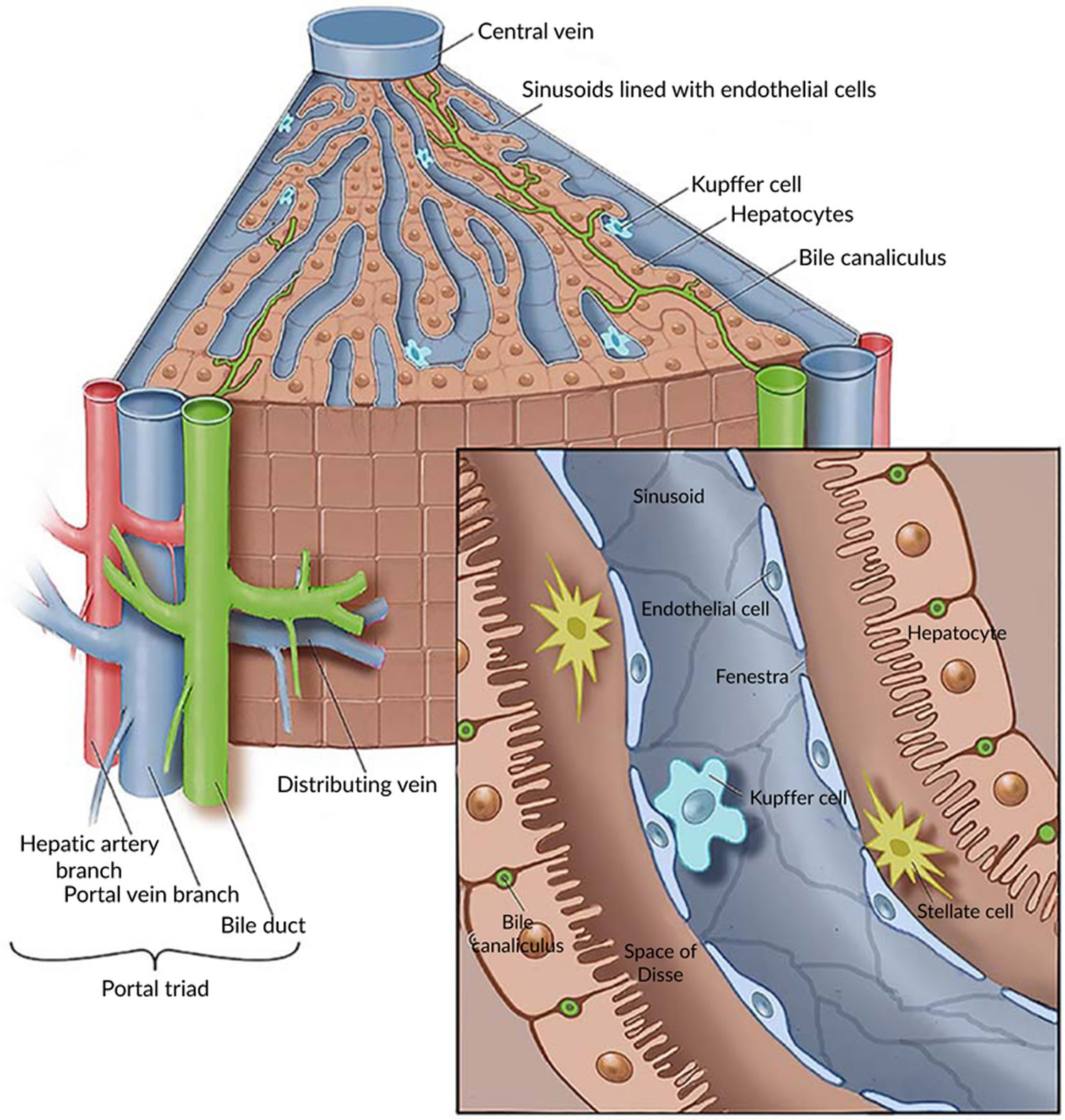
To establish structure-function relationships between organelle architecture and metabolic function in homeostasis and disease, we chose to study hepatocytes in their native liver tissue.
Liver (Anatomy, Histology and Functions) Online Science Notes
Progressive loss of hepatic architecture impairs function, leading to hepatic insufficiency; it manifests as coagulopathy, acute kidney injury Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) (hepatorenal syndrome), and hepatic encephalopathy Portosystemic Encephalopathy .Hepatic encephalopathy is characterized by asterixis, confusion, or hepatic coma and is the result of the liver's inability to metabolize the.
Functions of the liver The A Level Biologist Your Hub
The liver is a critical organ in the human body that is responsible for an array of functions that help support metabolism, immunity, digestion, detoxification, vitamin storage among other functions. It comprises around 2% of an adult's body weight. The liver is a unique organ due to its dual blood supply from the portal vein (approximately 75%) and the hepatic artery (approximately 25%).
Frontiers Pathogenesis of Viral HepatitisInduced Chronic Liver
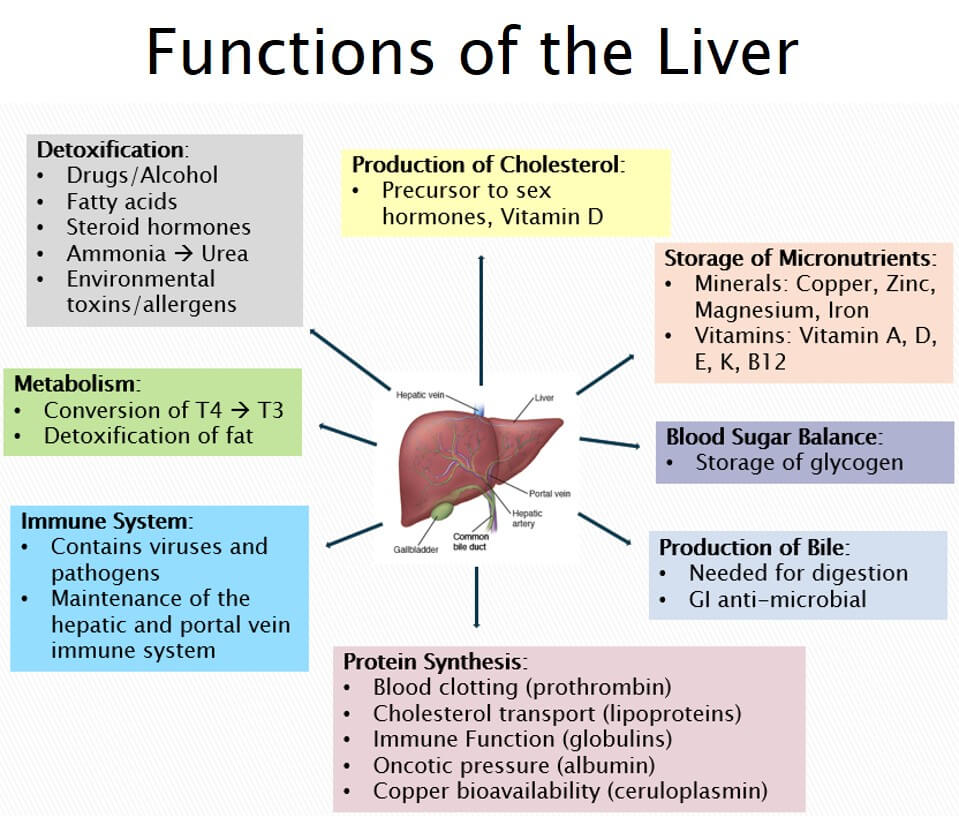
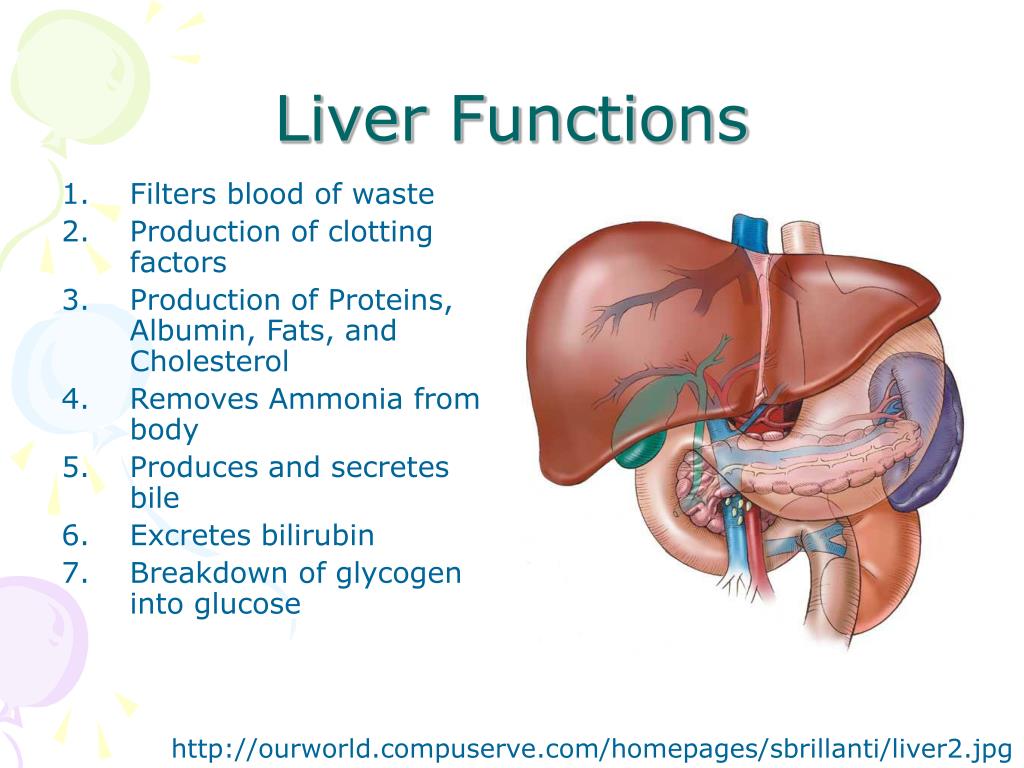
Hepatocytes (liver parenchymal cells) perform the liver's metabolic functions: Formation and excretion of bile as a component of bilirubin metabolism (see Overview of bilirubin metabolism ) Regulation of carbohydrate homeostasis. Lipid synthesis and secretion of plasma lipoproteins. Control of cholesterol metabolism.
Anatomy and Function of the Liver Solution Parmacy
The liver stores fat-soluble vitamins as well as minerals such as copper and iron, releasing them if the body needs them. It also helps to break down fats in a person's diet. It either.

Functions of liver
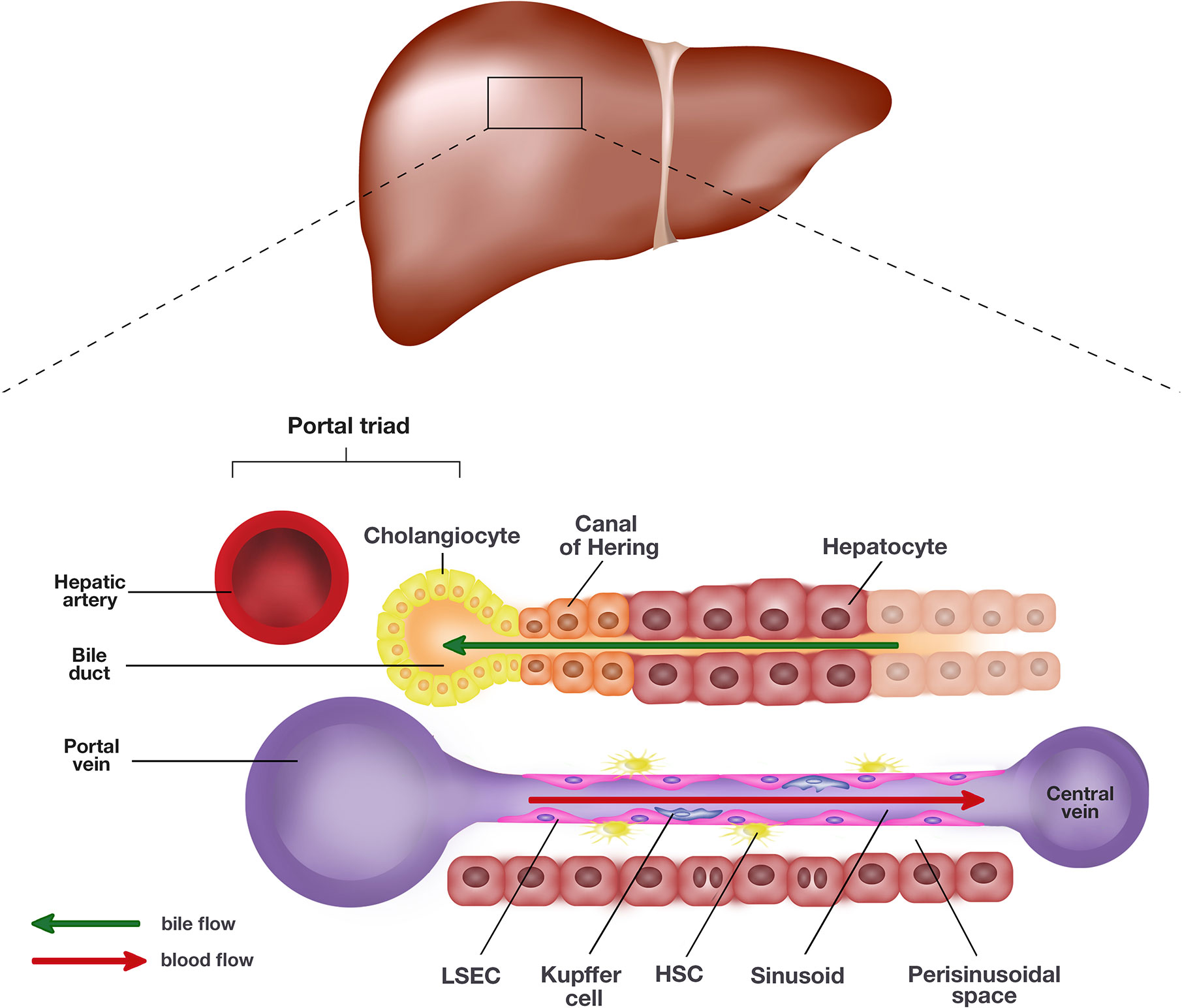
The liver is composed of three principal components: hepatocytes, blood vessels, and bile ducts. The microscopic anatomy is fairly basic, especially in light of the liver's plethora of functions (Figs. 1.2, 1.3 and 1.4).Hepatocytes form the bulk of the organ and are arranged in interconnecting trabeculae.
PPT Nursing Care of the Pediatric Patient with Liver Disease and
Hepatocytes. These large and polyhedral (six surfaces) cells make up 80% of the total cells of the liver. They can contain between two and four nuclei, which are large and spherical, occupying the centre of the cells. Each nucleus has at least two nucleoli. The typical lifespan of a hepatocyte is five months.